Source www.mesotheliomaveterans.org
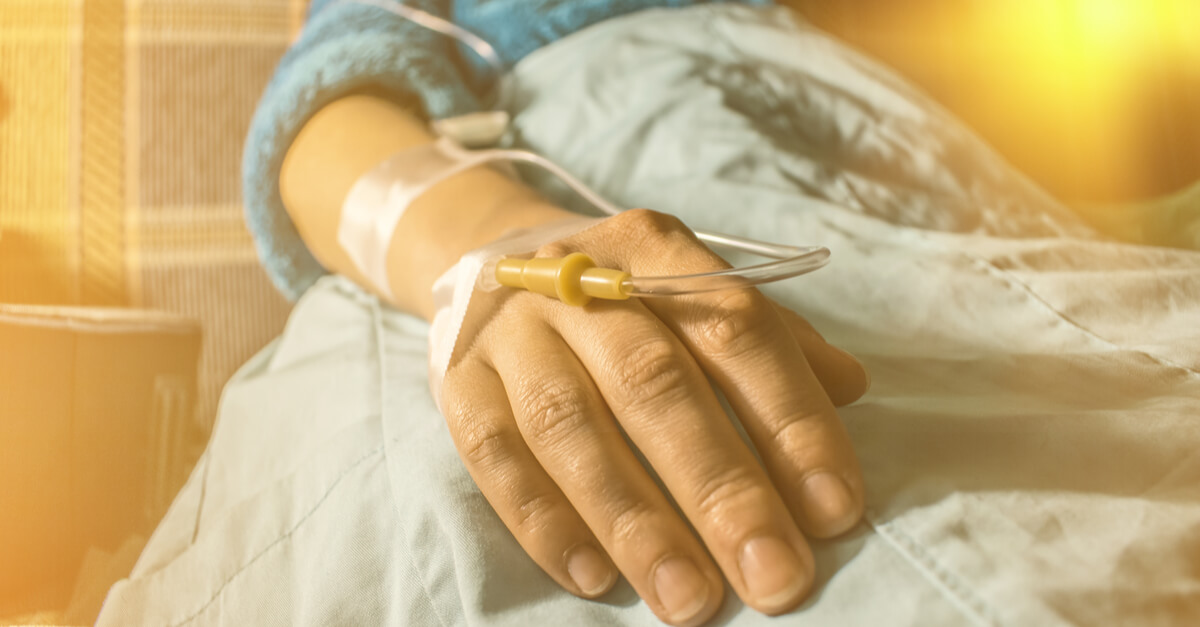
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive type of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, heart or abdomen. It is caused by exposure to asbestos fibers and can take up to 50 years to develop. Mesothelioma symptoms include chest pain, difficulty breathing, fatigue and weight loss. To treat mesothelioma, doctors may recommend a combination of treatments, including chemotherapy drugs.
Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs work by targeting and destroying rapidly dividing cells in the body. While chemotherapy cannot cure mesothelioma, it can often help to slow down the progression of the disease and alleviate symptoms. There are several different types of chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma, each with its own unique benefits and side effects.
One of the most common drugs used in mesothelioma chemotherapy is cisplatin. Cisplatin works by binding to DNA in cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and growing. Another drug commonly used in mesothelioma chemotherapy is pemetrexed. Pemetrexed blocks the production of certain enzymes that cancer cells need to grow and divide, effectively killing them. Paclitaxel is also a common chemotherapy drug used to treat mesothelioma. It works by preventing cancer cells from dividing, effectively stopping the growth of the tumor.
Chemotherapy may be given in different ways, depending on the person’s individual circumstances. It may be given orally as a pill, or intravenously through a vein. It may also be delivered directly into the abdominal or chest cavity, depending on where the cancer is located.
While mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can be effective in slowing down the disease, they do come with side effects. These may include nausea, vomiting, hair loss, fatigue, anemia, and an increased risk of infection. However, the benefits of chemotherapy often outweigh the potential side effects.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it is important to speak with your doctor about all of your treatment options, including chemotherapy. There are many different chemotherapy drugs available, and your doctor can help you determine which ones are right for you based on your individual circumstances and medical history.
Overall, mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can be a valuable tool in the fight against this aggressive cancer. While they may not be able to completely cure the disease, they can help to slow down its progression and improve quality of life. If you are considering mesothelioma chemotherapy, it is important to stay informed about the potential benefits and risks, and to work closely with your medical team to find the treatment plan that is right for you.
Introduction to Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive type of cancer that originates in the mesothelium of the body, which is a thin layer of tissue that lines the organs. The majority of mesothelioma cases are caused by exposure to asbestos. Due to the late diagnosis of the disease and the limited treatment options available, mesothelioma has a poor prognosis.
Chemotherapy is one of the main treatment options for mesothelioma, and it involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are aimed at slowing down the progression of the disease and improving the quality of life of the patient.
Types of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs
The types of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs used and the way they are administered depend on the location and stage of the disease, as well as the overall health of the patient.
The most common mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs include:
| Drug Name | Class of Drug | Mode of Administration | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alimta (Pemetrexed) | Antimetabolite | IV infusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cisplatin | Platinum-containing drug | IV infusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carboplatin | Platinum-containing drug | IV infusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gemcitabine | Nucleoside analogue | IV infusion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Onconase (Ranpirnase) | Ribonuclease enzyme | IV infusion |
| Drug Name | How it Works |
|---|---|
| Alimta (pemetrexed) | Targets enzymes that cancer cells require for replication |
| Cisplatin | Binds to DNA molecules and causes DNA damage that interferes with cancer cells’ ability to divide |
| Carboplatin | Induces DNA damage in cancer cells to prevent cell division |
| Gemcitabine | Prevents DNA synthesis in cancer cells and stops cell division |
| Methotrexate | Inhibits enzymes required for DNA synthesis and prevents cell division |
Side Effects of Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma
While chemotherapy is effective in treating mesothelioma, it comes with some common side effects that patients often experience. These side effects are due to the drugs’ ability to target fast-growing cells, a feature that is shared by healthy body cells like those in the hair, nails, and gut.
One common side effect of chemotherapy is hair loss, caused by the destruction of hair follicles. Patients may also experience nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite due to the digestive system lining’s fast-growing cells’ destruction. Fatigue and breathlessness are also common side effects due to the drugs’ effect on blood cells.
Rarely, chemotherapy can cause severe side effects like allergic reactions and damage to vital organs like the heart, nerves, and kidneys. Patients should discuss the potential side effects of chemotherapy with their doctor and report any unusual symptoms to the medical team.
Conclusion
Chemotherapy is a significant treatment option for mesothelioma, and it can improve survival and quality of life for many patients. There are several chemotherapy drugs available, and they work by disrupting cancer cell division and metabolism. Using different drugs in combination enhances their effectiveness, and it can reduce the likelihood of drug resistance. However, chemotherapy comes with common side effects, and patients should discuss the potential risks and benefits of chemotherapy with their medical team.
Importance of Choosing the Right Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that affects the tissue lining of internal organs most commonly the lungs and chest wall. This cancer is primarily caused by prolonged exposure to asbestos, a hazardous mineral that was commonly used in industries and construction sites several decades ago. While there are different types of treatment options that can be used to manage Mesothelioma cancer, chemotherapy is often the primary treatment that is used to slow down the progression of the disease and improve the quality of life of the patient.
Unfortunately, chemotherapy has several side effects that can be debilitating to the patient, including nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and fatigue. This makes it crucial for the treatment team to choose the right chemotherapy drugs for Mesothelioma.
What is Mesothelioma Chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that involves the administration of drugs that kill cancer cells or slow down their growth. These drugs are usually given through an IV (intravenous) drip, and they travel through the bloodstream to attack cancer cells anywhere in the body.
Mesothelioma chemotherapy is typically administered in cycles, with each cycle consisting of several weeks of treatment followed by a period of rest. Mesothelioma chemotherapy can be used as a standalone treatment or in combination with other treatments such as surgery and radiation therapy.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs
When choosing Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs, several factors need to be taken into account, including the tumor type, the stage of the cancer, the overall health of the patient, and the potential side effects of the drugs.
1. Tumor Type
There are three main types of Mesothelioma: pleural, peritoneal, and pericardial. Pleural Mesothelioma, which affects the lining of the lungs, is the most common type. Peritoneal Mesothelioma affects the lining of the abdomen, while pericardial Mesothelioma affects the lining of the heart. The choice of chemotherapy drugs will depend on the type of Mesothelioma that the patient has.
2. Stage of the Cancer
The stage of the cancer refers to how advanced it is. Mesothelioma is typically classified into four stages. In the early stages, the cancer is localized and can be treated more effectively. However, in the later stages, the cancer may have spread to other parts of the body, making it more difficult to treat. The stage of the cancer will influence the choice of chemotherapy drugs and the duration and frequency of treatment.
3. Overall Health of the Patient
The overall health of the patient is an essential consideration when selecting Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs. It is crucial to assess the patient’s ability to tolerate the side effects of chemotherapy drugs and their overall health before recommending any medication. Chemotherapy drugs can have debilitating side effects, and some patients may require additional support during treatment.
4. Potential Side Effects of the Drugs
Different Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs have adverse effects, and the choice of drugs will depend on the patient’s tolerance level and the potential side effects of the medication. Some chemotherapy drugs can cause hair loss, fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. It is essential to explain these side effects to the patient and provide support during treatment.
Common Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs
Several chemotherapy drugs are used to treat Mesothelioma. Some of the most common Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs include:
| Chemotherapy Drug Name | How it Works |
|---|---|
| Alimta (Pemetrexed) | Alimta works by inhibiting the growth and replication of cancer cells. It is usually administered in combination with Cisplatin. |
| Cisplatin | Cisplatin is an anti-cancer medication that works by interfering with the DNA of cancer cells, causing them to die. It is usually given in combination with other chemotherapy drugs. |
| Gemcitabine | Gemcitabine is an anti-cancer drug that is used to treat several types of cancer, including Mesothelioma. It is typically administered in combination with other chemotherapy drugs. |
| Methotrexate | Methotrexate is a chemotherapy drug that works by slowing down the growth of cancer cells. It is commonly used to treat pleural Mesothelioma. |
Conclusion
Chemotherapy is a vital treatment option for Mesothelioma cancer. The choice of chemotherapy drugs will depend on several factors, including the type of cancer, the stage of the disease, the patient’s overall health, and the potential side effects of the drugs. By carefully weighing these factors, medical professionals can select the most suitable chemotherapy drugs for each Mesothelioma patient, improving the effectiveness of the treatment and reducing the risk of adverse side effects.
Commonly Used Chemotherapy Drugs for Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a rare but aggressive cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, and heart. It is caused by exposure to asbestos, a mineral that was widely used in construction, manufacturing, and other industries until the 1970s.
Many mesothelioma patients undergo chemotherapy, which involves using powerful drugs to kill cancer cells and slow down the growth of the tumor. While chemotherapy can cause side effects, including nausea, fatigue, and hair loss, it can also help patients live longer and improve their quality of life.
How Chemotherapy Works
Chemotherapy drugs work by targeting fast-growing cells, such as cancer cells. They can be delivered in different ways, depending on the type of mesothelioma and the patient’s overall health. Common chemotherapy treatments for mesothelioma include:
1. Alimta (Pemetrexed)
Alimta is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with cisplatin for mesothelioma. It works by blocking an enzyme that is needed for the growth of cancer cells. Alimta is typically given through an IV infusion every three weeks, along with supplements of folic acid and vitamin B12 to reduce side effects.
A study published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology found that patients who received Alimta and cisplatin had a median survival time of 12.1 months, compared to 9.3 months for those who only received cisplatin.
2. Cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy drug that has been used for many years to treat various types of cancer, including mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA in cancer cells, which prevents them from growing and dividing. Cisplatin is usually given through an IV infusion every three to four weeks, along with plenty of fluids to help protect the kidneys.
A study published in the Lancet found that patients who received cisplatin had a median survival time of 9.3 months, compared to 7.6 months for those who only received supportive care.
3. Carboplatin
Carboplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is similar to cisplatin but is less toxic to the kidneys. It works by interfering with the DNA in cancer cells, which causes them to stop dividing and growing. Carboplatin is typically given through an IV infusion every four to six weeks, depending on the patient’s response.
A study published in the Annals of Oncology found that patients who received carboplatin had a median survival time of 9.1 months, compared to 7.5 months for those who only received best supportive care.
4. Gemcitabine
Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin for mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the DNA in cancer cells, which prevents them from growing and dividing. Gemcitabine is usually given through an IV infusion every week for several weeks, followed by a week of rest.
In a study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, patients who received gemcitabine and cisplatin had a median survival time of 9.3 months, compared to 7.6 months for those who only received cisplatin alone.
Side Effects of Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy can cause side effects, including:
| Side Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Nausea and vomiting | Feeling sick and throwing up |
| Fatigue | Feeling tired and weak |
| Hair loss | Losing hair from the scalp, eyebrows, and other parts of the body |
| Mouth sores | Sores and ulcers in the mouth and throat |
| Decreased appetite | Lack of interest in food and weight loss |
| Bone marrow suppression | A reduction in the number of blood cells, which can lead to anemia, infection, and bleeding |
However, many of these side effects can be managed with medication, rest, and a healthy diet. Patients should discuss their options and concerns with their doctor before starting chemotherapy.
Conclusion
Chemotherapy can be an effective treatment for mesothelioma, especially when combined with other therapies such as surgery and radiation. Alimta, cisplatin, carboplatin, and gemcitabine are commonly used chemotherapy drugs that can help kill cancer cells and slow down the growth of the tumor. While chemotherapy can cause side effects, many patients are able to tolerate them and maintain a good quality of life with the help of their healthcare team.
Pemetrexed (Alimta) for Mesothelioma Treatment
Pemetrexed is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma, a rare cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, and heart. Pemetrexed is marketed under the brand name Alimta and is typically used in combination with other drugs to provide a more effective treatment regimen for mesothelioma patients.
How Pemetrexed Works
Pemetrexed is a multitargeted antifolate drug that works by inhibiting the production of enzymes that are essential for cell division and growth. Cancer cells require these enzymes in order to divide and multiply rapidly, and by inhibiting their production, Pemetrexed can help to slow the growth of cancer cells.
Pemetrexed is typically administered through an intravenous infusion, and in combination with other drugs, such as cisplatin or carboplatin, it can be an effective treatment for mesothelioma. However, because mesothelioma is a particularly aggressive cancer, treatment with Pemetrexed may not be effective on its own, and patients may require other types of therapy as well.
Side Effects of Pemetrexed
Like all chemotherapy drugs, Pemetrexed can cause a range of side effects, including fatigue, nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and anemia. In addition, Pemetrexed can also cause more serious side effects, such as kidney damage, liver damage, and low white blood cell counts.
To minimize the risk of these side effects, patients who are receiving Pemetrexed will typically require ongoing monitoring and support from their healthcare team. This may include regular blood tests, imaging tests, and other assessments in order to ensure that the drug is being well-tolerated and that any adverse effects are being managed appropriately.
How to Prepare for Pemetrexed Treatment
Prior to starting Pemetrexed treatment, patients will need to undergo a thorough evaluation to ensure that they are strong enough to undergo chemotherapy and that they do not have any other health issues that could impact their treatment. This may include blood tests, imaging tests, and consultations with various members of their healthcare team, such as oncologists, radiation therapists, and nurses.
During this evaluation, patients will also be given detailed information about the risks and benefits of Pemetrexed treatment, as well as any potential side effects that they may experience. They will also have the opportunity to ask questions and to discuss any concerns that they may have with their healthcare team.
Conclusion
Pemetrexed is an important chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma, a rare form of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, and heart. By inhibiting the production of enzymes that are essential for cell division and growth, Pemetrexed can help to slow the growth of cancer cells and can be an effective treatment in combination with other drugs. However, like all chemotherapy drugs, Pemetrexed can also cause a range of side effects, and patients who are receiving the drug will require ongoing monitoring and support from their healthcare team in order to manage these effects effectively.
| Drug Name | Brand Name | Chemical Name | Indications and Dosage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pemetrexed | Alimta | N-{4-[2-(2-amino-4,7-dihydro-4-oxo-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl)ethyl]benzoyl}-L-glutamic acid disodium salt hemipentahydrate | Indications: Treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma, in combination with cisplatin. Also indicated as a first-line treatment in locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, in combination with cisplatin and, in patients whose tumors are ALK or EGFR mutation-positive or with tumors expressing anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) as detected by an FDA-approved test, crizotinib. Dosage: Alimta intravenous infusion should be administered in combination with cisplatin as follows: 500 mg/m2 IV over 10 minutes on the first day of each 21-day cycle. |
Cisplatin as a Chemotherapy Drug for Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a rare form of cancer that is caused by exposure to asbestos. It mostly affects the lining of the lungs, but it can also occur in the lining of the abdomen, heart, or testicles. Treatment for mesothelioma often involves a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Cisplatin is one of the chemotherapy drugs that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma.
Cisplatin is a type of platinum-containing chemotherapy drug that works by blocking the replication of cancer cells. It is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs to improve the effectiveness of treatment. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key facts about cisplatin.
How does Cisplatin work?
Cisplatin is a type of platinum-containing chemotherapy drug that works by damaging the DNA in cancer cells. This prevents them from replicating and dividing, which slows down the growth of the tumor. Cisplatin also triggers a process called apoptosis, which causes cancer cells to die. Because cisplatin targets rapidly dividing cells, it can also damage healthy cells in the body, leading to side effects.
What are the side effects of Cisplatin?
Like all chemotherapy drugs, cisplatin can cause side effects. The most common side effects of cisplatin include nausea and vomiting, hair loss, fatigue, and kidney damage. Other less common side effects may include hearing loss, nerve damage, and an increased risk of infection. To minimize the risk of side effects, cisplatin is usually administered in combination with other drugs and under the supervision of a medical professional.
What is the dosage for Cisplatin?
The dosage of cisplatin will vary based on the individual patient’s needs. It is typically administered as an intravenous infusion, which means it is given directly into the vein. The dose and frequency of cisplatin will depend on factors such as the patient’s age, weight, overall health, and the stage of the cancer.
What are the benefits of Cisplatin for mesothelioma patients?
Studies have shown that cisplatin can be an effective treatment for mesothelioma. It is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as pemetrexed and carboplatin, to improve the overall effectiveness of treatment. Cisplatin has been shown to slow down the growth of tumors, decrease the size of tumors, and improve overall survival rates for mesothelioma patients.
What are some potential risks of using Cisplatin?
Like all chemotherapy drugs, cisplatin can cause side effects. The most common side effects of cisplatin include nausea and vomiting, hair loss, fatigue, and kidney damage. However, some patients may be at a higher risk of experiencing certain side effects, such as hearing loss or nerve damage. These risks depend on factors such as the patient’s age, overall health, and the dose and frequency of cisplatin.
What other chemotherapy drugs are used in combination with Cisplatin for mesothelioma?
Cisplatin is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs to improve the overall effectiveness of treatment for mesothelioma. Some of the most commonly used drugs in combination with cisplatin include pemetrexed and carboplatin. These drugs work by targeting different aspects of cancer cell replication and growth, helping to slow down the progression of the disease and improve overall survival rates.
Conclusion
Cisplatin is an important chemotherapy drug for the treatment of mesothelioma. While it can cause side effects, it has been shown to be effective at slowing down the growth of tumors and improving overall survival rates. When used in combination with other drugs under the supervision of a medical professional, cisplatin can be an important tool in the fight against mesothelioma. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it is important to consult with a medical professional to discuss the best treatment options.
| Factors to consider when using Cisplatin for Mesothelioma treatment |
|---|
| Patient’s age and overall health |
| Stage of the cancer |
| Frequency and dosage of cisplatin |
| Other medications or treatments being used |
Asbestos exposure can lead to mesothelioma, a rare and deadly cancer. Asbestos disease mesothelioma affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen or heart, and can take years to develop.
Carboplatin as a Treatment Option for Mesothelioma
Introduction
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that affects the mesothelium, a thin layer of tissue that covers the lungs, chest cavity, heart, and abdomen. It’s caused by exposure to asbestos, a group of naturally occurring minerals that were widely used in the construction, shipbuilding, and automotive industries until the 1980s. Asbestos fibers can enter the body through inhalation or ingestion and cause mutations in the cells that line the mesothelium, leading to the growth of malignant tumors.
Unfortunately, mesothelioma is difficult to diagnose and treat because it’s often asymptomatic until it’s in advanced stages and has spread to other parts of the body. Chemotherapy drugs are one of the main treatment options for mesothelioma because they can target cancer cells throughout the body and slow down their growth. One of the chemotherapy drugs that’s commonly used for mesothelioma is carboplatin, which we’ll explore in more detail in this article.
What is Carboplatin?
Carboplatin is a type of chemotherapy drug that belongs to the group of platinum-containing compounds. It works by interfering with the DNA replication process of cancer cells, which stops them from dividing and growing. Carboplatin is typically given to mesothelioma patients intravenously, either alone or in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as pemetrexed.
Benefits of Carboplatin as a Treatment Option for Mesothelioma
Carboplatin has several benefits as a treatment option for mesothelioma patients. Firstly, it’s been shown to improve the survival rates of mesothelioma patients. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showed that mesothelioma patients who received carboplatin and pemetrexed had a median survival rate of 12.1 months, compared to 9.3 months for patients who received pemetrexed alone.
Side Effects of Carboplatin
Like all chemotherapy drugs, carboplatin can cause side effects. Some of the common side effects of carboplatin include nausea and vomiting, fatigue, hair loss, decreased appetite, and anemia. However, most of these side effects are manageable and can be reduced with supportive care, such as anti-nausea medications and blood transfusions.
Combination Therapy
As mentioned earlier, carboplatin is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as pemetrexed, for mesothelioma treatment. This approach is known as combination therapy, and it aims to target cancer cells in multiple ways and reduce the risk of chemotherapy resistance. Carboplatin and pemetrexed combination therapy has become the standard of care for mesothelioma patients, and it’s been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for this use.
Alternatives to Carboplatin
Although carboplatin is an effective chemotherapy drug for mesothelioma, it’s not the only option available. Other platinum-containing chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin and oxaliplatin, can also be used for mesothelioma treatment. Additionally, immunotherapy drugs, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, have recently been approved for mesothelioma treatment and can be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy.
Conclusion
Mesothelioma is a challenging disease to treat, but chemotherapy drugs, such as carboplatin, are one of the main treatment options that can improve patients’ survival rates and quality of life. Carboplatin works by interfering with the DNA replication process of cancer cells and can be given alone or in combination with other chemotherapy drugs or immunotherapy drugs. Despite the side effects of carboplatin and other chemotherapy drugs, they have shown to be effective in controlling the growth of mesothelioma tumors and prolonging patients’ lives.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Improves the survival rates of mesothelioma patients | Can cause side effects such as nausea, fatigue, and anemia |
| Can be given alone or in combination with other chemotherapy drugs | May not work for all mesothelioma patients |
| Targets cancer cells throughout the body and slows down their growth | Requires careful monitoring and management of side effects |
Gemcitabine (Gemzar) Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is an aggressive cancer caused by inhalation of asbestos fibers. While mesothelioma is not curable, it can be treated with chemotherapy. Chemotherapy drugs are used to kill cancer cells, shrink tumors, and relieve symptoms. One of the chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma is Gemcitabine (Gemzar).
What is Gemcitabine (Gemzar)?
Gemcitabine (Gemzar) is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. It is a nucleoside analogue that disrupts DNA synthesis, preventing cancer cells from dividing and growing. Gemcitabine is administered intravenously, usually as a single agent or in combination with other chemotherapy drugs.
How does Gemcitabine (Gemzar) work?
Gemcitabine (Gemzar) works by disrupting DNA synthesis in cancer cells. It is a prodrug that is metabolized by the body into its active form. Once in the cell, Gemcitabine inhibits the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase, which is needed for the production of DNA building blocks. This prevents DNA replication and cell division, ultimately killing the cancer cell.
What are the side effects of Gemcitabine (Gemzar)?
Like all chemotherapy drugs, Gemcitabine (Gemzar) can cause side effects. Some common side effects of Gemcitabine include:
| Side Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Nausea and vomiting | Feeling sick to your stomach or throwing up |
| Fatigue | Feeling tired or weak |
| Hair loss | Losing hair on your head or other parts of your body |
| Low blood cell counts | Decreased white and red blood cells and platelets, leading to increased risk of infection, anemia, and bleeding problems |
Other side effects of Gemcitabine may include fever, chills, flu-like symptoms, mouth sores, and skin rash.
What is the effectiveness of Gemcitabine (Gemzar) in treating mesothelioma?
Gemcitabine (Gemzar) has been shown to be effective in treating mesothelioma. Studies have demonstrated that Gemcitabine can be used as a first-line treatment or in combination with other chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology found that Gemcitabine in combination with Cisplatin, another chemotherapy drug, improved survival in patients with malignant mesothelioma, compared to Cisplatin alone.
What is the dosage of Gemcitabine (Gemzar)?
The dosage of Gemcitabine (Gemzar) varies depending on the patient’s weight, general health, and other factors. It is typically administered intravenously once a week for several weeks. The treatment cycle may be repeated every three to four weeks. The dosage and treatment schedule will be determined by the patient’s oncologist.
Conclusion
Gemcitabine (Gemzar) is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. It works by disrupting DNA synthesis in cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and growing. While it can cause side effects, Gemcitabine has been shown to be effective in treating mesothelioma, either as a single agent or in combination with other chemotherapy drugs. Patients with mesothelioma should discuss their treatment options with their oncologist to determine the best course of action.
Vinorelbine (Navelbine) for Mesothelioma Treatment
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the mesothelial cells, which are the cells lining the chest and abdominal cavities. As it is a rare form of cancer, treatment options are limited and often involve a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Vinorelbine, also known as Navelbine, is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used as a treatment option for mesothelioma.
What is Vinorelbine?
Vinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that belongs to the class of vinca alkaloids. It works by interfering with the growth and division of cancer cells. Vinorelbine is given intravenously, which means that it is administered directly into a vein, either through a catheter or through an injection. Vinorelbine is used to treat a number of different types of cancer, including breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, and mesothelioma.
How Does Vinorelbine Work?
Vinorelbine works by inhibiting the formation of microtubules, which are the structural components of the cell that are responsible for dividing the DNA during cell division. By preventing the formation of new microtubules, vinorelbine causes the cancer cells to stop dividing and eventually die.
Vinorelbine is generally considered to be a cell-cycle-specific drug, which means that it is most effective when the cancer cells are actively dividing. However, vinorelbine may also have some effect on cells that are not actively dividing.
What Are the Side Effects of Vinorelbine?
Like all chemotherapy drugs, vinorelbine can have a number of side effects, some of which can be quite severe. Common side effects of vinorelbine include:
| Side effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Nausea and Vomiting | Many patients experience nausea and vomiting during treatment with vinorelbine. This can often be managed with medications to minimize the symptoms. |
| Fatigue | Patients may feel very tired during treatment with vinorelbine, and may need to rest more frequently than usual. |
| Neutropenia | Vinorelbine can cause a decrease in the number of white blood cells, which can increase the risk of infections. Patients may need to have their blood counts monitored closely during treatment with vinorelbine. |
| Hair Loss | Vinorelbine can cause hair loss, which can be a distressing side effect for patients. |
Other less common side effects can include nerve damage, skin reactions, and stomach ulcers. Patients should notify their healthcare provider if they experience any unusual symptoms while undergoing treatment with vinorelbine.
How Is Vinorelbine Administered?
Vinorelbine is typically administered in a hospital or clinic setting, as the drug must be given intravenously. The drug is usually given on a weekly basis, with doses and treatment schedules varying depending on the individual patient and the stage and type of the cancer being treated. The length of the treatment will also depend on various factors, such as the patient’s response to the drug and the severity of the side effects.
What Are the Benefits of Vinorelbine?
While vinorelbine can have some serious side effects, it is an effective treatment option for many mesothelioma patients. Studies have found that vinorelbine can help to decrease the size of tumors and can lead to longer periods of disease-free survival in some patients. Vinorelbine is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs to maximize its effectiveness.
Conclusion
Vinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used as a treatment option for mesothelioma. While it can have some serious side effects, it is an effective treatment option for many patients. Vinorelbine works by inhibiting the formation of microtubules, which prevents the growth and division of cancer cells. It is usually given intravenously in a hospital or clinic setting, with doses and treatments schedules varying depending on the patient and the stage and type of the cancer being treated.
Bevacizumab (Avastin) as a Chemotherapy Drug for Mesothelioma
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, chemotherapy may be a necessary part of treatment. Bevacizumab, also known as Avastin, is a chemotherapy drug that may be used in the treatment of mesothelioma.
What is Bevacizumab?
Bevacizumab is a type of chemotherapy drug that works by inhibiting the growth of blood vessels. This can be helpful in the treatment of mesothelioma because it starves the cancer cells of the oxygen and nutrients they need to grow and spread.
How is Bevacizumab Administered?
Bevacizumab is typically administered through intravenous infusion, meaning that it is given directly into a vein. It is usually given once every two to three weeks, depending on the specific treatment plan.
What are the Common Side Effects of Bevacizumab?
As with any chemotherapy drug, there are potential side effects associated with Bevacizumab. Common side effects may include:
- Headache
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- High blood pressure
- Bleeding or clotting issues
It is important for patients to discuss potential side effects with their healthcare team, as well as any measures that can be taken to manage them.
What are the Benefits of Bevacizumab for Mesothelioma Patients?
Studies have shown that Bevacizumab may improve progression-free survival (PFS) in mesothelioma patients. PFS refers to the amount of time that a patient’s cancer does not grow or spread after treatment. In addition, Bevacizumab may be helpful in managing symptoms such as pleural effusions (fluid buildup around the lungs).
What are the Risks of Bevacizumab for Mesothelioma Patients?
As with any chemotherapy drug, there are potential risks associated with Bevacizumab. These risks may include:
- Bleeding or clotting issues
- High blood pressure
- Heart and/or kidney problems
- GI perforation (a hole in the stomach or intestines)
- Wound healing complications
It is important for patients to discuss potential risks with their healthcare team, as well as any measures that can be taken to minimize them.
How Effective is Bevacizumab for Mesothelioma?
As with any treatment, the effectiveness of Bevacizumab for mesothelioma can vary depending on a number of factors. Studies have shown that Bevacizumab may improve progression-free survival in mesothelioma patients. In addition, a combination of Bevacizumab and other chemotherapy drugs may also be effective in some cases.
Is Bevacizumab Right for You?
The decision to use Bevacizumab as part of your mesothelioma treatment plan should be made in consultation with your healthcare team. Factors such as the stage and location of your cancer, as well as your overall health, will be taken into consideration when determining the best course of treatment.
How Can You Learn More?
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it is important to work closely with your healthcare team to explore all of your treatment options. In addition, there are a number of resources available to help you learn more about mesothelioma and the available treatment options. Some helpful resources may include:
- The Mesothelioma Applied Research Foundation
- The American Cancer Society
- The National Cancer Institute
Conclusion
Bevacizumab may be an effective chemotherapy drug for mesothelioma patients. However, as with any treatment option, it is important to discuss the potential benefits and risks with your healthcare team to determine the best course of action for you. With the help of your healthcare team and the available resources, you can make informed decisions about your mesothelioma treatment plan.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| May improve progression-free survival (PFS) | Potential side effects, such as high blood pressure and bleeding or clotting issues |
| May be helpful in managing symptoms such as pleural effusions | Potential risks, such as heart and/or kidney problems |
| A combination of Bevacizumab and other chemotherapy drugs may be effective | May not be right for all mesothelioma patients |
Trial and Off-label Mesothelioma Treatments Using Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a common mesothelioma treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells. While standard chemotherapy drugs like cisplatin and pemetrexed are commonly used, there are also other drugs that are still in clinical trials or are used off-label for mesothelioma treatment. Here are some of the most promising new drugs being tested in clinical trials, as well as some off-label treatments that are showing promise.
1. Nivolumab
Nivolumab is a checkpoint inhibitor that is being tested in clinical trials for mesothelioma treatment. It targets a protein called PD-1, which is found on the surface of certain immune cells. By blocking PD-1, nivolumab can help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. In a phase II clinical trial, nivolumab was shown to be effective for treating malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM), a type of mesothelioma that affects the lining of the lungs.
| Drug Name | Category | Mode of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Nivolumab | Checkpoint Inhibitor | Blocks PD-1 to help immune system attack cancer cells |
| Pembrolizumab | Checkpoint Inhibitor | Blocks PD-1 to help immune system attack cancer cells |
| CBP501 | Cell Cycle Inhibitor | Disrupts DNA replication and limits tumor growth |
2. Pembrolizumab
Pembrolizumab is another checkpoint inhibitor that is being tested in clinical trials for mesothelioma treatment. Like nivolumab, it targets PD-1 to help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. A phase Ib clinical trial found that pembrolizumab was well-tolerated and showed promising activity in patients with MPM.
3. CBP501
CBP501 is a cell cycle inhibitor that is being studied for mesothelioma treatment. It disrupts DNA replication and limits tumor growth, making it a promising treatment option for mesothelioma. A phase II clinical trial found that CBP501 in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin resulted in a higher response rate and longer progression-free survival than pemetrexed and cisplatin alone in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer, a disease that is similar to mesothelioma.
4. Vorinostat
Vorinostat is a histone deacetylase inhibitor that is used off-label for mesothelioma treatment. Histone deacetylase inhibitors are a new class of drugs that target enzymes involved in gene expression. By inhibiting these enzymes, vorinostat can cause cancer cell death. A phase II clinical trial found that vorinostat in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin resulted in a higher response rate and longer survival time than pemetrexed and cisplatin alone in patients with mesothelioma.
5. Bevacizumab
Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that is used off-label for mesothelioma treatment. It targets a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which is involved in the growth of blood vessels that supply tumors with nutrients and promote their growth. By blocking VEGF, bevacizumab can starve tumors of nutrients and limit their growth. A phase II clinical trial found that bevacizumab in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin resulted in a higher response rate and longer progression-free survival than pemetrexed and cisplatin alone in patients with mesothelioma.
6. Gemcitabine
Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is used off-label for mesothelioma treatment. It is a nucleoside analogue that interferes with DNA synthesis, causing cancer cell death. A phase II clinical trial found that gemcitabine in combination with cisplatin resulted in a higher response rate and longer progression-free survival than cisplatin alone in patients with mesothelioma.
7. Vinorelbine
Vinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is used off-label for mesothelioma treatment. It is a vinca alkaloid that interferes with cell division, causing cancer cell death. A phase II clinical trial found that vinorelbine in combination with cisplatin resulted in a higher response rate and longer progression-free survival than cisplatin alone in patients with mesothelioma.
8. Thalidomide
Thalidomide is a drug that is used off-label for mesothelioma treatment. It has anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic properties, meaning it can reduce inflammation and limit the growth of blood vessels that supply tumors with nutrients. A phase II clinical trial found that thalidomide in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin resulted in a higher response rate and longer progression-free survival than pemetrexed and cisplatin alone in patients with mesothelioma.
9. Interferon Alpha
Interferon alpha is a cytokine that is used off-label for mesothelioma treatment. It has antiviral, anti-tumor, and anti-angiogenic properties. By stimulating the immune response and limiting tumor growth, interferon alpha can be effective in treating mesothelioma. A randomized phase III clinical trial found that interferon alpha in combination with cisplatin and vinblastine resulted in a longer overall survival time than cisplatin and vinblastine alone in patients with mesothelioma.
10. Galinpepimut-S
Galinpepimut-S is a cancer vaccine that is being tested in clinical trials for mesothelioma treatment. It works by stimulating the immune system to attack cancer cells that express the mesothelin protein, which is found on the surface of mesothelioma cells. A phase II clinical trial found that galinpepimut-S in combination with chemotherapy resulted in longer progression-free survival than chemotherapy alone in patients with mesothelioma.
11. Immunotherapy Combinations
Another promising approach for mesothelioma treatment is to combine different types of immunotherapy drugs. By using multiple drugs that target different parts of the immune system, it may be possible to enhance the immune response against cancer cells and improve treatment outcomes. A phase II clinical trial is currently underway to study the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab, two checkpoint inhibitors that target different immune proteins, in patients with mesothelioma. Preliminary data suggests that this combination may be well-tolerated and may result in longer progression-free survival than nivolumab alone.
Overall, it is clear that there are many promising drugs and treatment strategies for mesothelioma that are currently being studied in clinical trials or used off-label. Patients with mesothelioma are encouraged to speak with their doctors about the latest treatment options and to participate in clinical trials when possible to help advance our understanding of this disease.
Combination Therapy with Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs
Combination therapy involves using two or more mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs to treat the disease. The approach is taken to maximize the therapeutic benefits while minimizing the side effects of each drug. The idea here is that the drugs work in synergy, increasing the overall effectiveness of the therapy. Below are some mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used in combination therapy:
Cisplatin and Pemetrexed
Cisplatin and pemetrexed are the most commonly used drugs for combination therapy to treat mesothelioma. The two drugs work together, with cisplatin damaging the DNA of cancer cells and pemetrexed inhibiting their ability to repair this damage. This combination has shown significant efficacy in reducing the symptoms and improving the overall survival of mesothelioma patients.
| Drug Name | Mode of Action | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Cisplatin | Damages the DNA of cancer cells by forming covalent bonds with the DNA molecules, thereby preventing DNA replication and transcription. | Nephrotoxicity, Ototoxicity, Peripheral neuropathy. |
| Pemetrexed | Inhibits the production of key enzymes and proteins involved in DNA synthesis, thereby preventing mesothelioma cells from dividing and multiplying. | Fatigue, Nausea, Loss of appetite. |
Cisplatin and Gemcitabine
Cisplatin and gemcitabine are another combination therapy that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. Gemcitabine works by interfering with the DNA replication process of cancer cells. Cisplatin, on the other hand, disrupts DNA synthesis, leading to the death of the cells. This combination has shown to be effective in treating mesothelioma and improving the quality of life of patients.
| Drug Name | Mode of Action | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Cisplatin | Damages the DNA of cancer cells by forming covalent bonds with the DNA molecules, thereby preventing DNA replication and transcription. | Nephrotoxicity, Ototoxicity, Peripheral neuropathy. |
| Gemcitabine | Interferes with the DNA replication process of cancer cells and causes cell death. | Nausea, Vomiting, Anemia. |
Carboplatin and Pemetrexed
Carboplatin and pemetrexed are sometimes used as an alternative to cisplatin and pemetrexed for combination therapy in mesothelioma patients. Carboplatin works similarly to cisplatin in damaging the DNA and inhibiting cancer cell growth. It has fewer side effects, making it a better option for some patients.
| Drug Name | Mode of Action | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Carboplatin | Damages the DNA of cancer cells and inhibits their ability to divide and multiply. | Nausea, Vomiting, Anemia, Fatigue. |
| Pemetrexed | Inhibits the production of key enzymes and proteins involved in DNA synthesis, thereby preventing mesothelioma cells from dividing and multiplying. | Fatigue, Nausea, Loss of appetite. |
Side Effects of Combination Therapy
The side effects of combination therapy with mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs depend on the specific drugs being used. The most common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, hair loss, and anemia. However, more serious side effects such as kidney or liver damage, nerve damage, and hearing loss may occur.
Your oncologist will work with you to manage the side effects of chemotherapy drugs. Medications may be prescribed to alleviate the symptoms, or the drug dosages may be adjusted to reduce the severity of the side effects.
Conclusion
Mesothelioma is a challenging cancer to treat and requires a combination of therapies to achieve the best outcome possible. Combining mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs is an effective way of treating mesothelioma, as it allows a higher dose of the drug to be given, and this can be more effective than a single drug. However, this approach also comes with more significant side effects. It is essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks of combination therapy with your oncologist before starting treatment.
Side Effects of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs
Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are medications that are used to destroy cancer cells in the body. They help slow down the growth of cancer cells and can also help to reduce the size of tumors. However, like any other chemotherapy drugs, mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs have side effects that can cause discomfort and even lead to complications.
1. Fatigue
One of the most common side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs is fatigue. The drugs can cause extreme tiredness and lack of energy. Patients may need to rest more than usual and may not be able to perform their regular activities.
2. Hair Loss
Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can cause hair loss, which can be distressing for some patients. The hair loss can include the hair on the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes. However, hair loss is usually temporary, and hair normally grows back after treatment ends.
3. Nausea and Vomiting
Chemotherapy drugs can cause nausea and vomiting, which can further cause dehydration. Some patients may also experience loss of appetite, feeling bloated, and changes in their bowel movements.
4. Mouth Sores
Chemotherapy drugs can also cause sores or ulcers in the mouth, which can be painful and uncomfortable. This can lead to difficulty in eating and drinking, which can cause dehydration and malnutrition.
5. Infections
Chemotherapy can weaken the immune system, making patients more susceptible to infections. Patients should take steps to avoid exposure to germs and viruses, such as avoiding crowded places and washing their hands frequently.
6. Bruising and Bleeding
Chemotherapy drugs can also affect the body’s blood clotting ability, which can cause bruising and bleeding. Patients may experience nosebleeds, bleeding gums, or blood in their stools. If these symptoms occur, patients should seek medical attention immediately.
7. Diarrhea and Constipation
Chemotherapy drugs can also cause problems with bowel movements. Patients may experience diarrhea, constipation, or alternating episodes of both. It is important to stay hydrated and eat a balanced diet to prevent dehydration and malnutrition.
8. Peripheral Neuropathy
Some chemotherapy drugs can cause damage to the nerves that control sensation and movement in the limbs. This can result in numbness, tingling, or pain in the hands and feet. Patients should report any symptoms of peripheral neuropathy to their healthcare provider.
9. Kidney and Liver Damage
Chemotherapy drugs can affect the function of the kidneys and liver. Patients may experience changes in urine color, frequency, or volume, or yellowing of the skin and eyes. These symptoms can indicate liver or kidney damage, which requires prompt medical attention.
10. Heart Damage
Some chemotherapy drugs can also cause damage to the heart, leading to heart failure, irregular heartbeat, or decreased heart function. Patients should report chest pain, shortness of breath, or irregular heartbeats to their healthcare provider.
11. Lung Damage
Chemotherapy drugs can also cause damage to the lungs, leading to shortness of breath, cough, or difficulty breathing. Patients should report changes in their breathing to their healthcare provider.
12. Allergic Reactions
Patients can develop allergic reactions to chemotherapy drugs, which can range from mild to severe. Symptoms of an allergic reaction include rash, itching, swelling, and difficulty breathing. Patients should seek medical attention immediately if they experience these symptoms.
13. Chemo Brain
Some patients who undergo chemotherapy may experience cognitive changes, such as difficulty concentrating, memory loss, or a decrease in attention span. This condition is commonly known as chemo brain. While the exact cause of chemo brain is still not fully understood, it is believed to be a result of the chemotherapy drugs affecting the brain and nervous system.
Chemo brain can range from mild to severe and can improve over time after treatment ends. Patients should discuss any cognitive changes with their healthcare provider to develop strategies to manage and improve these symptoms.
| Side Effect | Symptoms | Treatment/Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Fatigue | Tiredness, lack of energy | Rest, exercise, balanced diet |
| 2. Hair Loss | Hair loss on scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes | Wigs, hats, scarves, hair regrowth after treatment |
| 3. Nausea and Vomiting | Feeling sick, vomiting, loss of appetite | Anti-nausea medication, small meals, ginger, acupuncture |
| 4. Mouth Sores | Sores or ulcers in the mouth | Mouth rinses, topical anesthetics, avoid spicy/acidic foods |
| 5. Infections | Fever, coughing, shortness of breath, weakness, fatigue | Wash hands regularly, avoid crowded places, antibiotics |
| 6. Bruising and Bleeding | Bruising, bleeding from gums or nose | Avoid sharp objects, report symptoms to healthcare provider |
| 7. Diarrhea and Constipation | Changes in bowel movements, diarrhea, constipation | Hydration, balanced diet, stool softeners, laxatives |
| 8. Peripheral Neuropathy | Numbness, tingling, pain in hands and feet | Avoid tight shoes and gloves, report symptoms to healthcare provider |
| 9. Kidney and Liver Damage | Changes in urine color, volume, or frequency, yellowing of skin and eyes | Monitor liver and kidney function, report symptoms to healthcare provider |
| 10. Heart Damage | Chest pain, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat | Report symptoms to healthcare provider, monitor heart function |
| 11. Lung Damage | Shortness of breath, coughing, difficulty breathing | Report symptoms to healthcare provider, monitor lung function |
| 12. Allergic Reactions | Rash, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing | Immediate medical attention, avoid triggering substances |
| 13. Chemo Brain | Difficulty concentrating, memory loss, decreased attention span | Cognitive rehabilitation therapy, relaxation techniques, physical exercise |
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer that originates in the lining of the lungs, heart, or abdomen. The disease is caused by exposure to asbestos, a toxic mineral that was widely used in various industries such as construction, manufacturing, and shipbuilding prior to the 1980s. The symptoms of mesothelioma may take decades to appear, and the cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage when it is difficult to treat.
Chemotherapy is one of the main treatments for mesothelioma, and it involves the use of powerful drugs that kill cancer cells or prevent them from growing and spreading. Chemotherapy drugs can be administered intravenously or orally, and they may be given alone or in combination with surgery or radiation therapy. The choice of chemotherapy drugs depends on various factors including the type and stage of mesothelioma, the patient’s overall health, and the potential side effects of the drugs.
Common Chemotherapy Drugs for Mesothelioma
There are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used to treat mesothelioma. These drugs work by targeting different aspects of cancer cells and disrupting their ability to divide and grow. Some of the most common chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma include:
| Drug Name | Mode of Administration | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Cisplatin | Intravenous | Nausea, vomiting, kidney damage, hearing loss, nerve damage, low blood counts |
| Carboplatin | Intravenous | Nausea, vomiting, kidney damage, nerve damage, low blood counts |
| Alimta (Pemetrexed) | Intravenous | Fatigue, nausea, vomiting, low blood counts |
| Gemcitabine | Intravenous | Nausea, vomiting, low blood counts, rash, fever |
| Onconase (Ranpirnase) | Intravenous | Fatigue, fever, flu-like symptoms, low blood counts |
| Methotrexate | Oral or Intravenous | Nausea, vomiting, fatigue, mouth sores, low blood counts |
Strategies to Manage Chemotherapy Side Effects in Mesothelioma Patients
Chemotherapy drugs can cause a range of side effects, some of which may be severe and affect a patient’s quality of life. However, there are several strategies that can help manage these side effects and improve the overall experience of chemotherapy treatment for mesothelioma patients. Here are some of the most common strategies:
1. Anti-nausea Medication:
Nausea and vomiting are common side effects of chemotherapy, and they can be debilitating for some patients. However, there are several anti-nausea medications available that can help alleviate these symptoms. Some of the most commonly used anti-nausea medications include Ondansetron, Granisetron, and Metoclopramide. These drugs work by blocking the signals in the brain that trigger nausea and vomiting.
2. Fluids and Electrolytes:
Chemotherapy drugs can affect the body’s fluid and electrolyte balance, which can lead to dehydration and other complications. To prevent this, many mesothelioma patients receive fluids and electrolytes intravenously during chemotherapy treatment. These fluids help maintain hydration and balance the body’s electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium.
3. Pain Management:
Some chemotherapy drugs can cause pain or discomfort, such as mouth sores, nerve damage, or bone pain. To manage these symptoms, pain medications may be prescribed, such as Acetaminophen or Ibuprofen. In some cases, stronger opioids may be necessary to control severe pain.
4. Blood Count Monitoring:
Chemotherapy drugs can also affect the production of blood cells, which can lead to anemia, low platelet counts, or low white blood cell counts. To prevent complications from these conditions, blood counts are monitored regularly during chemotherapy treatment. If necessary, medications or blood transfusions may be used to manage low blood counts.
5. Diet and Nutrition:
During chemotherapy, it is important to maintain a healthy diet and proper nutrition to support the body’s immune system and healing processes. Mesothelioma patients may be advised to eat a balanced diet that includes protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats. Additionally, some patients may benefit from supplements such as Vitamin D, Calcium, or Iron.
6. Exercise and Activity:
Although mesothelioma patients may experience fatigue or weakness during chemotherapy treatment, it is important to engage in regular exercise and activity to maintain muscle strength, improve mood, and reduce the risk of blood clots or other complications. Patients may be advised to engage in light or moderate exercise, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, depending on their overall health and ability.
7. Emotional Support:
Chemotherapy treatment can be emotionally challenging for mesothelioma patients and their families. Thus, it is important to seek emotional support and resources throughout treatment, such as counseling, support groups, or spiritual care. These resources can provide a safe and supportive environment to discuss concerns, fears, and coping strategies.
8. Avoid Alcohol and Smoking:
During chemotherapy treatment, it is important to avoid smoking and drinking alcohol, as they can interfere with the drugs’ effectiveness and increase the risk of side effects. Additionally, smoking and alcohol can cause further damage to the lungs and other organs affected by mesothelioma, potentially worsening the prognosis.
9. Skin Care:
Some chemotherapy drugs can cause skin reactions or sensitivity, such as rash, itching, or dryness. To manage these symptoms, patients may be advised to use gentle skin care products, avoid exposure to extreme temperatures or sunlight, and wear protective clothing or sunscreen.
10. Follow-Up Care:
After completing chemotherapy treatment, mesothelioma patients require regular follow-up care to monitor for any recurrence or side effects of treatment. Follow-up care may include imaging tests, blood counts, or physical exams. Additionally, patients may need ongoing support and resources to manage any long-term effects of mesothelioma treatment.
11. Inform Your Doctor of Any Concerns:
It is important to communicate any concerns or symptoms to your doctor or healthcare team during chemotherapy treatment. They can work with you to adjust your treatment plan or provide additional resources to manage any side effects effectively.
12. Psychological Support:
Chemotherapy treatment can cause emotional distress to patients, which may lead to feelings of anxiety, depression, and insecurity. It is essential to receive emotional support from your family members, friends, or professionals. Talking to a psychologist or counselor can uplift patients’ mood and assist in coping with treatment-related stress.
13. Practice Post-Chemotherapy Instructions:
It’s common for doctors to give mesothelioma patients specific instructions to follow at home after chemotherapy. Patients must monitor themselves for any signs of pain, fever, bleeding, or discomfort. They may require to come to the clinic for blood tests and further examinations.
14. Relaxation Techniques:
Stress is a part of cancer treatment, and patients may feel physically drained, so they need enough rest and relaxation time. Relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises immediately before treatment sessions reduce anxiety and depression, and it peaceful mind.
In conclusion, mesothelioma is a rare cancer disease with very few effective treatments, and chemotherapy is one of them. Chemotherapy drugs are effective against mesothelioma cells, but they cause many side effects. Fortunately, there are numerous ways to manage these side effects and improve patients’ quality of life during chemotherapy. Mesothelioma patients require ongoing support and follow-up care to ensure long-term health and manage any potential side effects of treatment.
How to Prepare for Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, and heart. One of the main treatments for mesothelioma is chemotherapy, which uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells. While chemotherapy can be effective, it can also cause side effects, such as nausea, fatigue, and hair loss. Therefore, it is important to prepare for chemotherapy treatment to make the process as smooth as possible. Below are some tips on how to prepare for mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment.
1. Understand the Types of Chemotherapy Drugs
Before starting chemotherapy treatment, it is important to understand the different types of chemotherapy drugs that may be used. There are many different chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma, including:
| Chemotherapy Drug | Brand Names |
|---|---|
| Cisplatin | Platinol |
| Carboplatin | Paraplatin |
| Pemetrexed | Alimta |
| Gemcitabine | Gemzar |
| Vinorelbine | Navelbine |
Each drug has different side effects and may be used in combination with other drugs to maximize the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
2. Discuss the Treatment Plan with the Medical Team
It is important to discuss the chemotherapy treatment plan with the medical team, including the frequency and duration of treatments. The medical team will be able to provide more information about what to expect during treatment and how to manage side effects.
3. Prepare for Side Effects
Most chemotherapy drugs have side effects, including nausea, fatigue, hair loss, and infections. It is important to talk to the medical team about how to manage these side effects, such as taking anti-nausea medication or resting when tired. In some cases, the medical team may recommend taking preventive measures, such as antibiotics or antiviral medication, to avoid infections.
4. Consider Nutrition
Chemotherapy can affect the body’s ability to absorb nutrients, leading to weight loss and malnutrition. It is important to maintain a healthy diet during chemotherapy, focusing on nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. The medical team may recommend working with a registered dietitian to create a meal plan that meets the body’s nutritional needs.
5. Stay Hydrated
Chemotherapy can cause dehydration, so it is important to drink enough fluids before, during, and after treatment. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water per day, and consider drinking electrolyte-rich fluids such as sports drinks or coconut water to replenish lost minerals.
6. Get Adequate Rest
Chemotherapy can cause fatigue, so it is important to get adequate rest during treatment. Try to stick to a regular sleep schedule, and take naps as needed to avoid overexertion.
7. Dress for Comfort
Wear comfortable clothing to chemotherapy appointments, taking into consideration the location of the injection site and accessibility of the veins. Dressing in layers can also help regulate body temperature, as chemotherapy can cause fluctuations in body temperature.
8. Have a Support System
Chemotherapy can be emotionally taxing, so it is important to have a support system in place. This can include friends, family, or support groups for people with mesothelioma or cancer in general.
9. Stay Active
While chemotherapy can cause fatigue, it is still important to stay active and engage in regular physical activity. This can help maintain muscle mass, improve mood, and boost energy levels. Talk to the medical team about what types of physical activity are appropriate during treatment.
10. Plan Ahead for Transportation
Chemotherapy appointments can be time-intensive, so it is important to plan ahead for transportation to and from the appointments. This may involve arranging for a ride with a friend or family member, taking a taxi, or using a ride-sharing service.
11. Prepare for Hair Loss
Chemotherapy can cause hair loss, so it is important to prepare emotionally for this possibility. This may involve cutting hair short before treatment or purchasing wigs or head coverings to wear during treatment.
12. Practise Good Hand Hygiene
Chemotherapy can weaken the immune system, making it more susceptible to infections. It is important to practise good hand hygiene, washing hands frequently with soap and water and avoiding contact with people who are sick.
13. Avoid Over-the-Counter Medications
Before taking any over-the-counter medications during chemotherapy treatment, it is important to consult with the medical team. Some medications can interact with chemotherapy drugs or cause unwanted side effects.
14. Communicate with the Medical Team
During chemotherapy treatment, it is important to communicate openly and honestly with the medical team about any side effects or concerns. The medical team can adjust the treatment plan or provide additional support as needed.
15. Take Care of Emotional Health
Chemotherapy can be emotionally challenging, so it is important to take care of emotional health during treatment. This may involve counselling, joining a support group, or engaging in activities that promote relaxation and stress reduction, such as yoga or meditation.
How Chemotherapy is Administered for Mesothelioma Patients
Mesothelioma is a rare but aggressive type of cancer that develops in the lining of certain internal organs, most commonly the lungs. Like other types of cancer, mesothelioma is treated using a combination of different therapies, including chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to slow down or destroy cancer cells.
Here we provide some important information about how chemotherapy is administered for mesothelioma patients.
1. Which Chemotherapy Drugs Are Used for Mesothelioma Treatment?
There are several chemotherapy drugs used in mesothelioma treatment. Some of the most common drugs include:
| Chemotherapy Drug | Common Brand Name |
|---|---|
| Carboplatin | Paraplatin |
| Cisplatin | Platinol |
| Gemcitabine | Gemzar |
| Pemetrexed | Alimta |
Each of these drugs works in a slightly different way and is used under different circumstances.
2. What Is the Process for Administering Chemotherapy?
There are several ways chemotherapy drugs can be administered to mesothelioma patients. The most common methods include:
Intravenous Infusion
During intravenous infusion, chemotherapy drugs are injected into a vein in the arm or hand using a needle. The drugs are mixed with a solution and administered slowly over a period of time.
Oral Medications
Some chemotherapy drugs come in the form of a pill or capsule that can be taken orally. These medicines are usually given in cycles, with specific days for taking the drugs and rest time between cycles.
Injections
Some chemotherapy drugs can be injected directly into the mesothelioma tumor. This method is known as intratumoral chemotherapy and it is typically performed using a syringe.
Other Methods
Other methods of administering chemotherapy for mesothelioma may include a catheter or port, which is a small tube inserted under the skin that allows for easy injections of the drugs.
3. How Long Does Chemotherapy Last for Mesothelioma Patients?
The duration of chemotherapy for mesothelioma patients can vary based on the specific drugs being used, the stage of the cancer, and the patient’s overall health. Most patients will receive chemotherapy in cycles, typically lasting around three to four weeks. A cycle of chemotherapy is often followed by a period of rest to allow the body time to recover.
4. What Are the Side Effects of Chemotherapy?
While chemotherapy is an effective treatment for mesothelioma, it can also cause unpleasant side effects. These side effects will vary from person to person and may include:
- nausea
- vomiting
- loss of appetite
- hair loss
- fatigue
- anemia
- diarrhea
- mouth sores
If you experience side effects during chemotherapy, it is important to talk to your doctor right away. There may be medications or other treatments that can help alleviate these symptoms.
5. What Are the Benefits of Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma?
Chemotherapy can be an effective treatment option for mesothelioma patients in certain circumstances. Some of the benefits of using chemotherapy may include:
- shrinking the size of the mesothelioma tumor
- relieving pain and other mesothelioma symptoms
- improving overall survival rates
Ultimately, the effectiveness of mesothelioma chemotherapy will depend on a variety of factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and the specific drugs being used.
6. What Should Patients Expect During Chemotherapy Treatment?
Chemotherapy can be a long and difficult process, both physically and emotionally. Patients receiving chemotherapy treatment for mesothelioma can expect to undergo numerous blood tests and scans to monitor their cancer progression and the effectiveness of their chemotherapy treatment.
It is common for patients to experience fatigue during chemotherapy, and some patients may require time off work or other daily routines to rest and recover. Support from family and friends can be an important part of the treatment process for mesothelioma patients undergoing chemotherapy.
7. Conclusion
Chemotherapy is a common treatment option for mesothelioma patients. While it can come with side effects, it is a valuable therapy for many patients in improving overall survival rates and reducing the size and symptoms of mesothelioma tumors. Patients considering chemotherapy as part of their mesothelioma treatment plan should have an open conversation with their doctor and carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks.
Types of Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma
Chemotherapy is an important treatment option for mesothelioma patients. It involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. There are different types of chemotherapy drugs that can be used for mesothelioma treatment. The type of chemotherapy that a patient receives depends on factors such as the stage of cancer, the location of cancer, and the patient’s overall health. Below are the different types of chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma.
1. Alimta (Pemetrexed)
Alimta is one of the most common chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma. It is usually administered in combination with another drug called Cisplatin. Alimta works by inhibiting the division of cancer cells and reducing the growth of tumors. It is administered intravenously once every three weeks. Alimta has become the standard first-line chemotherapy for mesothelioma treatment.
2. Cisplatin
Cisplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with Alimta. It works by damaging DNA in cancer cells, causing the cells to die. The drug is given through an IV once every three to four weeks. Common side effects of Cisplatin include nausea, vomiting, and kidney damage.
3. Carboplatin
Carboplatin is another platinum-based chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. It is less toxic than Cisplatin and is therefore preferred for patients with pre-existing kidney problems. Carboplatin is usually given in combination with Alimta once every three to four weeks.
4. Gemcitabine
Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat various types of cancer, including mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the division of cancer cells and reducing the size of tumors. Gemcitabine is usually given every week for several months through an IV. Common side effects of the drug include fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
5. Vinorelbine
Vinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is often used to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the division of cancer cells and slowing down tumor growth. The drug is administered through an IV once every week for several months. Common side effects of Vinorelbine include fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
6. Methotrexate
Methotrexate is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma in combination with other drugs. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and reducing the size of tumors. Methotrexate is given through an IV once every week for several months. Common side effects of the drug include fatigue, nausea, and mouth sores.
7. Doxorubicin
Doxorubicin is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and reducing the size of tumors. Doxorubicin is usually given through an IV once every three to four weeks. Common side effects of the drug include fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
8. Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and reducing the size of tumors. The drug is given through an IV once every three to four weeks. Common side effects of Cyclophosphamide include fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
9. Mitomycin-C
Mitomycin-C is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and reducing the size of tumors. The drug is given through an IV once every three to four weeks. Common side effects of Mitomycin-C include fatigue, nausea, and mouth sores.
10. Ifosfamide
Ifosfamide is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and reducing the size of tumors. The drug is given through an IV once every three to four weeks. Common side effects of Ifosfamide include fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
11. Etoposide
Etoposide is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and reducing the size of tumors. The drug is given through an IV once every three to four weeks. Common side effects of Etoposide include fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
12. Vincristine
Vincristine is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and reducing the size of tumors. The drug is given through an IV once every three to four weeks. Common side effects of Vincristine include fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
13. Amsacrine
Amsacrine is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and reducing the size of tumors. The drug is given through an IV once every three to four weeks. Common side effects of Amsacrine include fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
14. Bleomycin
Bleomycin is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and reducing the size of tumors. The drug is given through an IV once every three to four weeks. Common side effects of Bleomycin include fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
15. Docetaxel
Docetaxel is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and reducing the size of tumors. The drug is given through an IV once every three to four weeks. Common side effects of Docetaxel include fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
16. Paclitaxel
Paclitaxel is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and reducing the size of tumors. The drug is given through an IV once every three to four weeks. Common side effects of Paclitaxel include fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
17. Erlotinib
Erlotinib is a targeted therapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking the activation of a protein called Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) which is known to stimulate the growth of cancer cells. The drug is taken orally once every day. Common side effects of Erlotinib include skin rash, diarrhea, and nausea.
| Chemotherapy Agent | Mode of Administration | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Alimta (Pemetrexed) | IV infusion every 3 weeks | Nausea, vomiting, fatigue, anemia, neutropenia |
| Cisplatin | IV infusion every 3-4 weeks | Nausea, vomiting, kidney damage, hearing loss |
| Carboplatin | IV infusion every 3-4 weeks | Nausea, vomiting, anemia, fatigue |
| Gemcitabine | IV infusion weekly for several months | Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, low white blood cells |
| Vinorelbine | IV infusion weekly for several months | Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, low white blood cells |
| Methotrexate | IV infusion weekly for several months | Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, mouth sores |
| Doxorubicin | IV infusion every 3-4 weeks | Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, heart damage |
| Cyclophosphamide | IV infusion every 3-4 weeks | Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, low white blood cells |
| Mitomycin-C | IV infusion every 3-4 weeks | Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, mouth sores |
| Ifosfamide | IV infusion every 3-4 weeks | Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, low white blood cells |
| Etoposide | IV infusion every 3-4 weeks | Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, low white blood cells |
| Vincristine | IV infusion every 3-4 weeks | Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, low white blood cells |
| Amsacrine | IV infusion every 3-4 weeks | Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, low white blood cells |
| Bleomycin | IV infusion every 3-4 weeks | Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, lung damage |
| Docetaxel | IV infusion every 3-4 weeks | Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, low white blood cells |
| Paclitaxel | IV infusion every 3-4 weeks | Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, low white blood cells |
| Erlotinib | Oral, once daily | Skin rash, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting |
Each patient’s condition is unique, and the type of chemotherapy administered may vary depending on factors such as the stage and progression of the disease, underlying health conditions, and overall health of the patient. The decision to undergo chemotherapy treatment should be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare provider who is experienced in treating mesothelioma.
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy as a Mesothelioma Treatment
Mesothelioma is a rare and fatal type of cancer that is caused by asbestos exposure. It develops in the linings of the lungs, abdomen, or heart and can take decades to manifest after exposure to the carcinogenic fibers. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are commonly used to treat the disease, either alone or in combination with surgery or radiation therapy.
What is Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy?
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is a type of chemotherapy treatment that is given before the main treatment, which is usually surgery for mesothelioma. The aim of neoadjuvant chemotherapy is to shrink the tumor and make it easier to remove.
The use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy has become increasingly popular in recent years in the treatment of mesothelioma. For example, in some cases, neoadjuvant chemotherapy is used in conjunction with an aggressive surgery called extrapleural pneumonectomy (EPP). The aim of this approach is to remove as much of the tumor as possible and help improve the patient’s chances of survival.
How Does Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Work?
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy works by providing a potent combination of drugs that target the cancerous cells and help to shrink the tumor. The drugs are administered in cycles, and each cycle typically lasts for about four weeks.
The choice of drugs that are used in neoadjuvant chemotherapy for mesothelioma treatment depends on various factors. These include the type and stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and any other treatments that the patient has undergone. Typically, chemotherapy drugs like cisplatin, carboplatin, gemcitabine, and pemetrexed are used for neoadjuvant chemotherapy for mesothelioma treatment.
Pros and Cons of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
What to Expect During Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma
If your doctor recommends neoadjuvant chemotherapy for mesothelioma, it is important to understand what to expect before, during, and after treatment.
Before treatment: Before your treatment, you will undergo a series of tests to determine the most effective treatment plan for your specific case. These tests may include a physical exam, blood tests, imaging tests, or other diagnostic tests.
During treatment: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is typically administered in cycles, with each cycle lasting about four weeks. The drugs are administered through an IV, and you may need to stay in the hospital during treatment. During this time, you may experience side effects such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue, or hair loss.
After treatment: After your neoadjuvant chemotherapy treatment is complete, you will need to undergo further tests to determine its effectiveness. Your doctor will monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as necessary.
Conclusion
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is a promising option for the treatment of mesothelioma. While it is not without its risks and side effects, it can help shrink tumors, improve survival rates, and make other treatments more effective. If you have been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it is important to discuss all of your treatment options with your doctor to determine the best course of action for your specific case.
Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that is often associated with exposure to asbestos. It typically affects the lining of the lungs, but can also occur in other parts of the body, such as the abdomen or heart. Mesothelioma is usually diagnosed at an advanced stage, which limits treatment options and makes it difficult to cure. However, chemotherapy is one treatment method that has shown promise in improving survival rates and quality of life for mesothelioma patients.
What is Adjuvant Chemotherapy?
Adjuvant chemotherapy is a type of chemotherapy that is given after surgery to remove the mesothelioma tumor. This treatment is designed to kill any remaining cancer cells and prevent the cancer from returning. Adjuvant chemotherapy may also be given before surgery to shrink the tumor and make it easier to remove. Chemotherapy drugs used in adjuvant therapy target rapidly dividing cancer cells, which are more sensitive to the effects of chemotherapy than healthy cells.
How is Adjuvant Chemotherapy Administered?
Adjuvant chemotherapy can be delivered in different ways, depending on the individual patient’s situation and overall health. The most common method is intravenous (IV) infusion, where the chemotherapy drugs are administered directly into a vein. This allows the drugs to circulate throughout the body and reach any cancer cells that may have spread beyond the site of the original tumor. Oral chemotherapy is also an option for some patients, where the drugs are taken in pill form. This method may be used for patients who are unable to tolerate IV chemotherapy or for those who live far from the hospital and need to manage their treatment at home.
Types of Chemotherapy Drugs Used in Adjuvant Therapy
Several chemotherapy drugs are used in adjuvant therapy for mesothelioma, either alone or in combination. Some of the commonly used drugs include:
| Chemotherapy Drug | Mode of Action |
|---|---|
| Cisplatin | Interferes with DNA replication in cancer cells, causing them to die |
| Carboplatin | Similar to cisplatin, but with fewer side effects |
| Gemcitabine | Disrupts cell division and kills cancer cells |
| Pemetrexed | Inhibits enzymes necessary for cell division, leading to cancer cell death |
Side Effects of Adjuvant Chemotherapy
While adjuvant chemotherapy can be an effective treatment for mesothelioma, it also has some potential side effects. Because chemotherapy drugs target rapidly dividing cells, they can also damage healthy cells that divide quickly, such as those in the digestive tract, hair follicles, and bone marrow. Some of the most common side effects of adjuvant chemotherapy include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hair loss
- Fatigue
- Mouth sores
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Low white blood cell count, which can increase the risk of infection
While these side effects can be difficult to manage, they are usually temporary and can be treated with medication or lifestyle changes. Patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy will be monitored closely by their healthcare team to assess their response to treatment and manage any side effects as they arise.
Effectiveness of Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma
Studies have shown that adjuvant chemotherapy can improve survival rates and quality of life for mesothelioma patients. One study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology found that patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy after surgery had a median survival time of 29.1 months, compared to 16.8 months for those who received surgery alone. Another study published in the Annals of Oncology found that adjuvant chemotherapy significantly improved overall survival and progression-free survival in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Is Adjuvant Chemotherapy Right for You?
If you have been diagnosed with mesothelioma, you may be wondering if adjuvant chemotherapy is right for you. The decision of whether to undergo adjuvant chemotherapy will depend on several factors, including the stage and location of the cancer, your overall health and fitness level, and your personal preferences. Your healthcare team will work with you to develop an individualized treatment plan that takes these factors into account.
It is important to note that adjuvant chemotherapy, like all cancer treatments, is not without risks. Some patients may not be able to tolerate the side effects of chemotherapy or may have other health conditions that make it too risky. Your healthcare team will carefully assess your case and weigh the potential benefits and risks of adjuvant chemotherapy against other available treatment options.
In Conclusion
Adjuvant chemotherapy is a promising treatment option for mesothelioma patients who have undergone surgery to remove the tumor. It can improve survival rates and quality of life by killing any remaining cancer cells and preventing the cancer from returning. While adjuvant chemotherapy has some potential side effects, these are usually temporary and can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes. If you have been diagnosed with mesothelioma, talk to your healthcare team about whether adjuvant chemotherapy is right for you.
Maintenance Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a rare type of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, heart, or abdomen. It is mainly caused by the exposure to asbestos, a naturally occurring fibrous mineral that was widely used in construction, insulation, and other industries until the 1980s.
The symptoms of mesothelioma can take several years, even decades to develop, and are often mistaken for other respiratory or digestive conditions. The diagnosis of mesothelioma is usually confirmed by imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or PET scans, and confirmed by a biopsy.
Mesothelioma is a difficult cancer to treat, as it is often diagnosed at an advanced stage and does not respond well to conventional cancer therapies such as surgery and radiation. However, chemotherapy drugs have shown some promise in improving the quality of life and extending the survival rate of mesothelioma patients, especially when used as part of a maintenance treatment.
What is maintenance chemotherapy?
Maintenance chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that involves the use of chemotherapy drugs at a lower dose and frequency to keep cancer cells from growing or spreading after the initial treatment has been completed or the cancer has gone into remission. This approach is different from the standard chemotherapy, which uses high doses of chemotherapy drugs to kill cancer cells.
Maintenance chemotherapy is typically used after the initial treatment, such as surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, to prevent cancer recurrence or progression and prolong the remission period. This type of chemotherapy is also used in some cases when the cancer has spread too widely to control with other types of therapy.
How does maintenance chemotherapy work?
Maintenance chemotherapy works by targeting and killing cancer cells that may still be present in the body after the initial treatment. The goal of maintenance chemotherapy is to keep cancer cells in check by suppressing their growth and preventing them from spreading to other parts of the body. By doing so, maintenance chemotherapy can help prevent cancer recurrence and improve overall survival rates.
There are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used for maintenance treatment in mesothelioma patients. These drugs include:
| Chemotherapy drugs | How they work |
|---|---|
| Pemetrexed (Alimta) | It blocks the formation of DNA and RNA, which cancer cells need to grow and multiply. |
| Cisplatin | It damages the DNA in cancer cells and prevents them from dividing and multiplying. |
| Carboplatin | It works in a similar way to cisplatin, but it is less toxic and has fewer side effects. |
| Gemcitabine | It interferes with the production of DNA and RNA, which slows down the growth of cancer cells. |
| Methotrexate | It inhibits the synthesis of DNA and RNA, which slows down the growth of cancer cells. |
These chemotherapy drugs can be administered in different ways, including intravenously (IV), orally, or in combination with other drugs. The choice of the chemotherapy drugs and the dosages depend on various factors, such as the stage and location of the cancer, the patient’s overall health condition, and the potential side effects of the drugs.
Benefits of maintenance chemotherapy
Maintenance chemotherapy has several benefits for mesothelioma patients, such as:
Preventing cancer recurrence
Maintenance chemotherapy can help keep cancer cells in check and reduce the risk of cancer recurrence after the initial treatment. This can prolong the patient’s survival and improve their quality of life.
Minimizing the side effects
Due to the lower dosages and frequencies of the chemotherapy drugs used for maintenance treatment, patients may experience fewer and less severe side effects than those who undergo standard chemotherapy. This can lead to better tolerability of the treatment and fewer interruptions in the therapy.
Improved quality of life
Maintenance chemotherapy can help improve the patient’s quality of life by reducing the symptoms of mesothelioma, such as pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. This can allow them to continue their daily activities and maintain their independence.
Limitations of maintenance chemotherapy
Maintenance chemotherapy also has some limitations, such as:
Costs
Maintenance chemotherapy can be expensive, as patients may need to undergo regular check-ups and tests to monitor their response to the treatment. Moreover, some of the chemotherapy drugs used for maintenance treatment may not be covered by health insurance or may require prior authorization.
Side effects
Maintenance chemotherapy can still cause side effects, although they may be milder than those experienced during the initial treatment. Some of the common side effects of chemotherapy drugs include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, hair loss, and decreased appetite.
Resistance to treatment
Some cancer cells may become resistant to chemotherapy drugs over time, which can reduce the effectiveness of maintenance treatment. This can lead to cancer recurrence or progression despite ongoing chemotherapy.
Conclusion
Maintenance chemotherapy is a promising treatment option for mesothelioma patients, especially for those who have undergone surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy as the initial treatment. This approach can help prevent cancer recurrence or progression, improve quality of life, and prolong survival by keeping cancer cells in check and minimizing the side effects. However, it is important to note that maintenance chemotherapy is not suitable for everyone, and the choice of drugs and dosages should be carefully evaluated by a qualified healthcare professional based on the patient’s individual needs and preferences.
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma Treatment
Mesothelioma is a rare type of cancer that affects the lining of the chest and abdomen. It is usually caused by exposure to asbestos, and it can take decades for the disease to develop after exposure. Unfortunately, mesothelioma is usually not diagnosed until it is in its advanced stages, making treatment more difficult. Chemotherapy is one of the main treatments for mesothelioma, and intraperitoneal chemotherapy is a promising approach that has shown some success.
Intraperitoneal chemotherapy involves administering chemotherapy drugs directly into the abdominal cavity, where the cancer is located. This approach allows for higher concentrations of the drugs to be delivered to the cancer cells, while minimizing the amount of drug that reaches the rest of the body. This can help to reduce side effects and improve the effectiveness of the treatment.
There are several chemotherapy drugs that have been used in intraperitoneal chemotherapy for mesothelioma. Here are 21 of the most commonly used drugs:
1. Cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. It is a platinum-based drug that works by damaging the DNA inside cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and multiplying. Cisplatin is usually given in combination with other chemotherapy drugs.
2. Carboplatin
Carboplatin is another platinum-based chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works in a similar way to cisplatin by damaging the DNA in cancer cells.
3. Alimta
Alimta, also known as pemetrexed, is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the enzymes that cancer cells need to grow and divide.
4. Doxorubicin
Doxorubicin is a chemotherapy drug that works by interfering with the DNA inside cancer cells. It is often used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma.
5. Methotrexate
Methotrexate is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by blocking enzymes that cancer cells need to grow and divide.
6. Gemcitabine
Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with cisplatin for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the DNA inside cancer cells.
7. Vinorelbine
Vinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with cisplatin for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the microtubules inside cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and multiplying.
8. Mitomycin C
Mitomycin C is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA inside cancer cells.
9. Paclitaxel
Paclitaxel is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with carboplatin for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the microtubules inside cancer cells.
10. Oxaliplatin
Oxaliplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA inside cancer cells.
11. Irinotecan
Irinotecan is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the DNA inside cancer cells.
12. 5-Fluorouracil
5-Fluorouracil is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the enzymes that cancer cells need to grow and divide.
13. Topotecan
Topotecan is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the DNA inside cancer cells.
14. Epirubicin
Epirubicin is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the DNA inside cancer cells.
15. Bleomycin
Bleomycin is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA inside cancer cells.
16. Docetaxel
Docetaxel is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the microtubules inside cancer cells.
17. Ifosfamide
Ifosfamide is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA inside cancer cells.
18. Etoposide
Etoposide is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the DNA inside cancer cells.
19. Vincristine
Vincristine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the microtubules inside cancer cells.
20. Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA inside cancer cells.
21. Mitoxantrone
Mitoxantrone is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the DNA inside cancer cells.
Intraperitoneal chemotherapy for mesothelioma is usually administered in a hospital or clinic setting, and the drugs are delivered through a catheter that is placed into the abdominal cavity. Patients are generally given a combination of drugs over a period of several weeks, with breaks in between cycles to allow the body to recover.
While intraperitoneal chemotherapy can be effective for some patients with mesothelioma, it is not without its drawbacks. The procedure can be invasive and may require hospitalization, and there is a risk of complications such as infection. Additionally, not all patients are good candidates for this type of treatment, as it depends on factors such as the stage of the cancer and the overall health of the patient.
Overall, intraperitoneal chemotherapy is a promising approach to the treatment of mesothelioma, and it is an option that should be considered for eligible patients. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it is important to talk to your doctor about all of the treatment options that are available, including intraperitoneal chemotherapy. With the right treatment plan, it is possible to manage the symptoms of mesothelioma and improve your quality of life.
| Chemotherapy Drug | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|
| Cisplatin | Interferes with DNA inside cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and multiplying. |
| Carboplatin | Interferes with DNA inside cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and multiplying. |
| Alimta | Interferes with enzymes that cancer cells need to grow and divide. |
| Doxorubicin | Interferes with the DNA inside cancer cells. |
| Methotrexate | Blocks enzymes that cancer cells need to grow and divide. |
| Gemcitabine | Interferes with the DNA inside cancer cells. |
| Vinorelbine | Interferes with microtubules inside cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and multiplying. |
| Mitomycin C | Interferes with the DNA inside cancer cells. |
| Paclitaxel | Interferes with microtubules inside cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and multiplying. |
| Oxaliplatin | Interferes with the DNA inside cancer cells. |
| Irinotecan | Interferes with the DNA inside cancer cells. |
| 5-Fluorouracil | Interferes with the enzymes that cancer cells need to grow and divide. |
| Topotecan | Interferes with the DNA inside cancer cells. |
| Epirubicin | Interferes with the DNA inside cancer cells. |
| Bleomycin | Interferes with the DNA inside cancer cells. |
| Docetaxel | Interferes with microtubules inside cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and multiplying. |
| Ifosfamide | Interferes with the DNA inside cancer cells. |
| Etoposide | Interferes with the DNA inside cancer cells. |
| Vincristine | Interferes with microtubules inside cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and multiplying. |
| Cyclophosphamide | Interferes with the DNA inside cancer cells. |
| Mitoxantrone | Interferes with the DNA inside cancer cells. |
Intravenous Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is an aggressive form of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, and heart. Surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy are the most common types of treatments for mesothelioma. However, mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs have been found to be a more effective treatment option for this type of cancer. With chemotherapy, drugs are administered into the bloodstream, and they circulate throughout the entire body to attack and kill cancer cells. In this article, we will be discussing the various mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs that are administered intravenously.
The Goals of Mesothelioma Intravenous Chemotherapy
The primary goal of mesothelioma chemotherapy is to slow down or stop the growth and spread of cancer cells. In some cases, mesothelioma chemotherapy can even shrink tumors, which can improve the patient’s quality of life. The goals of mesothelioma chemotherapy are:
| Goal | Description |
|---|---|
| Control the cancer | Reduce the size of the tumors and keep them from spreading to other parts of the body |
| Eliminate the cancer | Destroy all of the cancer cells in the body, but this is not always possible with mesothelioma due to how it spreads and affects the body’s internal organs. |
| Relieve the symptoms associated with mesothelioma | Reduce pain, maintain lung and heart function, and improve the patient’s quality of life. |
The Types of Mesothelioma Intravenous Chemotherapy Drugs
There are different types of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs that are administered intravenously. The most common types of drugs used for this are:
Alimta (Pemetrexed)
Alimta, also known as pemetrexed, is a chemotherapy drug that is used for the treatment of mesothelioma. This drug is given intravenously, and it works by inhibiting the enzymes that are needed for the division of cancer cells. Alimta is often used in combination with another chemotherapy drug called cisplatin, and the two together are considered the standard of care for mesothelioma treatment.
Cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with Alimta for the treatment of mesothelioma. This drug works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, which can prevent them from replicating and growing. Cisplatin is given intravenously, and it is often administered over the course of several hours. Side effects of cisplatin can include nausea, vomiting, and kidney damage.
Carboplatin
Carboplatin is another chemotherapy drug that is often used to treat mesothelioma. This drug is similar to cisplatin, but it is less toxic, making it a good option for patients who cannot tolerate cisplatin. Carboplatin works by disrupting the DNA of cancer cells, which can prevent them from multiplying. Carboplatin is given intravenously, and it is often used in combination with Alimta.
Gemcitabine
Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is often used to treat mesothelioma. This drug works by stopping the growth and spread of cancer cells by interrupting their DNA replication processes. Gemcitabine is given intravenously, and it is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs such as cisplatin. Some side effects of gemcitabine include anemia, low white blood cell counts, and low platelet counts.
Onconase (Ranpirnase)
Onconase, also known as ranpirnase, is a chemotherapy drug that is specifically designed to treat mesothelioma. This drug is derived from frog eggs and works by preventing the production of proteins that are necessary for cancer cell growth. Onconase is given intravenously, and it can be administered over the course of several weeks. Some side effects of Onconase include fatigue, nausea, and skin irritation.
Choosing the Right Mesothelioma Intravenous Chemotherapy Drug Treatment
The type of mesothelioma chemotherapy drug that is chosen for treatment depends on several factors, such as the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and the presence of other medical conditions. Your oncologist will evaluate your specific situation and provide recommendations for the appropriate chemotherapy drugs to use for your treatment.
It is essential to work with a medical team that is knowledgeable about treating mesothelioma, as the disease can be difficult to manage. Oncologists who specialize in mesothelioma have expertise in using intravenous chemotherapy drugs such as Alimta, cisplatin, carboplatin, gemcitabine, and onconase for the treatment of this type of cancer. They can also recommend new emerging treatments that may be available through clinical trials.
The Major Benefits and Risks of Mesothelioma Intravenous Chemotherapy
Intravenous chemotherapy for mesothelioma can have significant benefits, such as:
- Reducing the size of tumors and keeping them from spreading
- Improving the quality of life by reducing pain and other symptoms associated with the cancer
- Prolonging survival in some patients and extending the time between treatments, which can help improve the patient’s quality of life.
However, chemotherapy drugs also have risks and side effects that must be considered. The most common side effects of mesothelioma intravenous chemotherapy drugs include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hair loss
- Fatigue
- Low white blood cell counts
- Low red blood cell counts
- Low platelet counts
While these side effects can be uncomfortable, they are generally temporary, and they can be treated with medications or other supportive therapies. Depending on your specific medical history and the type of mesothelioma chemotherapy drug used, there may be other, less common side effects that you may experience. Your oncologist will be able to provide a detailed overview of your treatment plan and discuss the potential risks and benefits of mesothelioma intravenous chemotherapy drugs.
Conclusion
Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs that are administered intravenously have proven to be a very effective treatment option for people diagnosed with mesothelioma. The drugs can slow, stop, or even shrink cancer cells, helping to improve the patient’s quality of life. Working with a medical team that has expertise in treating mesothelioma is essential for comprehensive evaluation and treatment. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, contact an oncologist to explore the best possible treatment options and discuss the potential benefits and risks of mesothelioma intravenous chemotherapy drugs.
Clinical Trials for Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs
Introduction
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that arises from the lining of the lungs, abdomen, and heart. It is primarily caused by exposure to asbestos fibers, and its symptoms may take decades to manifest. Mesothelioma can be difficult to diagnose, and current treatment options are limited. However, chemotherapy drugs have shown promise in extending patients’ lives and improving their quality of life. The development of new chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma is an active area of research, and clinical trials are essential for evaluating their efficacy and safety.
Why Clinical Trials are Important
Clinical trials are studies that involve human subjects to evaluate the efficacy and safety of new drugs or treatment methods. They are essential for advancing medical knowledge and improving patient outcomes. Clinical trials evaluate new drugs by testing them against existing treatments or a placebo. They may also compare different doses, schedules, or combinations of drugs. Clinical trials are conducted in phases, each with specific objectives and eligibility criteria. The phases of a clinical trial are:
| Phase | Objective | Eligibility |
|---|---|---|
| Phase I | Evaluate safety and dosage | Open to a small number of patients |
| Phase II | Evaluate effectiveness and side effects | Open to a larger number of patients with specific characteristics |
| Phase III | Compare new treatment to standard of care | Open to a large number of patients with specific characteristics |
| Phase IV | Monitor long-term safety and effectiveness | Open to patients who have completed previous phases |
Current Chemotherapy Drugs for Mesothelioma
The current standard of care for mesothelioma includes chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy. Chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma typically target rapidly dividing cancer cells and include the following:
- Platinum-based drugs: Cisplatin and carboplatin
- Antifolates: Pemetrexed (Alimta)
- Antimitotics: Vinorelbine (Navelbine) and gemcitabine (Gemzar)
These drugs have shown to improve survival rates, alleviate symptoms, and improve quality of life for mesothelioma patients. However, they are not curative and have significant side effects.
New Chemotherapy Drugs in Clinical Trials
There are several new chemotherapy drugs in various stages of clinical trials for mesothelioma. Some of the most promising ones are:
Tazemetostat
Tazemetostat is a selective inhibitor of the EZH2 methyltransferase enzyme that is overexpressed in mesothelioma and other solid tumors. By inhibiting this enzyme, Tazemetostat prevents the growth of cancer cells and induces apoptosis. Tazemetostat has shown promising results in preclinical studies and in early-phase clinical trials. In a phase 2 study of 74 mesothelioma patients with BAP1 loss, Tazemetostat showed a disease control rate of 56%. Tazemetostat is currently in phase 3 clinical trials for mesothelioma and other solid tumors.
Osimertinib
Osimertinib is a selective inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase that is mutated in certain types of mesothelioma. Osimertinib has shown to improve progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Osimertinib is currently in phase 2 clinical trials for mesothelioma with EGFR mutations.
Apatinib
Apatinib is a small-molecule inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) that is overexpressed in mesothelioma and contributes to tumor angiogenesis and progression. Apatinib has shown to improve progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with advanced gastric cancer and other solid tumors. Apatinib is currently in phase 2 clinical trials for mesothelioma.
Melflufen
Melflufen is a novel peptide-drug conjugate that delivers an alkylating agent to cancer cells. Melflufen has shown potent antitumor activity in preclinical studies and in phase 1 and 2 clinical trials for multiple myeloma and other solid tumors. Melflufen is currently in phase 2 clinical trials for mesothelioma.
Conclusion
Clinical trials are essential for evaluating the safety and effectiveness of new chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma. The development of new drugs is an active area of research, and several promising drugs are currently in various stages of clinical trials. These drugs offer hope for improving the survival rates and quality of life of mesothelioma patients, and their success in clinical trials will pave the way for more effective treatments in the future.
Promising New Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs in Development
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer, which affects the tissue lining of the lungs, abdomen, and heart. It is primarily caused due to asbestos exposure. Mesothelioma has a very poor prognosis, and the five-year survival rate is approximately 5%. However, advancements in research and development of new drugs are bringing hope to mesothelioma patients and their families. In this article, we will look at some of the promising new mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs in development.
1. Tumor Treating Fields (TTFields)
Tumor Treating Fields (TTFields) is a new technology that uses electric fields to slow or stop the growth of cancer cells. It is a non-invasive treatment that involves wearing a cap-like device on the head that delivers electric fields to the tumors. TTFields are currently being tested in clinical trials for mesothelioma. The preliminary results of the trials have been promising, and the technology has been shown to improve the median overall survival rate of mesothelioma patients.
2. Nivolumab
Nivolumab is an immunotherapy drug that works by blocking the PD-1 protein, which prevents the immune system from attacking cancer cells. Nivolumab has shown promising results in treating different types of cancer, and it is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma. Preliminary results have shown that Nivolumab in combination with another immunotherapy drug, Ipilimumab, have been effective in shrinking tumors in patients with mesothelioma.
3. Avelumab
Avelumab is a monoclonal antibody that works by blocking the PD-L1 protein, which prevents the immune system from attacking cancer cells. Avelumab has shown promising results in treating different types of cancer, and it is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma. Preliminary results have indicated that Avelumab has been effective in shrinking tumors in patients with mesothelioma.
4. Durvalumab
Durvalumab is a monoclonal antibody that works similarly to Avelumab by blocking the PD-L1 protein. Durvalumab has shown promising results in treating lung cancer and bladder cancer, and it is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma. Preliminary results have indicated that Durvalumab has been effective in shrinking tumors in patients with mesothelioma.
5. Pembrolizumab
Pembrolizumab is another immunotherapy drug that works by blocking the PD-1 protein, which prevents the immune system from attacking cancer cells. Pembrolizumab has been approved for the treatment of different types of cancer, including melanoma and lung cancer, and it is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma. Preliminary results have indicated that Pembrolizumab has been effective in treating mesothelioma.
6. Lurbinectedin
Lurbinectedin is a drug that works by targeting cancer cells’ DNA repair mechanisms, making them more susceptible to chemotherapy. Lurbinectedin has shown promising results in clinical trials for a variety of cancers, including mesothelioma. Preliminary results have indicated that Lurbinectedin in combination with another chemotherapy drug, Doxorubicin, has been effective in treating mesothelioma.
7. ONCOS-102
ONCOS-102 is a type of immunotherapy drug that is designed to activate the body’s immune system to attack cancer cells. ONCOS-102 is a virus-based therapy that releases cancer-specific antigens into the body, which activates an immune response against cancer cells. ONCOS-102 is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma, and the preliminary results have been promising.
8. ADI-PEG 20
ADI-PEG 20 is a drug that works by starving cancer cells of the amino acid arginine, which they need to survive. ADI-PEG 20 has shown promising results in clinical trials for different types of cancer, including mesothelioma. Preliminary results have indicated that ADI-PEG 20 in combination with another chemotherapy drug, Pemetrexed, has been effective in treating mesothelioma.
9. Vemurafenib
Vemurafenib is a drug that targets a specific gene mutation that is found in some mesothelioma tumors. Vemurafenib has shown promising results in clinical trials for melanoma, which has the same gene mutation as some mesothelioma tumors. Vemurafenib is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma patients with the specific gene mutation, and the preliminary results have been promising.
10. LY3022855
LY3022855 is a drug that works by inhibiting the signaling pathway of a protein called Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (FGFR). FGFR is found to be overactive in some mesothelioma tumors, and LY3022855 is designed to target this protein. LY3022855 is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma.
11. TSR-042
TSR-042 is a monoclonal antibody drug that targets the PD-1 protein, which prevents the immune system from attacking cancer cells. TSR-042 is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma, and the preliminary results have shown that the drug has been effective in treating mesothelioma.
12. Osimertinib
Osimertinib is a drug that targets a specific gene mutation in cancer cells called Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR). Osimertinib has been approved for the treatment of lung cancer, which has the same gene mutation as some mesothelioma tumors. Osimertinib is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma patients with the specific gene mutation, and the preliminary results have been promising.
13. CPI-613
CPI-613 is a drug that works by inhibiting a protein called Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (MTP), which is necessary for cancer cells’ survival. CPI-613 has shown promising results in clinical trials for different types of cancer, including mesothelioma. Preliminary results have indicated that CPI-613 in combination with Pemetrexed and Carboplatin has been effective in treating mesothelioma.
14. Dendritic Cell Therapy
Dendritic Cell Therapy is a type of cancer immunotherapy that involves extracting dendritic cells from a patient’s blood, which are then treated with cancer-specific antigens in a laboratory. The treated dendritic cells are then injected back into the patient’s body, where they activate the immune system to attack cancer cells. Dendritic Cell Therapy is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma.
15. E7080
E7080 is a drug that works by inhibiting a protein called Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor (VEGFR), which is necessary for cancer cells’ growth and survival. E7080 has been approved for the treatment of different types of cancers, including thyroid cancer and renal cell carcinoma. E7080 is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma.
16. CBP501
CBP501 is a drug that works by inhibiting the cell division process, which is necessary for cancer cells to grow and divide. CBP501 has shown promising results in clinical trials for different types of cancer, including mesothelioma. Preliminary results have indicated that CBP501 in combination with another chemotherapy drug, Pemetrexed, has been effective in treating mesothelioma.
17. Tazemetostat
Tazemetostat is a drug that targets a specific gene mutation in cancer cells called Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 (EZH2). EZH2 is found to be overactive in some mesothelioma tumors, and Tazemetostat is designed to target this protein. Tazemetostat has been approved for the treatment of different types of cancer, including lymphoma. Tazemetostat is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma patients with the specific gene mutation.
18. S63845
S63845 is a drug that works by inhibiting a protein called MCL1, which is necessary for cancer cells’ survival. S63845 has shown promising results in preclinical studies for different types of cancer, including mesothelioma. S63845 is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma.
19. MEDI9197
MEDI9197 is a type of immunotherapy drug that activates a specific type of immune cell called plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs). pDCs are responsible for activating the immune system’s anti-tumor response. MEDI9197 is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma, and the preliminary results have shown that the drug has been effective in treating mesothelioma.
20. Bintrafusp Alfa
Bintrafusp Alfa is a bifunctional fusion protein that targets two proteins called PD-1 and TGF-beta, which are necessary for cancer cells’ survival. Bintrafusp Alfa has shown promising results in clinical trials for different types of cancer, including mesothelioma. Preliminary results have indicated that Bintrafusp Alfa has been effective in treating mesothelioma.
21. MTG201
MTG201 is a drug that works by inhibiting the expression of a protein called MUC1, which is found to be overexpressed in mesothelioma tumors. MTG201 has shown promising results in preclinical studies for mesothelioma. MTG201 is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma.
22. CMB305
CMB305 is a type of immunotherapy drug that is designed to activate the immune system to attack cancer cells. CMB305 is a vaccine-based therapy that delivers cancer-specific antigens into the body, which activates an immune response against cancer cells. CMB305 is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma, and the preliminary results have been promising.
23. BGB-A425
BGB-A425 is a drug that works by inhibiting a protein called TIM-3, which is necessary for cancer cells to evade the immune system. BGB-A425 has shown promising results in preclinical studies for different types of cancer, including mesothelioma. BGB-A425 is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma.
24. IPI-549
IPI-549 is a drug that works by inhibiting a protein called Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K), which is necessary for cancer cells’ growth and survival. IPI-549 has shown promising results in preclinical studies for different types of cancer, including mesothelioma. IPI-549 is currently under clinical trials for mesothelioma.
| Drug | Drug Type | Mechanism of Action | Current Status | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor Treating Fields (TTFields) | Technology | Electric fields to stop the growth of cancer cells | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nivolumab | Immunotherapy | Blocking PD-1 protein to activate immune system against cancer cells | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Avelumab | Monoclonal Antibody | Blocking PD-L1 protein to activate immune system against cancer cells | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Durvalumab | Monoclonal Antibody | Blocking PD-L1 protein to activate immune system against cancer cells | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pembrolizumab | Immunotherapy | Blocking PD-1 protein to activate immune system against cancer cells | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lurbinectedin | Chemotherapy | Targeting DNA repair mechanisms of cancer cells to make them more susceptible to chemo drugs | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ONCOS-102 | Immunotherapy | Activating the immune system to attack cancer cells via a virus-based therapy | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADI-PEG 20 | Chemotherapy | Starving cancer cells of the amino acid arginine, which they need to survive | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vemurafenib | Targeted Therapy | Targeting a specific gene mutation found in some mesothelioma tumors | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LY3022855 | Targeted Therapy | Inhibiting the signaling pathway of a protein called Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (FGFR), found to be overactive in some mesothelioma tumors | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TSR-042 | Monoclonal Antibody | Blocking PD-1 protein to activate immune system against cancer cells | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Osimertinib | Targeted Therapy | Targeting a specific gene mutation in cancer cells called Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CPI-613 | Chemotherapy | Inhibiting a protein called Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (MTP), necessary for cancer cells’ survival | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dendritic Cell Therapy | Immunotherapy | Activating the immune system to attack cancer cells via cancer-specific antigens | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E7080 | Targeted Therapy | Inhibiting a protein called Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor (VEGFR), necessary for cancer cells’ growth and survival | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CBP501 | Chemotherapy | Inhibiting the cell division process necessary for cancer cells to grow and divide | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tazemetostat | Targeted Therapy | Targeting a specific gene mutation in cancer cells called Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 (EZH2) | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S63845 | Chemotherapy | Inhibiting a protein called MCL1, necessary for cancer cells’ survival | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MEDI9197 | Immunotherapy | Activating plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) to activate the immune system’s anti-tumor response | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bintrafusp Alfa | Bifunctional Fusion Protein | Targeting two proteins called PD-1 and TGF-beta, necessary for cancer cells’ survival | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MTG201 | Targeted Therapy | Inhibiting the expression of a protein called MUC1, found to be overexpressed in mesothelioma tumors | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CMB305 | Immunotherapy | Activating the immune system to attack cancer cells via cancer-specific antigens | Under Clinical Trials | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BGB-A425 | Chem
Immunotherapy Combined with Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma TreatmentMesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, heart, or abdomen. It is a very aggressive type of cancer that is often caused by exposure to asbestos. Mesothelioma is considered a rare type of cancer, and it is often difficult to diagnose in the early stages. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are often prescribed to patients who have been diagnosed with mesothelioma, either on their own or in combination with immunotherapy. What is Chemotherapy?Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. The drugs can be given orally or through an injection into a vein. Chemotherapy drugs target cells that are rapidly dividing, which is why they are effective against cancer cells. However, chemotherapy also affects healthy cells that divide rapidly, such as those found in the hair follicles, digestive system, and bone marrow. This is why chemotherapy often causes side effects such as nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and fatigue. What is Immunotherapy?Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. The immune system is the body’s natural defense against disease. It works by recognizing and attacking foreign substances, such as viruses and bacteria. However, cancer cells can evade the immune system by producing proteins that prevent the immune system from recognizing them as foreign. Immunotherapy drugs work by blocking these proteins, allowing the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Some immunotherapy drugs also stimulate the immune system to produce more cancer-fighting cells. Combining Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy for Mesothelioma TreatmentCombining chemotherapy and immunotherapy for mesothelioma treatment has been found to be more effective than using either treatment alone. The chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells, while the immunotherapy drugs stimulate the immune system to attack cancer cells. Combining the two treatments can increase the effectiveness of both. Studies have shown that combining chemotherapy and immunotherapy can improve survival rates and reduce the risk of recurrence in patients with mesothelioma. One study found that patients who received a combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy had a median survival of 18.8 months, compared to 12.1 months for those who received chemotherapy alone. Types of Chemotherapy Drugs for Mesothelioma TreatmentSeveral chemotherapy drugs are used to treat mesothelioma, either alone or in combination with other drugs. The most common chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma include:
Types of Immunotherapy Drugs for Mesothelioma TreatmentThere are several immunotherapy drugs that are FDA-approved for the treatment of mesothelioma. These drugs work by blocking certain proteins that cancer cells produce to evade the immune system. The most common immunotherapy drugs for mesothelioma include:
Benefits of Combining Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy for Mesothelioma TreatmentThe main benefit of combining chemotherapy and immunotherapy for mesothelioma treatment is that it can increase the effectiveness of both treatments. Chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells, while immunotherapy drugs stimulate the immune system to attack cancer cells. Combining the two treatments can lead to a stronger overall response to the cancer. Combining chemotherapy and immunotherapy can also help reduce the risk of recurrence in patients with mesothelioma. Studies have shown that patients who receive a combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy have a lower risk of their cancer returning compared to those who receive chemotherapy alone. ConclusionMesothelioma is a rare and aggressive type of cancer that is often caused by exposure to asbestos. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are often prescribed to patients who have been diagnosed with mesothelioma, either on their own or in combination with immunotherapy. Combining chemotherapy and immunotherapy can increase the effectiveness of both treatments and reduce the risk of recurrence in patients with mesothelioma. There are several chemotherapy drugs and immunotherapy drugs that are FDA-approved for the treatment of mesothelioma. Advancements in Mesothelioma Chemotherapy TreatmentMesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart. It is primarily caused by exposure to asbestos – a mineral that was commonly used in construction and manufacturing industries. Due to its long latency period, mesothelioma is often diagnosed at advanced stages, making it difficult to treat. Chemotherapy is a commonly used treatment method for mesothelioma, and continuous research and advancements in chemotherapy drugs have been witnessed in recent years. This article outlines the recent advancements in mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment. First-Line Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsFirst-line chemotherapy drugs are the primary treatment option for mesothelioma patients. They are administered as a part of the initial treatment process and include two or more drugs that are given in combination. The most common first-line chemotherapy drugs used for mesothelioma treatment are pemetrexed and cisplatin. This combination has proven to be effective in extending the life of mesothelioma patients. However, in recent years, new drugs have emerged, which have shown promising results in improving the survival rate of mesothelioma patients. Keytruda (Pembrolizumab)Keytruda is an immunotherapy drug that has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of several types of cancer, including mesothelioma. It is a monoclonal antibody that can trigger the patient’s immune system to attack cancer cells. Several studies have reported positive results in using Keytruda in combination with chemotherapy drugs – pemetrexed and cisplatin for treating mesothelioma. Keytruda can be used as a first-line treatment option or as a second-line treatment after chemotherapy. Opdivo (Nivolumab)Opdivo is another immunotherapy drug that has shown promising results in treating mesothelioma. It is also a monoclonal antibody that can target and activate the patient’s immune system to fight cancer cells. Opdivo has been approved by the FDA as a second-line treatment for mesothelioma patients who have already gone through chemotherapy. Several studies have reported an improvement in the survival rate of mesothelioma patients who have received Opdivo treatment. TremelimumabTremelimumab is a new immunotherapy drug that is still in the clinical trial stage for mesothelioma treatment. It is a checkpoint inhibitor that can stimulate T-cells in the patient’s immune system to attack cancer cells. Studies have shown that tremelimumab can effectively treat mesothelioma patients and improve the survival rate. While it has not yet been approved by the FDA, tremelimumab holds promise as a treatment option for mesothelioma patients. Second-Line Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsSecond-line chemotherapy drugs are used for treating mesothelioma patients who have already undergone the initial chemotherapy treatment and have experienced a recurrence of the disease. The second-line chemotherapy drugs have shown promising results in extending the life of mesothelioma patients. Alimta (Pemetrexed)Alimta is a chemotherapy drug that is a modified version of pemetrexed – the primary drug used in first-line chemotherapy treatment. Alimta has been approved by the FDA as a second-line chemotherapy drug for mesothelioma patients. It can be used alone or in combination with other drugs, and it has shown promising results in treating mesothelioma patients who have undergone first-line chemotherapy. GemcitabineGemcitabine is another chemotherapy drug that is used as a second-line treatment option for mesothelioma patients. It is administered through an IV every week for three weeks, followed by a period of rest before resuming the treatment. Studies have shown that gemcitabine can effectively treat mesothelioma patients, and it has been included in several clinical trials. CarboplatinCarboplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used in combination with other drugs for treating several types of cancer. It has also proven to be effective in treating mesothelioma as a second-line chemotherapy drug. Carboplatin is primarily used for treating mesothelioma patients who have experienced a recurrence of the disease after the initial treatment. Combination Mesothelioma Chemotherapy TreatmentCombination chemotherapy treatment involves using more than two drugs simultaneously for treating mesothelioma patients. The combination of drugs can provide a more effective treatment option, as it can attack cancer cells through multiple pathways. The most common combination chemotherapy drugs used for mesothelioma treatment are cisplatin and pemetrexed. However, researchers are studying a new combination of drugs that could provide better treatment outcomes for mesothelioma patients. Atezolizumab, Bevacizumab, and Cisplatin/PemetrexedAtezolizumab and Bevacizumab are two immunotherapy drugs that have shown promising results in treating other types of cancer. A recent study has shown that the combination of atezolizumab, bevacizumab, and first-line chemotherapy drugs (cisplatin/pemetrexed) can effectively treat mesothelioma patients. The study reported an improvement in the overall survival rate of mesothelioma patients, with a median overall survival of 18.8 months compared to 14.1 months observed in patients who received only first-line chemotherapy drugs. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy treatment has had significant advancements in recent years, providing more effective treatment options for mesothelioma patients. The emergence of immunotherapy drugs such as Keytruda, Opdivo, and tremelimumab have shown promising results in treating mesothelioma. Second-line chemotherapy drugs such as Alimta, gemcitabine, and carboplatin have extended the life of mesothelioma patients after the recurrence of the disease. The combination of drugs such as atezolizumab, bevacizumab, and cisplatin/pemetrexed has shown better treatment outcomes than the traditional chemotherapy treatment approach. These advancements are a ray of hope for mesothelioma patients and their families and provide a glimpse of a better future for those affected by this deadly disease.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Life ExpectancyMesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, chest wall, and abdomen. Because of its aggressive nature, treatment options are limited and life expectancy is often short. However, chemotherapy drugs have been shown to help improve quality of life, slow the growth of mesothelioma tumors, and in some cases, extend life expectancy. Here we will discuss the most common mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and their impact on life expectancy. 1. How Chemotherapy Drugs WorkChemotherapy drugs are designed to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells. They work by interfering with the cancer cell’s ability to divide, grow, and spread. Because mesothelioma is often resistant to other forms of treatment, such as surgery and radiation, chemotherapy is often the primary treatment option. 2. Common Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsThere are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used in the treatment of mesothelioma:
Alimta and Cisplatin are the most common drugs used in mesothelioma treatment. They work together to damage cancer cells, making it difficult for them to divide and spread. Carboplatin and Gemcitabine are also used in treating mesothelioma, either alone or in combination with other drugs. 3. Side Effects of ChemotherapyWhile chemotherapy drugs can help slow the growth of mesothelioma tumors, they can also cause a range of side effects. Common side effects include:
It’s important for patients to discuss potential side effects with their doctor and to report any unusual symptoms during treatment. Supportive care, such as anti-nausea medication and pain management, can help manage side effects and improve patients’ quality of life. 4. Impact on Life ExpectancyWhile chemotherapy drugs can improve quality of life and slow the growth of mesothelioma tumors, they are unlikely to cure the disease. The impact of chemotherapy on life expectancy depends on several factors, including the stage of the cancer and the patient’s overall health. In general, patients who undergo chemotherapy for mesothelioma can expect to live an average of six to twelve months longer than those who do not receive treatment. However, some patients may live longer or experience a better quality of life, especially if the cancer is caught early and treated aggressively. ConclusionWhile mesothelioma is a challenging and often devastating disease, chemotherapy drugs can offer hope and improve patients’ quality of life. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it’s important to discuss all treatment options with your doctor and to make an informed decision that takes into account your overall health, stage of the cancer, and goals for care. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Survival RatesMesothelioma is a rare type of cancer that forms in the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart. It is caused by exposure to asbestos fibers. Mesothelioma is difficult to diagnose and treat, and it has a poor prognosis. However, there are several mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs available that can improve the life expectancy of patients. Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that utilizes drugs to stop the growth and spread of cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs can be administered orally, intravenously, or through injection. The goal of chemotherapy is to target cancer cells and destroy them, thus reducing the size of tumors. There are several chemotherapy drugs that are used to treat mesothelioma. These drugs can be used alone or in combination. The most commonly used mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are listed below: 1. Alimta (Pemetrexed)Alimta is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. It is usually administered in combination with another drug called cisplatin. Alimta works by blocking the enzymes that cancer cells need to grow and divide. This drug has been proven to improve survival rates for patients with mesothelioma. 2. CarboplatinCarboplatin is another chemotherapy drug that is often used to treat mesothelioma. It is usually administered in combination with Alimta or another drug called paclitaxel. Carboplatin works by damaging the DNA in cancer cells, thus preventing them from dividing and multiplying. 3. CisplatinCisplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. It is usually administered in combination with Alimta. Cisplatin works by damaging the DNA in cancer cells, thus preventing them from dividing and multiplying. This drug has been proven to improve survival rates for patients with mesothelioma. 4. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by stopping the growth and spread of cancer cells. Gemcitabine is usually administered in combination with carboplatin or cisplatin. 5. VinorelbineVinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is occasionally used to treat mesothelioma. It works by disrupting the process of cell division in cancer cells. Vinorelbine is usually administered in combination with cisplatin. 6. BevacizumabBevacizumab is a targeted therapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking the growth of blood vessels that feed tumors. Bevacizumab is usually administered in combination with chemotherapy drugs like carboplatin and paclitaxel. 7. OnconaseOnconase is a chemotherapy drug that is currently being tested as a treatment for mesothelioma. It works by disrupting the RNA in cancer cells, thus preventing them from growing and dividing. Onconase has shown promise in clinical trials and is expected to be approved by the FDA soon. 8. Immunotherapy DrugsImmunotherapy drugs are medications that help the body’s immune system fight cancer. These drugs are not chemotherapy drugs, but they are often used in combination with chemotherapy to improve treatment outcomes. Immunotherapy drugs that are currently being tested as treatments for mesothelioma include Keytruda, Opdivo, and Durvalumab. Survival RatesSurvival rates for mesothelioma vary widely depending on the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed, the patient’s age and overall health, and the treatment plan that is chosen. The overall survival rate for mesothelioma is around 12 months, but some patients have survived for several years or more. According to the American Cancer Society, the 5-year survival rate for mesothelioma is around 10%. This means that 10% of patients who receive a mesothelioma diagnosis will survive for 5 years or more. However, this survival rate varies widely depending on the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed. For example, the 5-year survival rate for patients with stage 1 mesothelioma is around 40%, while the rate for patients with stage 4 mesothelioma is less than 5%. It is important to note that survival rates are constantly changing as new treatments become available and more clinical trials are conducted. Patients with mesothelioma should work closely with their medical team to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to their specific needs. ConclusionMesothelioma is a rare and deadly form of cancer that is caused by exposure to asbestos fibers. Chemotherapy drugs can improve the life expectancy of mesothelioma patients by targeting and destroying cancer cells. The most commonly used mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs include Alimta, carboplatin, cisplatin, gemcitabine, vinorelbine, and bevacizumab. Immunotherapy drugs are also being tested as treatments for mesothelioma. Survival rates for mesothelioma vary widely depending on the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed and the treatment that is chosen. Patients with mesothelioma should work closely with their medical team to determine the best course of treatment for their specific needs. Choosing a Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment PlanChemotherapy, or chemo, is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It is a popular treatment for mesothelioma, a rare cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are usually given in combination with other treatments, such as surgery and radiation, to improve the chances of survival. How Chemotherapy WorksChemotherapy drugs target fast-growing cancer cells by attacking their DNA or other important processes. The drugs are usually given intravenously (IV) or orally, although some drugs can be injected directly into the affected area. The drugs circulate through the bloodstream and reach all parts of the body, including cancer cells that may have spread beyond the original site. Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment, which means it can affect healthy cells as well as cancer cells. Healthy cells that grow quickly, such as hair follicles and the lining of the digestive tract, may also be damaged, leading to side effects. However, healthy cells can usually recover from this damage, while cancer cells may be destroyed. Factors that Affect the Choice of Chemotherapy DrugsThere are several factors that doctors consider when choosing a chemotherapy regimen for mesothelioma patients, including:
Types of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsThere are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used to treat mesothelioma, either alone or in combination. These drugs have different mechanisms of action, side effects, and dosage schedules, and may be administered according to a specific protocol or customized to the patient’s needs. Alkylating AgentsAlkylating agents are chemotherapy drugs that work by adding an alkyl group to the DNA molecule of cancer cells, causing the DNA strands to cross-link and break. This prevents the DNA from replicating and leads to cell death. Examples of alkylating agents used for mesothelioma include:
AntimetabolitesAntimetabolites are chemotherapy drugs that mimic the structure of natural substances in the body and interfere with DNA synthesis and repair. This can cause cancer cells to die or stop growing. Examples of antimetabolites used for mesothelioma include:
Antitumor AntibioticsAntitumor antibiotics are chemotherapy drugs that are derived from natural substances produced by soil bacteria. They work by interfering with DNA replication and RNA transcription, ultimately leading to cell death. Examples of antitumor antibiotics used for mesothelioma include:
Mitotic InhibitorsMitotic inhibitors are chemotherapy drugs that target the microtubules in cancer cells, which are essential for cell division. By disrupting the formation of these structures, mitotic inhibitors can stop cancer cells from dividing and cause them to die. Examples of mitotic inhibitors used for mesothelioma include:
ImmunotherapyImmunotherapy is a new type of cancer treatment that uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It involves the administration of drugs that activate or enhance the immune response against cancer cells. Immunotherapy is still being studied for mesothelioma, but some promising drugs are being developed. Combination Chemotherapy for MesotheliomaCombination chemotherapy is the use of two or more chemotherapy drugs together to increase their effectiveness and reduce side effects. This is a common approach for mesothelioma because the cancer is often resistant to single-drug treatment. Combination chemotherapy regimens may vary depending on the specific drugs used, the dosage and frequency of administration, and the length of the treatment cycle. Some examples of combination chemotherapy regimens for mesothelioma include:
Side Effects of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsChemotherapy drugs can cause a range of side effects, which may vary depending on the specific drug, dose, duration, and patient factors. Some common side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs include:
Patients who receive chemotherapy for mesothelioma may also be at risk for infection, bleeding, and other complications. It is important to discuss any side effects with the healthcare team and take steps to manage or reduce them. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs vs. Alternative TreatmentsMesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs OverviewChemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are typically administered intravenously or orally, and they can help slow down the growth of cancer cells and relieve symptoms. These drugs are often given in combination with other treatments like surgery or radiation therapy. Here are some of the most commonly used mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs:
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs Benefits and DrawbacksWhile mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can offer several benefits to patients, they also come with some drawbacks. The main advantage of chemotherapy is that it can help shrink mesothelioma tumors and improve symptoms, increasing the patient’s quality of life. However, chemotherapy does not cure mesothelioma, and it often comes with side effects that can make treatment challenging. The most common side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and decreased appetite. While these side effects are generally temporary, they can impact a patient’s quality of life during treatment. Additionally, chemotherapy can weaken a patient’s immune system, increasing their risk of infection and other complications. Alternative Treatments to Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsWhile mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are a well-established treatment option, there are alternative treatments that patients may consider. These alternative treatments aim to support the patient’s immune system, reduce inflammation, and improve overall health and quality of life. Immune-Based TherapiesImmune-based therapies aim to stimulate the patient’s immune system to fight cancer cells. Here are some of the most common immune-based therapies:
Natural and Herbal TreatmentsNatural and herbal treatments can help relieve mesothelioma symptoms and support the patient’s overall health. Here are some of the most common natural and herbal treatments:
Benefits and Drawbacks of Alternative Mesothelioma TreatmentsWhile alternative mesothelioma treatments can offer some benefits to patients, they also have drawbacks. For example, immune-based therapies are still being studied and may not be available to all patients. Additionally, natural and herbal treatments can be helpful in managing symptoms, but they are not a substitute for conventional medical treatment. It’s important for patients to discuss alternative treatments with their doctor and make sure they understand the potential benefits and risks of each option. Patients should also be aware that some alternative therapies may interfere with conventional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can offer several benefits to patients, including tumor shrinkage and symptom relief. However, these treatments also come with some drawbacks, including side effects that can impact a patient’s quality of life. Alternative mesothelioma treatments like immune-based therapies and natural remedies can also be helpful in supporting the patient’s health and well-being. Patients should weigh the benefits and risks of each treatment option and work with their doctor to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets their individual needs. How Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs WorkMesothelioma is a rare form of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, chest, abdomen, and sometimes, the heart. It is usually caused by long-term exposure to asbestos. Unfortunately, mesothelioma has a poor prognosis, with only around five to ten percent of patients surviving for five years or more. Chemotherapy is a common treatment for mesothelioma. The purpose of chemotherapy drugs is to target cancer cells in the body and destroy them. Unlike surgery, which removes the affected tissue, chemotherapy drugs are designed to kill or slow the growth of cancer cells in the body. The Different Types of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsThere are various types of chemotherapy drugs that are used to treat mesothelioma. Some of them include:
How Chemotherapy Drugs Are AdministeredMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are administered either systemically or intrapleurally, depending on the patient’s needs and condition. Systemic ChemotherapySystemic chemotherapy is administered via a vein, and the drugs then travel through the bloodstream to the cancer cells. Systemic chemotherapy is typically used to treat mesothelioma that has spread to other parts of the body. Intrapleural ChemotherapyIntrapleural chemotherapy involves inserting a catheter tube into the chest cavity to deliver chemotherapy drugs directly to the tumor site. This type of chemotherapy is often used to treat mesothelioma that is localized to the lungs and chest cavity. How Mesothelioma Chemotherapy WorksChemotherapy drugs work by targeting and affecting rapidly dividing cells, which include cancer cells. While healthy cells can also be affected, they tend to recover quickly compared to cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs work in different ways to destroy cancer cells. Some chemotherapy drugs, such as Alkylating agents, work by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and multiplying. Other drugs, such as Antimetabolites, work by disrupting the metabolic processes in cancer cells, which ultimately leads to their death. Chemotherapy drugs are often used in combination with other treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy, to increase their effectiveness in treating mesothelioma. This approach, also known as multimodal therapy, can help to improve the chances of survival for patients with mesothelioma. Possible Side Effects of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsWhile chemotherapy drugs can be effective in treating mesothelioma, they can also cause side effects. The severity and type of side effects vary depending on the drug used, the dosage, and the patient’s overall health. Some common side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs include:
Patients should discuss the possible side effects of chemotherapy drugs with their doctor before starting treatment. It is essential to report any side effects experienced during treatment to the healthcare team to ensure that they can be managed effectively. ConclusionChemotherapy drugs are a common treatment option for mesothelioma, a rare and aggressive form of cancer. These drugs work by targeting cancer cells in the body and disrupting their growth and division. While chemotherapy drugs can be effective, they can also cause side effects. Patients should discuss the risks and benefits of chemotherapy with their doctor before starting treatment. The Importance of Timing in Mesothelioma Chemotherapy TreatmentWhen it comes to treating mesothelioma with chemotherapy, timing is everything. This aggressive cancer is notoriously difficult to treat, and the timing of chemotherapy can play a significant role in determining the success of treatment. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at why timing is so important in mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment. Understanding MesotheliomaMesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the protective lining surrounding the lungs, heart, and abdomen. This lining, called the mesothelium, is made up of mesothelial cells which help protect and lubricate internal organs. When these cells become cancerous, they can grow and spread rapidly, leading to tumors and other complications. The Role of Chemotherapy in Treating MesotheliomaChemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells or slow their growth. In mesothelioma, chemotherapy is typically given alongside other treatments such as surgery or radiation therapy. In some cases, chemotherapy may be used as the primary treatment for mesothelioma. Timing is KeyWhen it comes to mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment, the timing of chemotherapy is critical. According to the American Cancer Society, the timing of chemotherapy can affect how well it works, how long it can be given, and what side effects it causes. There are generally two types of chemotherapy used to treat mesothelioma: neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is given before surgery or radiation therapy in order to shrink the tumor and make it easier to remove. Adjuvant chemotherapy is given after surgery or radiation therapy in order to kill any remaining cancer cells. Timing can also affect the number of chemotherapy cycles that a patient receives. In the case of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, timing can help ensure that the patient receives the right number of cycles before surgery. In the case of adjuvant chemotherapy, timing can help ensure that the patient receives the right number of cycles after surgery. The timing of chemotherapy can also play a role in managing side effects. By adjusting the timing of chemotherapy, doctors can help reduce the risk of complications and improve a patient’s quality of life. For example, administering chemotherapy at the right time can help minimize nausea, vomiting, and other common side effects. The Benefits of Timed ChemotherapyIn addition to improving the effectiveness of chemotherapy, timing can also help reduce the overall treatment time for mesothelioma patients. By giving chemotherapy at the right time, doctors can help speed up the recovery process and reduce the risk of complications. Timing can also help improve the long-term prognosis for mesothelioma patients. By giving neoadjuvant chemotherapy before surgery, doctors can help increase the chances of a successful surgical outcome. By giving adjuvant chemotherapy after surgery, doctors can help reduce the risk of cancer recurrence and improve overall survival rates. Finally, timing can help reduce the overall cost of treatment for mesothelioma patients. By avoiding unnecessary chemotherapy cycles, doctors can help reduce the cost of treatment and improve the financial burden on patients and their families. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy treatment is a critical part of managing this aggressive cancer. The timing of chemotherapy can affect everything from treatment effectiveness to recovery time to long-term prognosis. By working closely with their healthcare team, mesothelioma patients can ensure that they receive the right chemotherapy at the right time for the best possible outcome.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Quality of LifeMesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, heart, and abdomen. It is primarily caused by exposure to asbestos fibers and has a poor prognosis. However, there are different treatment options available, and mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs have been proven effective in improving the quality of life of patients. In this article, we will discuss mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and how they can positively impact the quality of life of patients. Overview of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsChemotherapy drugs are medications that attack cancer cells to slow down or stop the growth of cancerous tissues. The primary goal of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs is to shrink tumors, reduce symptoms, and improve the quality of life of patients. Mesothelioma treatment plans typically involve a combination of chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy. There are various chemotherapy drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of mesothelioma. These drugs may be used alone or in combination with other medications, depending on a patient’s health status and cancer stage. Some common mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs include: Cisplatin and PemetrexedCisplatin and Pemetrexed is a combination of chemotherapy drugs that are approved by the FDA for the treatment of mesothelioma. This drug combination has been shown to improve the survival rate of patients with mesothelioma. Cisplatin is a platinum-based drug that works by preventing cancer cells from dividing and multiplying. Pemetrexed stops cancer cells from producing DNA and RNA, which is necessary for cancer cell growth. The combination of these two drugs has been shown to be effective in shrinking tumors and slowing down the progression of mesothelioma. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is approved for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and multiplying. Gemcitabine is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs for better efficacy. CarboplatinCarboplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by preventing cancer cells from dividing and multiplying. Carboplatin is usually recommended for patients with advanced mesothelioma cancer. MitomycinMitomycin is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat a variety of cancers, including mesothelioma. It works by stopping the growth of cancer cells by interfering with their DNA. Mitomycin is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs for maximum effectiveness. Quality of Life and Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsThe symptoms of mesothelioma can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. Chemotherapy drugs have been shown to alleviate the symptoms of mesothelioma and improve the overall quality of life of patients. Some of the symptoms that mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs may help alleviate include:
Improved Physical FunctioningBy reducing cancer symptoms and improving overall health, mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can improve a patient’s physical functioning. Patients who receive chemotherapy often experience an increase in their energy levels and improved mobility, which leads to a better quality of life. Reduced Pain and DiscomfortMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs have been shown to reduce pain and discomfort caused by cancer symptoms. This is especially important for patients who have advanced mesothelioma cancer and are in constant pain. By reducing pain and discomfort, patients can lead a more comfortable life. Improvement in Emotional HealthMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can improve the mental and emotional health of patients. By reducing the number and severity of cancer symptoms, patients feel better, which improves their overall outlook on life. This can help patients cope with the stress of their disease and maintain a positive attitude. Increased Survival RatesMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs have been shown to improve the survival rate of patients. By attacking cancer cells, chemotherapy can shrink tumors and slow down the progression of the disease, which can prolong a patient’s life. In some cases, patients may experience complete remission and be cured of their mesothelioma. Side Effects of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsLike any medication, mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can cause some side effects. However, the side effects vary from patient to patient and depend on the type and dose of the chemotherapy drug. Some common side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs include:
These side effects are usually mild and can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes. For example, medication can be prescribed to alleviate nausea and vomiting, and a patient’s diet can be altered to improve energy levels. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are an essential part of mesothelioma treatment plans. They are approved by the FDA and have been shown to improve the quality of life of patients. By reducing cancer symptoms, mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can improve physical functioning, reduce pain and discomfort, improve emotional health, and increase survival rates. Although these drugs can cause some side effects, they are usually mild and can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes. The goal of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs is to help patients live a more comfortable and fulfilling life. Chemotherapy is an effective treatment for mesothelioma. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can reduce the size of tumors and alleviate symptoms. Palliative Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma PatientsMesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart. It is caused by exposure to asbestos, a mineral that was commonly used in construction, shipbuilding, and manufacturing industries. Unfortunately, mesothelioma is a very aggressive cancer that is often diagnosed at an advanced stage, making treatment challenging. While surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy are all options for treating mesothelioma, this article will focus on palliative chemotherapy, which is used to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life for mesothelioma patients. What is palliative chemotherapy?Palliative chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that is used to relieve symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients, rather than cure the disease. It is typically recommended for patients with advanced-stage cancer who are not candidates for surgery or radiation therapy. The goal of palliative chemotherapy is to shrink tumors and slow the progression of the disease, which can help alleviate symptoms such as pain, difficulty breathing, and fatigue. How is palliative chemotherapy administered?Palliative chemotherapy drugs can be administered in a variety of ways, including intravenously (through a vein), orally (in pill form), or intraperitoneally (into the abdomen). The specific method of administration will depend on the type of chemotherapy drug being used, as well as the patient’s individual medical needs. Chemotherapy drugs are typically given in cycles, with the patient receiving a specific number of treatments over a set period of time. What chemotherapy drugs are used palliatively for mesothelioma patients?There are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used palliatively for mesothelioma patients, including: CisplatinCisplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy drug that is commonly used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking the DNA in cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Some common side effects of cisplatin include nausea, vomiting, and kidney damage. CarboplatinCarboplatin is another platinum-based chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. Like cisplatin, it works by blocking the DNA in cancer cells to prevent them from dividing and growing. Carboplatin is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as pemetrexed. Some common side effects of carboplatin include nausea, vomiting, and low blood cell counts. PemetrexedPemetrexed is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking the synthesis of DNA and RNA in cancer cells, which slows their growth. Pemetrexed is typically given intravenously, and some common side effects include fatigue, nausea, and low blood cell counts. What are the side effects of palliative chemotherapy?While palliative chemotherapy can help relieve symptoms and improve quality of life for mesothelioma patients, it can also cause side effects. The specific side effects will depend on the type of chemotherapy drug being used, as well as the patient’s individual medical needs. Some common side effects of palliative chemotherapy for mesothelioma patients include: Nausea and vomitingChemotherapy drugs can irritate the lining of the stomach, which can cause nausea and vomiting. Anti-nausea medications can be prescribed to help alleviate these symptoms. FatigueChemotherapy can cause fatigue and weakness, which can make it difficult for patients to perform daily activities. Hair lossSome chemotherapy drugs can cause hair loss, although this side effect is not universal. Low blood cell countsChemotherapy drugs can cause a drop in the number of red and white blood cells in the body, which can increase the risk of infection and fatigue. Kidney damageSome chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin, can cause kidney damage, so it is important for patients to be closely monitored while receiving treatment. ConclusionWhile there is no cure for mesothelioma, palliative chemotherapy can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life for patients. Chemotherapy drugs such as cisplatin, carboplatin, and pemetrexed can help shrink tumors and slow the progression of the disease. However, these drugs can also cause side effects such as nausea, fatigue, and hair loss. It is important for patients to work closely with their healthcare team to determine the best treatment options and manage any side effects.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Tumor ResponseChemotherapy is a form of cancer treatment that uses drugs to destroy cancer cells. In mesothelioma treatment, chemotherapy may be used to shrink tumors in the body, reduce symptoms, improve quality of life, and prolong survival. There are many chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma, each with different mechanisms of action and varying degrees of success. In this article, we will explore mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and their tumor response. Alimta (Pemetrexed)Alimta is a chemotherapy drug that is primarily used in the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by blocking the enzymes that cancer cells need to grow and divide, thereby slowing down or stopping tumor growth. Alimta is usually administered in combination with cisplatin, another chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. Clinical trials have shown that the use of Alimta and cisplatin together can significantly improve survival rates for mesothelioma patients. In fact, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that the combination of Alimta and cisplatin improved median survival from 9.3 months to 12.1 months. GemcitabineGemcitabine is another chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by interfering with DNA synthesis in cancer cells, thereby preventing them from growing and dividing. Clinical trials have shown that gemcitabine is moderately effective in the treatment of mesothelioma, with response rates ranging from 10-30%. However, its effectiveness may be improved when used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin or carboplatin. CisplatinCisplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. It works by interfering with DNA synthesis in cancer cells, thereby causing them to die. Cisplatin is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as Alimta, gemcitabine, or vinorelbine. Clinical trials have shown that the use of cisplatin-based chemotherapy can improve survival rates for mesothelioma patients. CarboplatinCarboplatin is another chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by interfering with DNA synthesis in cancer cells, thereby preventing them from growing and dividing. Carboplatin is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as Alimta or gemcitabine. Clinical trials have shown that the use of carboplatin-based chemotherapy can improve survival rates for mesothelioma patients. VinorelbineVinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by stopping cancer cells from dividing and growing. Vinorelbine is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin or carboplatin. Clinical trials have shown that the use of vinorelbine-based chemotherapy can improve symptomatic control and survival rates for mesothelioma patients. Tumor ResponseThe effectiveness of chemotherapy in the treatment of mesothelioma can be measured by the tumor response. The tumor response is the degree to which a tumor responds to chemotherapy treatment. It is usually measured by imaging techniques, such as CT scans or PET scans, which can show the size of the tumor before and after treatment. The tumor response is usually classified into four categories:
The tumor response is an important measure of the effectiveness of chemotherapy in the treatment of mesothelioma. A complete or partial response indicates that the chemotherapy is successfully shrinking the tumor, while stable disease or progressive disease indicates that the chemotherapy is either not working or the tumor is growing despite treatment. ConclusionChemotherapy is an important treatment option for mesothelioma patients. There are several chemotherapy drugs available for mesothelioma, each with different mechanisms of action and varying degrees of success. Clinical trials have shown that the use of chemotherapy can improve survival rates for mesothelioma patients. The effectiveness of chemotherapy can be measured by the tumor response, which is an important measure of the success of treatment. If you have mesothelioma, it is important to discuss your treatment options with your doctor to determine the best course of action. Limitations of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy TreatmentChemotherapy for mesothelioma is an essential treatment option for many patients, but it has limitations. Chemotherapy uses drugs that kill rapidly dividing cancer cells, but they also attack normal cells, causing side effects. Mesothelioma chemotherapy side effects include hair loss, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and a weakened immune system. Chemotherapy drugs target cancer cells in the body, but they can also damage healthy cells, leading to unwanted side effects. Despite its effectiveness in controlling cancer growth, chemotherapy drugs can be limited because they may not cure mesothelioma entirely and can have adverse effects on the body. There are also other limitations that come with chemotherapy treatment. Types of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugsPatients with mesothelioma are generally prescribed one or more chemotherapy drugs. These drugs work to attack cancer cells by stopping their growth or cell division. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs come in different types depending on their active ingredient. Here are some of the types of chemotherapy drugs used in mesothelioma treatment:
Side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapyChemotherapy for mesothelioma has side effects that may depend on the type and dose of the drug. Common side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy include the following: Nausea and vomitingChemotherapy drugs can cause gastrointestinal problems such as nausea and vomiting. These side effects can be mild or severe, depending on the patient’s tolerance for chemotherapy. Doctors may prescribe anti-nausea drugs to manage these symptoms. FatigueChemotherapy drugs can cause fatigue, which may last for several weeks or months after treatment. Patients may experience weakness, low energy, and a general feeling of tiredness. Rest and exercise can help manage these symptoms. Hair lossChemotherapy drugs can cause hair loss, including hair loss from the head, face, and body. The hair may grow back after treatment, but it may be different in texture or color. Low blood cell countChemotherapy drugs can lower the patient’s white and red blood cell count, leading to an increased risk of infection and decreased oxygen supply to the body. Blood transfusions and medications can help manage blood cell counts. Other side effectsOther side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy may include mouth sores, diarrhea, constipation, and nerve damage. Benefits and limitations of mesothelioma chemotherapyMesothelioma chemotherapy is beneficial because it can shrink tumors and slow the progression of the disease. However, it can also be limited because it is not a cure for mesothelioma. Patients may need a combination of treatments, including surgery, radiation, and immunotherapy, to manage mesothelioma. Chemotherapy can also have adverse effects on the body, leading to side effects that may impact the patient’s quality of life. Factors that affect mesothelioma chemotherapy treatmentSeveral factors can influence how well mesothelioma chemotherapy works for a patient. These factors include: The stage of mesotheliomaThe stage of mesothelioma will determine the extent of cancer growth and the patient’s prognosis. Early-stage mesothelioma may respond better to chemotherapy treatment than late-stage mesothelioma. The type of mesotheliomaThere are different types of mesothelioma, including pleural mesothelioma, peritoneal mesothelioma, and pericardial mesothelioma. Each type may require different chemotherapy treatments due to the location of the cancer. The patient’s overall health and medical historyThe patient’s overall health and medical history will be evaluated to determine if chemotherapy is a suitable treatment option. Patients with pre-existing medical conditions or weakened immune systems may be at higher risk for chemotherapy side effects. The patient’s goals for treatmentThe patient’s goals for treatment will be considered when developing a treatment plan. Some patients may prioritize quality of life over curative treatment, while others may prioritize aggressive treatment to slow the progression of mesothelioma. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy is an effective treatment option for many patients, but it comes with limitations and side effects. While chemotherapy can shrink tumors and slow the progression of mesothelioma, it may not be a cure for the disease. Patients may need a combination of treatments, including chemotherapy, surgery, radiation, and immunotherapy, to manage mesothelioma effectively. When considering mesothelioma chemotherapy, patients should discuss their treatment goals and their medical history with their doctors to determine if it is the right treatment option for them. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Health Insurance CoverageChemotherapy is often the primary treatment for mesothelioma, a rare and aggressive type of cancer that develops in the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart. This form of treatment uses powerful drugs to destroy cancer cells and slow down the growth and spread of tumors. While there is no cure for mesothelioma, chemotherapy can help relieve symptoms, improve quality of life, and extend survival in some cases. However, chemotherapy drugs can be expensive and come with significant side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, hair loss, fatigue, and increased risk of infection. As a result, many patients may struggle to afford or tolerate the treatment, which can affect their outcomes and overall well-being. Therefore, it’s important for mesothelioma patients and their families to understand their options for accessing and paying for chemotherapy, including through health insurance coverage. In this article, we’ll explore some of the common mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs, their benefits and drawbacks, and how insurance policies may play a role in treatment decisions. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsMesothelioma is usually diagnosed at an advanced stage when surgery or radiation therapy may no longer be effective. The standard approach to treating the disease typically involves chemotherapy, either alone or in combination with other treatments. The following are some of the most commonly used chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma: 1. Alimta (Pemetrexed)Alimta is the only chemotherapy drug that has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) specifically for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the production of certain enzymes that cancer cells need to divide and grow. Alimta is typically given in combination with cisplatin, another type of chemotherapy drug, every three weeks. Studies have shown that Alimta-based chemotherapy can improve survival and quality of life in mesothelioma patients, particularly those with nonsquamous cell type. However, the side effects may include low blood cell counts, fatigue, nausea, and skin rash. 2. CisplatinCisplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy drug that targets rapidly dividing cells, including cancer cells. It works by binding to the DNA in cancer cells and preventing them from replicating. Cisplatin is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as pemetrexed or gemcitabine, to enhance its effectiveness. Cisplatin can cause significant side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, kidney damage, and hearing loss. Therefore, patients undergoing cisplatin-based chemotherapy may need to be closely monitored and receive supportive care. 3. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that interferes with the DNA synthesis in cancer cells, thereby blocking their growth and division. It’s often used in combination with cisplatin for mesothelioma patients who are not eligible for surgery or radiation therapy. Gemcitabine is generally well-tolerated, but it may cause side effects such as flu-like symptoms, mouth sores, and reduced blood cell counts. 4. CarboplatinCarboplatin is another platinum-based chemotherapy drug that works similarly to cisplatin. It’s sometimes used as an alternative to cisplatin for mesothelioma patients who cannot tolerate its side effects or have renal impairment. Carboplatin may cause some of the same side effects as cisplatin, such as nausea, vomiting, and low blood cell counts. However, it’s generally less toxic to the kidneys and nervous system. Health Insurance Coverage for Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsThe cost of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can vary widely depending on the type, duration, and frequency of treatment. According to a study by the American Cancer Society, the average annual cost of cancer drugs in the U.S. increased from $5,000 to $10,000 in the 1990s to over $100,000 in recent years. This can pose a significant financial burden for patients and their families, especially if they do not have adequate health insurance coverage. Fortunately, many health insurance policies cover at least some of the costs associated with mesothelioma treatment, including chemotherapy drugs. However, the extent of coverage can vary depending on the type of policy and the insurer. Here are some common types of health insurance and how they may apply to mesothelioma chemotherapy: 1. Private health insuranceMost private health insurance plans cover some or all of the costs related to cancer treatment, including chemotherapy drugs. However, the specific details of coverage may depend on the plan’s network, deductibles, co-payments, and annual limits. Patients may need to check with their insurer or employer to understand the scope of their benefits and any out-of-pocket costs. 2. MedicareMedicare is a federally-funded health insurance program that provides coverage for people who are 65 years or older or have certain disabilities. Medicare Part A covers hospital stays and some inpatient care, while Medicare Part B covers doctor visits, outpatient services, and some prescription drugs, including chemotherapy. Patients may need to pay deductibles, co-payments, and monthly premiums for Medicare coverage, depending on their income and eligibility. 3. MedicaidMedicaid is a joint federal-state program that offers health coverage to low-income individuals and families. Medicaid benefits may vary by state, but they generally include hospitalization, physician services, and prescription drugs, including chemotherapy. Eligibility for Medicaid is based on income and financial need, and patients may need to meet certain requirements to qualify. 4. Clinical trialsClinical trials are research studies that test new treatments or interventions for a specific disease or condition. They can offer access to cutting-edge treatments and drugs that may not be available outside of the trial. In some cases, the costs of the drugs and other medical procedures may be covered by the trial sponsor or insurer. Patients interested in participating in a clinical trial should talk to their doctor and research the options carefully. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can be lifesaving for some patients, but they also come with risks and costs that need to be carefully managed. Patients and their families should work closely with their healthcare providers and insurers to understand the available treatment options, the benefits and drawbacks of each, and the financial implications. By being proactive and informed, patients can maximize their chances of success and minimize their stress and financial burden. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Patient CostsIntroductionMesothelioma cancer is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that develops in the protective lining of the lungs, abdomen, and heart. It is primarily caused by exposure to asbestos, a naturally occurring mineral that was widely used in manufacturing and construction materials for many decades. The prognosis for mesothelioma is typically poor, with a five-year survival rate of only about 10%. However, chemotherapy drugs have been shown to improve survival rates in many patients. The treatment process can be extremely costly, and patients and their families may struggle to pay for the necessary drugs and medical care. In this article, we will explore some of the mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs available and the costs associated with these treatments. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsChemotherapy is a common treatment option for mesothelioma patients. It involves the use of drugs that kill or slow the growth of cancer cells. Some of the most commonly used chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma include: 1. CisplatinCisplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy drug that works by damaging the DNA in cancer cells, which makes it difficult for them to grow and divide. It is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs to improve its effectiveness in treating mesothelioma. Cisplatin can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and kidney damage. 2. CarboplatinCarboplatin is another platinum-based chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma. It works by disrupting the cancer cells’ ability to divide and grow. Carboplatin is often used along with other chemotherapy drugs to help improve results. Like Cisplatin, Carboplatin can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and kidney damage. 3. AlimtaAlimta is a chemotherapy drug that is specifically approved for the treatment of mesothelioma. It targets the rapidly dividing cancer cells and helps to slow down the spread of the cancer. Alimta is often used in combination with Cisplatin to improve its effectiveness. Side effects of Alimta can include fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. 4. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat a variety of cancers, including mesothelioma. It works by blocking the enzymes that cancer cells need to divide and grow. Gemcitabine is generally well tolerated, but it can cause side effects such as fatigue and nausea. 5. VinorelbineVinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by preventing the cancer cells from dividing and growing. Vinorelbine can cause side effects such as fatigue, nausea, and low blood cell counts. Patient CostsThe cost of mesothelioma treatment can be very high. The average cost of chemotherapy for mesothelioma patients is approximately $10,000 per month. However, the exact cost of treatment can vary widely depending on several factors, including the type of treatment, the stage of the cancer, and the patient’s insurance coverage. 1. Chemotherapy DrugsThe cost of chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma can range from several hundred to several thousand dollars per dose. The most commonly used drugs, like Cisplatin and Carboplatin, typically cost between $600 and $1,200 per dose. Other drugs, such as Alimta, can cost as much as $5,000 per dose. 2. Medical BillsIn addition to the cost of chemotherapy drugs, mesothelioma patients may face other medical expenses. These can include hospitalization, surgery, and diagnostic tests. The cost of these services can add up quickly and may not be covered by insurance. Additionally, many mesothelioma patients require ongoing medical care that can be very expensive. 3. Home CareMesothelioma patients may also require home care services, such as assistance with daily living activities. These services can be costly and may not be covered by insurance. Patients and their families may need to pay for these services out-of-pocket. 4. Travel and LodgingMesothelioma patients may need to travel to receive treatment at a specialized cancer center. This can involve additional costs for travel, lodging, and meals. These costs can be significant and may not be covered by insurance. 5. Loss of IncomeMesothelioma patients may need to take time off work to undergo treatment and recover. This can result in a loss of income, which can make it difficult to pay for medical expenses and other costs associated with the condition. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can be effective in slowing down the progression of the disease and improving patient outcomes. However, the costs associated with treatment can be very high and may be a barrier to accessing necessary care. Patients and their families may need to explore all available options for financial assistance, including insurance coverage, government programs, and charitable organizations. By working closely with healthcare providers and financial experts, mesothelioma patients can develop a comprehensive plan for managing the costs of treatment and maximizing their quality of life.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Hospice CareMesothelioma is a rare form of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, chest, abdomen, and heart. This cancer is caused by exposure to asbestos, a mineral that was widely used in construction and manufacturing industries until the 1980s. Today, there is still no known cure for mesothelioma, but there are treatments that can help manage the disease and improve a patient’s quality of life. One of the most common treatments for mesothelioma is chemotherapy. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsChemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. There are several chemotherapy drugs that are used to treat mesothelioma, including:
Chemotherapy drugs can be administered in several ways, including intravenously (through an IV), orally (in pill form), or injected directly into the affected area of the body. The specific dosage and frequency of chemotherapy treatments will depend on the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and other factors. Hospice Care for Mesothelioma PatientsWhile chemotherapy can help manage the symptoms of mesothelioma, it may not always be effective in stopping the progression of the disease. In some cases, mesothelioma patients may choose to stop chemotherapy treatments and focus on hospice care instead. Hospice care is a type of palliative care that focuses on providing comfort and support to patients who are nearing the end of their lives. Hospice care can be provided in a variety of settings, including the patient’s home, a hospital, or a hospice facility. The goal of hospice care is to help patients maintain their quality of life and manage their symptoms as comfortably as possible. Some of the services that can be provided as part of hospice care include:
Hospice care can be a valuable option for mesothelioma patients who have decided to stop chemotherapy treatments or who have exhausted all other treatment options. It can help patients and their families find peace and comfort during a difficult time. ConclusionMesothelioma is a devastating disease that affects thousands of people every year. While there is no cure for mesothelioma, chemotherapy can help manage the symptoms of the disease and improve a patient’s quality of life. Hospice care can also be a valuable option for mesothelioma patients who have decided to stop chemotherapy treatments or who are nearing the end of their lives. By working closely with medical professionals and palliative care providers, mesothelioma patients can find comfort and support during a difficult time. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and ChemobrainChemotherapy is the most common form of treatment for malignant mesothelioma, a rare cancer that affects the thin layer of tissue that covers most internal organs. The chemotherapy drugs used in mesothelioma treatment aim to slow down or kill cancer cells and prevent them from spreading to other parts of the body. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs work by attacking fast-dividing cells, including cancer cells. The most commonly used chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma include:
Cisplatin and carboplatin are platinum-based chemotherapy drugs that are often used in combination with other drugs such as pemetrexed or gemcitabine. These drugs work by damaging the DNA in cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Pemetrexed is a chemotherapy drug that blocks the production of certain enzymes that are essential for cancer cell growth. It is often used in combination with cisplatin and carboplatin for mesothelioma treatment. Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that interferes with the DNA synthesis process in cancer cells, which can lead to cell death. It is often used in combination with cisplatin for mesothelioma treatment. Side Effects of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsWhile chemotherapy drugs can be effective in treating mesothelioma, they can also cause unpleasant side effects. Some common side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs include:
Your doctor can provide you with more information about the potential side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and how to manage them. ChemobrainChemobrain, also known as chemo fog or chemo brain, is a common side effect of chemotherapy drugs. It refers to a range of cognitive symptoms that can affect cancer patients during and after treatment. These symptoms may include:
While the exact cause of chemobrain is not fully understood, it is thought to be related to the effects of chemotherapy drugs on the brain. Chemotherapy drugs can interfere with the normal functioning of brain cells, leading to cognitive symptoms. Chemobrain can be temporary or long-lasting, and its severity can vary from person to person. It can affect your ability to perform everyday tasks, including work, household chores, and social activities. Managing ChemobrainWhile there is no cure for chemobrain, there are several strategies that can help manage its symptoms, including:
Your doctor may also recommend certain medications or therapies to help manage the symptoms of chemobrain. With time and proper care, many people are able to recover from chemobrain and return to their normal activities. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can be effective in treating mesothelioma, but they can also cause side effects such as nausea, fatigue, and hair loss. Chemobrain is another potential side effect of chemotherapy drugs, but there are strategies that can help manage its symptoms. If you are undergoing chemotherapy for mesothelioma, it is important to speak with your doctor about potential side effects and strategies for managing them. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs: The Role of a Mesothelioma Specialist in Chemotherapy TreatmentMesothelioma is a deadly type of cancer that is caused by exposure to asbestos fibers. This disease affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, and heart. Currently, there is no cure for mesothelioma, but there are several treatment options available to patients. One of the most common treatments for the disease is chemotherapy, which uses drugs to kill cancer cells and slow the progression of the disease. Chemotherapy for mesothelioma can be administered in several ways, including intravenously, topically, or directly into the affected area. The chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma are designed to target rapidly dividing cancer cells in the body. The drugs work by disrupting the cancer cells’ ability to reproduce and grow, which can help slow the progression of the disease. While chemotherapy can be effective in treating mesothelioma, it also comes with several side effects. Chemotherapy drugs can cause damage to healthy cells in the body, which can lead to side effects like nausea, hair loss, fatigue, and anemia. However, a mesothelioma specialist can help patients manage these side effects and provide support throughout the treatment process. What is a Mesothelioma Specialist?A mesothelioma specialist is a healthcare professional who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of mesothelioma. These specialists have in-depth knowledge and expertise in the latest treatments for mesothelioma, including chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery. Mesothelioma specialists are typically oncologists, which are doctors who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Oncologists can specialize in various types of cancer, including mesothelioma. A mesothelioma specialist may also work closely with other healthcare professionals, such as radiologists, surgeons, and nurses, to provide holistic care to patients. The Role of a Mesothelioma Specialist in Chemotherapy TreatmentA mesothelioma specialist plays a crucial role in the chemotherapy treatment of mesothelioma. Here are some of the roles that a mesothelioma specialist can play during chemotherapy treatment: 1. Determine the Best Chemotherapy RegimenA mesothelioma specialist can work with the patient to determine the best chemotherapy regimen for their specific case. Different types of chemotherapy drugs may be used, depending on the stage of the disease, the patient’s overall health, and other factors. The specialist can help the patient understand the benefits and risks of each chemotherapy drug and develop a treatment plan that is tailored to their needs. 2. Monitor the Patient’s Response to TreatmentA mesothelioma specialist can monitor the patient’s response to chemotherapy treatment and adjust the treatment plan as needed. Regular check-ups and imaging tests can help the specialist determine if the chemotherapy is effectively reducing the size of the cancer cells and slowing the progression of the disease. 3. Manage Side EffectsChemotherapy drugs can cause several side effects, including nausea, hair loss, fatigue, and anemia. A mesothelioma specialist can help patients manage these side effects and provide support throughout the treatment process. They can also recommend medications and lifestyle changes that can help alleviate these side effects. 4. Provide Emotional SupportA mesothelioma diagnosis can be emotionally overwhelming for patients and their families. A mesothelioma specialist can provide emotional support to patients and their loved ones and help them navigate the complexities of the disease. They can also provide information and resources on support groups, counseling services, and other forms of support. 5. Coordinate with Other Healthcare ProfessionalsIn addition to providing medical care, a mesothelioma specialist can coordinate with other healthcare professionals to provide holistic care to patients. They may work closely with radiologists, surgeons, and nurses to develop a comprehensive treatment plan for the patient. ConclusionWhile chemotherapy can be an effective treatment option for mesothelioma, it also comes with several side effects. Working with a mesothelioma specialist can help patients manage these side effects and receive the best possible care during treatment. A mesothelioma specialist can also provide emotional support and coordinate with other healthcare professionals to ensure that patients receive holistic care throughout their treatment journey.
The Risk of Secondary Cancers with Mesothelioma Chemotherapy TreatmentMesothelioma is a rare but aggressive form of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, and heart. It is caused by exposure to asbestos, a fibrous mineral that was commonly used in construction, shipbuilding, and other industries until it was banned in the 1970s. Unfortunately, mesothelioma has a poor prognosis and limited treatment options. One of the primary treatments for mesothelioma is chemotherapy, which uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Understanding Mesothelioma ChemotherapyMesothelioma chemotherapy typically involves a combination of two or more drugs, which are given either intravenously (through a vein) or orally (in pill form). The goal of chemotherapy is to kill as many cancer cells as possible while minimizing damage to healthy cells. Unfortunately, chemotherapy drugs can also have side effects such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue, hair loss, and increased risk of infections. Some common mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs include:
The Risk of Secondary CancersWhile chemotherapy can be an effective treatment for mesothelioma, it also poses a risk of secondary cancers. This is because chemotherapy drugs can damage healthy cells in addition to cancer cells. Over time, this damage can lead to mutations in DNA that can cause other types of cancer to develop. One of the most significant risks of mesothelioma chemotherapy is the development of leukemia. Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow and can be fatal if not treated promptly. According to some studies, patients who receive chemotherapy for mesothelioma have a higher risk of developing leukemia within a few years after treatment. Reducing the Risk of Secondary CancersWhile the risk of secondary cancers is a concern for mesothelioma patients undergoing chemotherapy, there are steps that can be taken to reduce this risk. One of the most important is to work closely with your medical team to monitor your health and catch any potential problems early. Regular check-ups, blood tests, and imaging scans can help detect any changes in your body that could indicate a secondary cancer. It’s also important to maintain a healthy lifestyle throughout and after chemotherapy treatment. This includes eating a balanced diet, staying active, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. These habits can help improve your overall health and reduce your risk of developing other types of cancer. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy can be a lifesaving treatment for patients with this rare and aggressive form of cancer. However, it also poses a risk of secondary cancers, particularly leukemia. By working closely with your medical team, monitoring your health, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can reduce your risk of developing secondary cancers and improve your overall quality of life. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Palliative CareMesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsMesothelioma is a type of cancer that primarily affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart. It is caused by exposure to asbestos, a naturally occurring mineral that was used extensively in construction and manufacturing industries until the 1980s. Currently, there is no cure for mesothelioma, but chemotherapy treatment has proved beneficial in managing the disease and extending survival rates. Chemotherapy is the use of drugs that target and kill the rapidly dividing cancer cells. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are usually administered in cycles, with a rest period in between to allow the body to recover. The drugs may be given intravenously or orally, depending on the type and stage of the cancer. The following are some of the mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs used in treatment:
Alimta and Platinol are the most commonly used Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs, and the combination of these two drugs has shown positive results in numerous cancer patients. Alimta, in particular, has been approved by the FDA specifically for mesothelioma treatment. These mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can cause side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and fatigue. But these drugs have been modified in recent years, making them easier for patients to tolerate while still being effective in treating cancer. Recent Advancements in Mesothelioma ChemotherapyMedical researchers are continually exploring new drugs and treatments to improve the efficacy of mesothelioma chemotherapy. The following are some current developments in mesothelioma chemotherapy: Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy aims at identifying and attacking the specific cancer cells while leaving the healthy cells unharmed. This approach reduces the side effects of chemotherapy that harm healthy cells. Immunotherapy: Immune checkpoint inhibitors are drugs that strengthen the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells. Some of these drugs have shown promising results in mesothelioma patients. Gene Therapy: Gene therapy aims at fixing or replacing a person’s defective or missing genes that cause cancer. Recent advancements in gene therapy have shown potential in treating mesothelioma and other cancers. These recent advancements in mesothelioma chemotherapy are still under study, and their efficacy needs to be further assessed in clinical trials. However, they provide hope for a better future in mesothelioma cancer treatment. Palliative Care for Mesothelioma PatientsMost mesothelioma patients undergoing chemotherapy treatment may experience side effects, including nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. Palliative care is palliative care for such patients that provide relief from such symptoms, stress, and other complications associated with the disease or its treatment. Palliative care is about improving the quality of life of the patients and their families facing life-threatening illnesses by managing symptoms and providing psychosocial support. It is often used in cancer treatment to manage symptoms and improve overall comfort levels. The following are some of the palliative care options that may be provided to mesothelioma patients: Pain Management: Pain is one of the most distressing and debilitating symptoms experienced by mesothelioma patients. Pain management may include medication, nerve blocks, or other non-drug therapies like massage, acupuncture, or physical therapy. Nutrition Management: Chemotherapy and radiation can suppress the appetite of mesothelioma patients, leading to malnutrition. Proper nutrition management can help with maintaining healthy immune function, weight management, and managing side effects of chemotherapy and radiation. Emotional and Psychological Support: Palliative care includes counseling services or support groups that provide emotional and psychological support to mesothelioma patients and their families. These services help patients better cope with the mental health issues associated with mesothelioma, such as depression, anxiety, or fear. Conclusion: Chemotherapy drugs have proven to be an effective treatment option for mesothelioma cancer. Palliative care, along with chemotherapy, can significantly improve the patient’s quality of life by managing symptoms and providing emotional and psychological support. Recent advancements in mesothelioma chemotherapy, such as targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and gene therapy, show promising results and bring hope for better cancer treatment in the future. This, in combination with palliative care, will help mesothelioma patients live a better quality of life and manage the debilitating symptoms of this disease. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Older AdultsIf you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma cancer, one of the treatment options that your medical team might recommend is chemotherapy. This type of cancer treatment involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells in the body. While chemotherapy can be effective in treating mesothelioma, it can also come with a variety of side effects. Understanding how chemotherapy works and what to expect during treatment can help you make informed decisions about your health. What is Mesothelioma Chemotherapy?Chemotherapy for mesothelioma is a treatment that involves using drugs to destroy cancer cells. The drugs are typically given intravenously (through a vein) or orally (by mouth), and they travel throughout the body to target cancer cells that have spread beyond the initial tumor site. Chemotherapy drugs work by stopping cancer cells from dividing or by causing them to die. There are several different chemotherapy drugs that may be used to treat mesothelioma, including:
Your medical team will work with you to determine which combination of drugs is best for your specific type and stage of mesothelioma. They will also consider your age, overall health, and any other medical conditions you may have. How Effective is Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma?While chemotherapy can be effective in treating mesothelioma, its effectiveness can vary depending on several factors. These factors include the stage of your cancer, your overall health, and the specific chemotherapy drugs that are used. According to the American Cancer Society, the median survival time for patients with mesothelioma who receive chemotherapy is around 12 months. However, some patients may live longer than this, and others may experience a shorter survival time. It is important to keep in mind that chemotherapy is just one treatment option for mesothelioma. Your medical team may recommend other therapies, such as surgery or radiation therapy, to help improve your chances of survival. What are the Side Effects of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy?Chemotherapy can cause a variety of side effects, including:
These side effects can vary in severity depending on the type and dose of chemotherapy drugs that are used. Your medical team will work with you to manage these side effects and help you feel as comfortable as possible during treatment. Special Considerations for Older AdultsOlder adults who are diagnosed with mesothelioma may have some unique considerations when it comes to chemotherapy treatment. Some older adults may have other medical conditions that can affect their ability to tolerate chemotherapy, while others may be taking medications that can interact with chemotherapy drugs. To help ensure the safety and effectiveness of chemotherapy treatment for older adults with mesothelioma, your medical team may take the following steps:
In ConclusionChemotherapy can be an effective mesothelioma treatment option, but it can also come with side effects. If you are an older adult who has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, your medical team can work with you to determine if chemotherapy is the right treatment option for you. They can also help you manage any side effects that may occur during treatment, so that you can focus on your health and well-being. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Women and MenMesothelioma is a rare form of cancer caused by exposure to asbestos and can affect different parts of the body, such as the lungs, abdomen, and heart. Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to slow or stop the growth of cancer cells. If you are diagnosed with mesothelioma, your doctor may recommend chemotherapy as part of your treatment plan. Chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma can be administered orally or intravenously. The drugs travel throughout the body to target cancer cells and kill them. Chemotherapy can be administered alone or in combination with surgery and radiation therapy. Chemotherapy DrugsThere are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used to treat mesothelioma:
Each chemotherapy drug has its own set of side effects, which can include:
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for WomenWomen who are diagnosed with mesothelioma have similar treatment options to men. However, women may experience different side effects and may need to take additional precautions if they are pregnant or breastfeeding. Chemotherapy drugs can affect a woman’s fertility, causing early menopause or infertility. It is important for women to discuss their fertility concerns with their doctor before starting chemotherapy treatment. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should avoid chemotherapy drugs because they can be harmful to the developing fetus or infant. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for MenMen account for the majority of mesothelioma cases, and chemotherapy is a commonly used treatment option. Chemotherapy is often administered in combination with surgery and radiation therapy to improve the chances of destroying cancer cells and preventing the cancer from returning. Men who undergo chemotherapy treatment may experience side effects such as hair loss, fatigue, and nausea. These side effects usually go away after treatment is completed, but some men may experience long-term side effects such as nerve damage or hearing loss. ConclusionChemotherapy is a key part of treatment for mesothelioma, and it can help to improve survival rates and slow the progression of the disease. If you have been diagnosed with mesothelioma, make sure to discuss your treatment options with your doctor and ask about the potential side effects of chemotherapy. Whether you are a man or a woman, it is important to take care of your physical and emotional health during and after mesothelioma treatment. Joining a support group can help you to connect with others who are going through a similar experience and provide you with the emotional support you need to cope with the challenges of living with mesothelioma. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for VeteransMesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the thin layer of tissue that covers most of our internal organs. The disease is caused by exposure to asbestos, which is commonly found in building materials and industrial products. Mesothelioma can take several decades to develop, and it often goes undiagnosed until the later stages. Since veterans are more likely to be exposed to asbestos, they are also at a higher risk of developing mesothelioma. Chemotherapy is one of the most common treatments for mesothelioma. While it can’t cure the disease, chemotherapy can help manage symptoms and prolong a patient’s life. There are several chemotherapy drugs that are used to treat mesothelioma, each with its own set of benefits and side effects. The following are the most commonly used chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma: 1. CisplatinCisplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat many types of cancer, including mesothelioma. It works by attacking and damaging the DNA of cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. While cisplatin can be effective in slowing the growth of mesothelioma, it can have some serious side effects. The drug can cause hearing loss, kidney damage, and nerve damage, which can lead to numbness or tingling in the hands and feet. 2. AlimtaAlimta is a chemotherapy drug that is specifically approved to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the production of DNA and RNA, which prevents cancer cells from dividing and growing. Alimta is generally well-tolerated, but it can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and low white blood cell count. In some cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as lung problems and kidney damage. 3. CarboplatinCarboplatin is another chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. Like cisplatin, it works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, which prevents them from growing and dividing. While carboplatin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and low white blood cell count. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or changes in hearing. 4. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with another drug, such as cisplatin or carboplatin. It works by interfering with the DNA of cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Gemcitabine can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and low white blood cell count. In some cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or changes in vision. 5. VinorelbineVinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with another drug, such as cisplatin or carboplatin. It works by affecting the microtubules inside cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Vinorelbine can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and low white blood cell count. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or changes in heart rate. 6. PemetrexedPemetrexed is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with cisplatin to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the production of DNA and RNA inside cancer cells, which prevents them from growing and dividing. Pemetrexed can cause some side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and low white blood cell count. In some cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as skin rashes or problems with kidney function. 7. DoxorubicinDoxorubicin is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Doxorubicin can cause some side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and low white blood cell count. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as heart damage or problems with liver function. 8. MitomycinMitomycin is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Mitomycin can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and low white blood cell count. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as kidney damage or blood clotting problems. 9. MethotrexateMethotrexate is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the production of folic acid, which is essential for DNA synthesis inside cancer cells. Methotrexate can cause some side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and low white blood cell count. In some cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or lung problems. 10. CyclophosphamideCyclophosphamide is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Cyclophosphamide can cause some side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and low white blood cell count. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as kidney damage or bladder problems. 11. EpirubicinEpirubicin is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Epirubicin can cause some side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and low white blood cell count. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as heart problems or liver damage. 12. DocetaxelDocetaxel is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by interfering with microtubules inside cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Docetaxel can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and low white blood cell count. In some cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as heart problems or changes in vision. 13. PaclitaxelPaclitaxel is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by interfering with microtubules inside cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Paclitaxel can cause some side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and low white blood cell count. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as nerve damage or changes in heart rate. 14. VincristineVincristine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by interfering with microtubules inside cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Vincristine can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and low white blood cell count. In some cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as nerve damage or changes in vision. 15. BleomycinBleomycin is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Bleomycin can cause some side effects, such as fever, cough, and skin problems. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as lung problems or nerve damage. 16. InterferonInterferon is a type of biological therapy that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by boosting the immune system’s ability to fight cancer cells. Interferon can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, flu-like symptoms, and depression. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or thyroid problems. 17. BevacizumabBevacizumab is a type of targeted therapy that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking a protein called VEGF, which helps cancer cells grow new blood vessels. Bevacizumab can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, high blood pressure, and bleeding problems. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as heart problems or nerve damage. 18. NivolumabNivolumab is a type of immunotherapy that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking a protein called PD-L1, which helps cancer cells evade the immune system. Nivolumab can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, rash, and diarrhea. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as lung problems or liver damage. 19. PembrolizumabPembrolizumab is a type of immunotherapy that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking a protein called PD-1, which helps cancer cells evade the immune system. Pembrolizumab can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and skin problems. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as lung problems or liver damage. 20. IpilimumabIpilimumab is a type of immunotherapy that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking a protein called CTLA-4, which helps cancer cells evade the immune system. Ipilimumab can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, rash, and diarrhea. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or nerve problems. 21. DurvalumabDurvalumab is a type of immunotherapy that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking a protein called PD-L1, which helps cancer cells evade the immune system. Durvalumab can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, cough, and skin problems. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as lung problems or nerve damage. 22. AtezolizumabAtezolizumab is a type of immunotherapy that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking a protein called PD-L1, which helps cancer cells evade the immune system. Atezolizumab can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and skin problems. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as lung problems or liver damage. 23. TremelimumabTremelimumab is a type of immunotherapy that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking a protein called CTLA-4, which helps cancer cells evade the immune system. Tremelimumab can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, rash, and diarrhea. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or nerve problems. 24. TrabectedinTrabectedin is a type of chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by disrupting the DNA of cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Trabectedin can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and low white blood cell count. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or changes in heart rate. 25. ImatinibImatinib is a type of targeted therapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking a protein called BCR-ABL, which helps cancer cells grow and divide. Imatinib can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and skin problems. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or problems with blood clotting. 26. DasatinibDasatinib is a type of targeted therapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking a protein called BCR-ABL, which helps cancer cells grow and divide. Dasatinib can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and skin problems. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or changes in heart rate. 27. ErlotinibErlotinib is a type of targeted therapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking a protein called epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which helps cancer cells grow and divide. Erlotinib can cause some side effects, such as diarrhea, skin rash, and fatigue. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as lung problems or liver damage. 28. VandetanibVandetanib is a type of targeted therapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs), which helps cancer cells grow new blood vessels. Vandetanib can cause some side effects, such as diarrhea, skin rash, and low white blood cell count. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as heart problems or changes in thyroid function. 29. SorafenibSorafenib is a type of targeted therapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking a protein called VEGFRs, which helps cancer cells grow new blood vessels. Sorafenib can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and skin problems. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or changes in heart rate. 30. RegorafenibRegorafenib is a type of targeted therapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking several proteins, including VEGFRs, which helps cancer cells grow new blood vessels. Regorafenib can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and skin problems. In some cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or high blood pressure. 31. NintedanibNintedanib is a type of targeted therapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking several proteins, including VEGFRs and fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs), which helps cancer cells grow and divide. Nintedanib can cause some side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or heart problems. 32. PanobinostatPanobinostat is a type of chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the activity of proteins that control gene expression, which can prevent cancer cells from growing and dividing. Panobinostat can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and low white blood cell count. In some cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as heart problems or changes in liver function. 33. Interleukin-2Interleukin-2 is a type of biological therapy that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by boosting the immune system’s ability to fight cancer cells. Interleukin-2 can cause some side effects, such as fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms. In rare cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as lung problems or problems with blood clotting. 34. LenalidomideLenalidomide is a type of targeted therapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by activating the immune system’s ability to fight cancer cells. Lenalidomide can cause some side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and low white blood cell count. In some cases, the drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as blood clotting problems or nerve damage. 35. IxabepiloneIxabepilone is a type of chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the activity of proteins that control gene expression, which can prevent cancer cells from growing and dividing. Ixabepilone can cause Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Stage 1 and 2 MesotheliomaChemotherapy Drugs for Stage 1 and 2 MesotheliomaChemotherapy is a commonly used treatment for mesothelioma, especially for patients in stage 1 and 2. In these early stages, the cancer has not yet spread to other parts of the body, making it easier to eliminate. Chemotherapy drugs work by attacking cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and ultimately causing them to die. While chemotherapy can have unpleasant side effects, it is a crucial treatment option for many mesothelioma patients. There are several chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma. Some of the most common include:
How Chemotherapy is AdministeredChemotherapy drugs can be given orally (by mouth) or intravenously (by injection). The method of administration depends on the specific drug or combination of drugs being used. Some drugs, like pemetrexed and cisplatin, are often given together and require an intravenous infusion that can take several hours. Other drugs, like methotrexate, can be taken orally or injected into the muscle or vein. The frequency and duration of chemotherapy treatment also varies depending on the drug and the individual patient’s response. Possible Side Effects of ChemotherapyWhile chemotherapy can be an effective treatment for mesothelioma, it also has the potential to cause side effects. Some of the most common side effects of chemotherapy include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, hair loss, and anemia. Patients may also experience neuropathy, a type of nerve damage that can cause numbness, tingling, or weakness in the hands and feet. These side effects are usually temporary and can be managed with medication or other supportive care. In rare cases, chemotherapy can cause more serious side effects, such as infection or damage to the heart, lungs, or kidneys. Other Mesothelioma Treatment OptionsWhile chemotherapy is an important tool in the fight against mesothelioma, it is often used in combination with other treatment options. Radiation therapy, for example, can be used to shrink tumors and kill cancer cells in specific areas of the body. Surgery may also be an option for some patients, depending on the size and location of the tumors and the overall health of the patient. In addition to traditional treatments, many mesothelioma patients also explore alternative or complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, or herbal supplements. While there is limited scientific evidence to support these treatments, they may provide some relief from symptoms or an improved sense of well-being. Talk to Your DoctorIf you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it is important to explore all of your treatment options and work with a team of doctors who specialize in this rare form of cancer. Your doctor can help you understand the benefits and potential risks of chemotherapy and other treatments and create a personalized treatment plan that is right for you. While there is no cure for mesothelioma, early detection and treatment can improve outcomes and increase the chances of long-term survival. With the right treatment and support, many mesothelioma patients are able to maintain a good quality of life and continue to enjoy their daily activities for years to come. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Stage 3 and 4 MesotheliomaIf you or someone you love has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it’s natural to feel overwhelmed and unsure of where to turn next. Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer that affects the mesothelium, a thin layer of tissue that covers many of the body’s internal organs. The most common form of mesothelioma is caused by exposure to asbestos, a mineral that was once widely used in construction and manufacturing. Asbestos fibers can become lodged in the mesothelium and cause inflammation and scarring over time, leading to the development of cancer. The treatment options for mesothelioma depend on a number of factors, including the stage of the disease, the location of the tumors, and the overall health of the patient. One of the most common treatments for mesothelioma is chemotherapy, which involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the chemotherapy drugs used to treat stage 3 and 4 mesothelioma, as well as their potential side effects and effectiveness. Chemotherapy for Stage 3 MesotheliomaStage 3 mesothelioma is considered advanced, as the cancer has already spread to nearby lymph nodes and possibly other organs. Treatment for stage 3 mesothelioma often involves a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is typically administered after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells and prevent the cancer from recurring. The chemotherapy drugs used to treat stage 3 mesothelioma include cisplatin and pemetrexed, which are usually given together in a combination known as “cisplatin-pemetrexed.” This combination has been shown to be effective in slowing the growth of mesothelioma tumors and improving survival rates in some patients. However, it is also associated with a number of potential side effects, including nausea, vomiting, fatigue, hair loss, and an increased risk of infection. CisplatinCisplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy drug that works by damaging the DNA in cancer cells and preventing them from dividing and growing. It is often used in combination with other drugs, such as pemetrexed, to increase its effectiveness. Cisplatin is administered intravenously and is typically given in cycles, with several weeks of rest between treatments. Some of the potential side effects of cisplatin include nausea, vomiting, decreased appetite, fatigue, low blood counts, and an increased risk of infection. It can also cause damage to the kidneys and hearing loss, especially if given in high doses or for a prolonged period of time. PemetrexedPemetrexed is a chemotherapy drug that works by inhibiting the production of DNA and RNA in cancer cells, which slows their growth and division. It is usually given intravenously and is often combined with cisplatin to increase its effectiveness. Pemetrexed is typically administered once every three weeks, with several cycles of treatment. Some of the potential side effects of pemetrexed include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, decreased appetite, low blood counts, and an increased risk of infection. It can also cause skin rash and sensitivity to sunlight, so patients are advised to take precautions when going outside. Chemotherapy for Stage 4 MesotheliomaStage 4 mesothelioma is the most advanced stage of the disease, as the cancer has spread to distant organs and tissues throughout the body. Treatment for stage 4 mesothelioma is focused on palliative care, or relieving symptoms and improving quality of life. Chemotherapy can be an effective tool in managing pain and other symptoms of advanced mesothelioma, but it is not likely to cure the cancer or extend life expectancy significantly. The chemotherapy drugs used to treat stage 4 mesothelioma include many of the same drugs used in earlier stages, such as cisplatin and pemetrexed. However, in some cases, doctors may recommend alternative drugs or combinations of drugs based on the individual patient’s needs and health status. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat advanced mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the production of DNA and RNA in cancer cells, which slows their growth and division. Gemcitabine is typically administered intravenously and is given once a week for several weeks. Some of the potential side effects of gemcitabine include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, low blood counts, and an increased risk of infection. It can also cause skin rash and flu-like symptoms, such as fever and muscle aches. DoxorubicinDoxorubicin is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat advanced mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA in cancer cells and preventing their division and growth. Doxorubicin is typically administered intravenously and is given in cycles, with several weeks of rest between treatments. Some of the potential side effects of doxorubicin include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, low blood counts, and an increased risk of infection. It can also cause hair loss and damage to the heart and liver, especially if given in high doses. ConclusionChemotherapy can be an effective tool in the treatment of mesothelioma, especially in the earlier stages of the disease. However, it is also associated with a number of potential side effects and may not be a suitable option for all patients. If you or someone you love has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it’s important to work closely with your healthcare team to determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs and health status. With the right care and support, it is possible to manage the symptoms of mesothelioma and maintain a good quality of life.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Sarcomatoid MesotheliomaSarcomatoid mesothelioma is a rare subtype of mesothelioma cancer that has a poor prognosis and limited treatment options. Individuals diagnosed with sarcomatoid mesothelioma have a lower life expectancy compared to other subtypes of mesothelioma. Chemotherapy is a common treatment option for sarcomatoid mesothelioma, and it can be used in different ways including as a standalone treatment, before or after surgery, or as part of a multimodal treatment plan. Chemotherapy Drugs for Sarcomatoid MesotheliomaSeveral chemotherapy drugs are used to treat sarcomatoid mesothelioma, which can be administered in different combinations. The most common chemotherapy drugs used to treat sarcomatoid mesothelioma include:
How Chemotherapy Works for Sarcomatoid MesotheliomaChemotherapy works by targeting and killing rapidly dividing cancer cells in the body. Chemotherapy drugs circulate through the bloodstream and attack cancer cells throughout the body, including those that have spread beyond the primary tumor site. The side effects of chemotherapy depend on the type and dosage of the drugs administered, as well as an individual’s overall health and medical history. Common side effects of chemotherapy for sarcomatoid mesothelioma include:
Advancements in Mesothelioma ChemotherapyOver the years, several advancements have been made in mesothelioma chemotherapy, including the development of new drugs and combination therapies that can improve efficacy and reduce side effects. One of the most promising advancements in mesothelioma chemotherapy is immunotherapy, which uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells. Immunotherapy drugs known as checkpoint inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and nivolumab (Opdivo), have shown promise in clinical trials for mesothelioma treatment. Another promising approach in mesothelioma chemotherapy is targeted therapy, which uses drugs that target specific cells or molecules that are involved in cancer growth. For example, drugs that target the protein mesothelin, which is overexpressed in mesothelioma, have shown promise in preclinical studies and early clinical trials. ConclusionChemotherapy is a common treatment option for sarcomatoid mesothelioma, and it can be used alone or in combination with other treatments to improve outcomes and quality of life for patients. Several chemotherapy drugs are used to treat sarcomatoid mesothelioma, and advances in the field of mesothelioma treatment are promising for improving outcomes and survival rates for patients with this rare cancer subtype. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Biphasic MesotheliomaMesothelioma is a rare, aggressive form of cancer that originates in the lining that covers the internal organs. It is caused by asbestos exposure, typically in the workplace, and has a long latency period, often taking decades to manifest. Among the three major subtypes of mesothelioma, biphasic mesothelioma is the second most common, accounting for about 20-35% of all mesothelioma cases. Biphasic mesothelioma is characterized by a mixture of two types of cells, epithelioid and sarcomatoid, both of which can behave differently in response to treatment. The treatment for biphasic mesothelioma typically involves a combination of different approaches, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. While surgery and radiation therapy are aimed at controlling the local tumor growth, chemotherapy is often used to target the cancer cells that may have spread to other parts of the body. The Role of Chemotherapy in Biphasic Mesothelioma TreatmentChemotherapy for biphasic mesothelioma is often prescribed as a systemic therapy, which means that the drugs are administered through the bloodstream, allowing them to reach cancer cells in all parts of the body. The aim of chemotherapy is to destroy cancer cells or slow down their growth, thereby reducing the size of tumors and relieving the symptoms of mesothelioma. Chemotherapy can also be used after surgery (known as adjuvant therapy) to kill any remaining cancer cells that may have escaped surgery and reduce the risk of recurrence. Chemotherapy Drugs for Biphasic MesotheliomaThere are several chemotherapy drugs that are used to treat biphasic mesothelioma. Some of the commonly used drugs are:
While these drugs are often used in combination, the exact chemotherapy regimen will depend on several factors, including the stage of the disease, the extent of the tumor, the presence of other medical conditions, and the patient’s overall health. Side Effects of ChemotherapyLike all cancer treatments, chemotherapy for biphasic mesothelioma can cause several side effects. Some of the common ones are:
While these effects can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes, some patients may experience more serious side effects such as anemia, infections, and kidney damage. Therefore, it is important to discuss the potential benefits and risks of chemotherapy with your doctor before starting treatment. ConclusionWhile biphasic mesothelioma can be a challenging disease to manage, chemotherapy can play an important role in reducing the symptoms and extending the life of patients. By targeting cancer cells throughout the body, chemotherapy can help shrink tumors, slow down disease progression, and improve the quality of life of mesothelioma patients. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Epithelioid MesotheliomaEpithelioid mesothelioma is a type of mesothelioma that accounts for about 70% of all mesothelioma cases. It is the most common type of mesothelioma and also the most responsive to chemotherapy treatment. Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells in the body. Chemotherapy for mesothelioma is usually given as a combination of drugs. The most commonly used chemotherapy drugs for epithelioid mesothelioma are:
How Mesothelioma Chemotherapy WorksThe main goal of chemotherapy is to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors. Chemotherapy drugs work by targeting rapidly dividing cells, which is a hallmark of cancer cells. The drugs are usually given in cycles, with each cycle consisting of a period of treatment followed by a period of rest to allow the body time to recover. Chemotherapy for mesothelioma can be given in several ways: Systemic ChemotherapySystemic chemotherapy involves the use of drugs that are injected into the bloodstream. This allows the drugs to circulate throughout the body and reach cancer cells in different parts of the body. This type of chemotherapy is usually given intravenously (through a needle in the arm) or orally (in pill form). Intrapleural ChemotherapyIntrapleural chemotherapy involves the direct application of chemotherapy drugs to the lining of the lungs. This is done by inserting a catheter (thin tube) into the space between the lung and chest wall and then injecting the drugs directly into this space. The advantage of intrapleural chemotherapy is that it allows for a higher concentration of drugs to be delivered directly to the cancer cells in the lungs, which can increase the effectiveness of the treatment. Intrapleural chemotherapy is usually given in combination with systemic chemotherapy. Intraperitoneal ChemotherapyIntraperitoneal chemotherapy is similar to intrapleural chemotherapy, but involves the direct application of chemotherapy drugs to the lining of the abdomen. This is done by inserting a catheter into the abdomen and then injecting the drugs directly into this space. Intraperitoneal chemotherapy is usually used to treat peritoneal mesothelioma, which is a rare type of mesothelioma that affects the lining of the abdomen. Possible Side Effects of Mesothelioma ChemotherapyChemotherapy drugs can cause side effects, which can vary depending on the specific drugs used and the individual patient. Some common side effects of chemotherapy for mesothelioma include:
Some patients may also experience more serious side effects, such as kidney damage or nerve damage. ConclusionChemotherapy is a commonly used treatment for mesothelioma, especially for epithelioid mesothelioma. Chemotherapy drugs work by targeting rapidly dividing cells, which is a hallmark of cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be given in several ways, including systemic chemotherapy, intrapleural chemotherapy, and intraperitoneal chemotherapy. While chemotherapy can cause side effects, it can also help to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors, which can improve patient outcomes. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Recurrent MesotheliomaChemotherapy is a common treatment for mesothelioma, a rare but aggressive cancer caused by exposure to asbestos. It involves the use of drugs to kill the cancer cells and prevent them from multiplying. In some cases, chemotherapy drugs may also be used to shrink tumors before surgery or radiation therapy. However, mesothelioma is a challenging disease to treat, and even with chemotherapy, recurrence is a common problem. Recurrent mesothelioma refers to a cancer that has returned after being treated with chemotherapy. This can be a daunting and frustrating experience for patients and their families, as it may feel like starting over from scratch. However, there are several types of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs that can be effective in treating recurrent mesothelioma, either alone or in combination. 1. Alimta (Pemetrexed)Alimta is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking the enzymes that cancer cells need to grow and divide, ultimately causing the cancer cells to die. Alimta is often combined with cisplatin, another chemotherapy drug, for maximum effect. This combination has been shown to improve survival rates in patients with mesothelioma, both in the first-line treatment and in cases where it has recurred. 2. CarboplatinCarboplatin is another chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. It belongs to the platinum-based chemotherapy family, like cisplatin. Carboplatin is also often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as Alimta, to boost the effectiveness of treatment. 3. GemcitabineGemcitabine is another chemotherapy drug that has shown promise in the treatment of mesothelioma. It is often used in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin. Gemcitabine works by interfering with the DNA in cancer cells, which prevents the cells from dividing and growing. This ultimately leads to the death of the cancer cells. 4. VinorelbineVinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat lung cancer, but it has also been found to be effective in the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by stopping cancer cells from dividing and growing, which ultimately leads to the death of the cells. Vinorelbine is often used in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin as a second-line treatment for patients with recurrent mesothelioma. 5. DoxorubicinDoxorubicin is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat several types of cancer, including mesothelioma. It works by preventing cancer cells from dividing and growing, ultimately leading to their death. Like other chemotherapy drugs, doxorubicin can be used alone or in combination with other drugs to boost its effectiveness. It is often used as a second-line treatment for recurrent mesothelioma. 6. IrinotecanIrinotecan is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat several types of cancer, including mesothelioma. It works by preventing cancer cells from dividing and growing, ultimately leading to their death. Irinotecan is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin or carboplatin, for maximum effect. 7. CytarabineCytarabine is a chemotherapy drug that is primarily used to treat leukemia, but it has also been found to be effective in the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the DNA in cancer cells, which prevents the cells from dividing and growing. Cytarabine is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin or carboplatin, for maximum effect. 8. BevacizumabBevacizumab is a drug that works by inhibiting the growth of blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to cancer cells. This prevents the cancer cells from multiplying and growing. Bevacizumab has been found to be effective in the treatment of several types of cancer, including mesothelioma. It is often used in combination with chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin or carboplatin, for maximum effect. 9. PembrolizumabPembrolizumab is a drug that works by inhibiting the activity of proteins that prevent the immune system from attacking cancer cells. It has been found to be effective in the treatment of several types of cancer, including mesothelioma. Pembrolizumab is often used in combination with chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin or carboplatin, for maximum effect. Pembrolizumab is a relatively new drug, and more research is needed to determine its long-term effectiveness in the treatment of mesothelioma. 10. NivolumabNivolumab is another drug that inhibits the activity of proteins that prevent the immune system from attacking cancer cells. It has been found to be effective in the treatment of several types of cancer, including mesothelioma. Nivolumab is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin or carboplatin, for maximum effect. Like pembrolizumab, nivolumab is a relatively new drug, and more research is needed to determine its long-term effectiveness in the treatment of mesothelioma. 11. DurvalumabDurvalumab is a drug that works by inhibiting the activity of proteins that prevent the immune system from attacking cancer cells. It has been found to be effective in the treatment of several types of cancer, including mesothelioma. Durvalumab is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin or carboplatin, for maximum effect. Like pembrolizumab and nivolumab, durvalumab is a relatively new drug, and more research is needed to determine its long-term effectiveness in the treatment of mesothelioma. 12. OnconaseOnconase is a chemotherapy drug that is made from the eggs of the leopard frog. It works by blocking the production of proteins that cancer cells need to survive. Onconase has been found to be effective in the treatment of mesothelioma, both alone and in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin or carboplatin. Onconase is another relatively new drug, and more research is needed to determine its long-term effectiveness and safety. Chemotherapy Side EffectsLike all cancer treatments, chemotherapy drugs can cause side effects. The severity and type of side effects depend on the type of drugs used, the dosage, and the individual patient’s response. Common side effects of chemotherapy drugs include:
It is important for patients to discuss their concerns about side effects with their healthcare team, as they can provide advice and support to manage symptoms and ensure that treatment is as comfortable as possible. In some cases, certain side effects may be prevented or minimized with medications or lifestyle changes. ConclusionAlthough chemotherapy is not a cure for mesothelioma, it can help to prolong and improve the quality of life for patients with recurrent mesothelioma. Each patient’s treatment plan will depend on their individual circumstances, such as the type and stage of cancer, general health, and side effect profile. By working closely with their healthcare team, patients can make informed decisions about their care and find the treatment that is best for them. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Localized MesotheliomaWhen mesothelioma is in its early stages, it is often localized to one area of the body. In these cases, chemotherapy can be effective in treating the cancer and potentially improving the patient’s quality of life. There are several chemotherapy drugs that may be used for treating localized mesothelioma, each with unique benefits and potential side effects. 1. CisplatinCisplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used in the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the DNA of cancer cells, in turn killing these cells. Cisplatin is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs to maximize its effectiveness. Studies have shown that cisplatin can increase survival rates and improve symptoms in patients with mesothelioma. However, cisplatin can have side effects. These can include nausea, vomiting, kidney damage, and hearing loss. Patients who are prescribed cisplatin may also require additional medications to manage these side effects. Regular blood tests may be required to monitor kidney function and other potential complications. 2. CarboplatinCarboplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is similar in structure and effect to cisplatin. It too interferes with cancer cell DNA, and is sometimes used in place of cisplatin when a patient’s body cannot tolerate the latter. Carboplatin is often combined with other chemotherapy drugs, such as pemetrexed, to improve treatment outcomes. Like cisplatin, carboplatin can have side effects such as low blood cell count, nausea, and vomiting. Additional medications may be necessary to manage these side effects, and patients may require regular blood tests to monitor for complications. 3. PemetrexedPemetrexed is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin for mesothelioma treatment. It works by blocking folic acid production in cancer cells, which in turn slows their growth. Pemetrexed has been shown to increase survival rates and improve symptoms in mesothelioma patients. Some common side effects of pemetrexed treatment include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and decreased appetite. Pemetrexed can also cause low blood cell counts, which may require additional medications or transfusions. Patients typically undergo regular blood tests during pemetrexed treatment to monitor for complications. 4. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by disrupting the growth and replication of cancer cells. Gemcitabine is sometimes used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin or carboplatin, to improve treatment outcomes. Side effects of gemcitabine can include low blood cell counts, nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. Like other chemotherapy drugs, patients may require additional medications to manage these side effects, and regular blood tests are often necessary to monitor for complications. 5. VinorelbineVinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by disrupting the replication of cancer cells and preventing them from spreading. Vinorelbine is often used as a second-line treatment option when other chemotherapy drugs have not yielded positive results. Side effects of vinorelbine can include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and low blood cell counts. Patients may require additional medications, such as antiemetics, to manage these side effects. 6. CytarabineCytarabine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used in the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the replication of cancer cells and preventing them from spreading. Cytarabine is often used as a second-line treatment option when other chemotherapy drugs have not yielded positive results. Some common side effects of cytarabine include low blood cell counts, nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. Patients may require additional medications to manage these side effects, and regular blood tests may be necessary to monitor for complications. ConclusionChemotherapy can be an effective treatment option for mesothelioma, particularly when the cancer is localized to one area of the body. However, like all cancer treatments, chemotherapy drugs can have side effects that must be managed in order to maximize treatment benefit. Patients and their doctors must weigh the potential benefits against the risks when deciding on a treatment plan, and regular monitoring is necessary to ensure that complications are detected and treated promptly.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Advanced MesotheliomaMesothelioma is a rare type of cancer that affects the lining of lungs, abdomen, and other organs. The primary cause of mesothelioma is exposure to asbestos, a fibrous mineral that was widely used in construction and manufacturing before its ban in the 1970s. Due to the long latency period of mesothelioma, in many cases, the diagnosis of the disease is made when it is already advanced or has spread from the original site to distant locations. In such scenarios, chemotherapy is one of the standard treatments for mesothelioma. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells and can be used as a standalone treatment or in combination with other therapies, such as surgery and radiation. Chemotherapy drugs for mesotheliomaThe first-line chemotherapy drugs used for mesothelioma are pemetrexed and cisplatin. Pemetrexed is an antimetabolite that blocks the production of folic acid, which is necessary for the growth and division of cells. Cisplatin is a platinum-based compound that binds to DNA to prevent cancer cells from multiplying. These drugs are administered intravenously and cycle through the body over several weeks. The dosage and frequency of chemotherapy depend on various factors such as the stage of cancer, overall health of the patient, and the patient’s response to the treatment. Several clinical studies have evaluated the efficacy of various chemotherapy regimens for mesothelioma. In a meta-analysis of 14 randomized clinical trials, the combination of pemetrexed and cisplatin demonstrated a superior median overall survival and progression-free survival compared to single-agent chemotherapy or best supportive care. Other chemotherapy agents that have shown some activity against mesothelioma include carboplatin, gemcitabine, vinorelbine, and doxorubicin. However, their effectiveness as standalone treatments or in combination with other drugs is still debatable. Clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate new drugs and drug combinations for mesothelioma. Side effects of chemotherapyChemotherapy drugs not only target cancer cells but also affect normal cells that are rapidly dividing, such as those in the bone marrow, hair follicles, and digestive tract. Therefore, chemotherapy can cause several side effects. These include:
ConclusionChemotherapy is an essential component of mesothelioma treatment for advanced cases. The combination of pemetrexed and cisplatin is the standard first-line chemotherapy regimen. However, chemotherapy can cause various side effects, which can affect the quality of life of patients. Therefore, it is essential to manage these side effects adequately. The future of mesothelioma chemotherapy lies in the development of new drugs and drug combinations that can improve survival and reduce toxicity. Some mesothelioma patients may choose to file a lawsuit to seek compensation for asbestos exposure. A mesothelioma asbestos law firm can provide legal assistance and guide patients through the legal process. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Peritoneal MesotheliomaPeritoneal mesothelioma is a rare form of cancer that affects the lining of the abdomen. It is often caused by exposure to asbestos fibers and can take decades to develop after exposure. Chemotherapy is a common treatment option for peritoneal mesothelioma, either alone or in combination with surgery and radiation therapy. In this article, we will discuss the various chemotherapy drugs used to treat peritoneal mesothelioma. Chemotherapy Drugs for Peritoneal MesotheliomaChemotherapy for peritoneal mesothelioma involves the use of drugs that kill cancer cells or stop them from growing and dividing. There are several different drugs that are commonly used, either alone or in combination. They include:
These drugs are typically given through a vein in the arm, either as an infusion or through a portable pump that the patient carries with them. The treatment schedule may vary depending on the drugs used and the stage of the cancer, but typically involves several rounds of treatment over a period of weeks or months. Combination TherapyWhile chemotherapy drugs can be effective on their own, they are often used in combination with surgery or radiation therapy to achieve the best possible outcomes. For example, patients with peritoneal mesothelioma may undergo surgery to remove as much of the cancer as possible, followed by chemotherapy to kill any remaining cancer cells. This is known as neoadjuvant therapy. Alternatively, patients may receive chemotherapy before surgery to shrink the tumor and make it easier to remove. This is known as adjuvant therapy. Radiation therapy may also be used in combination with chemotherapy to further kill cancer cells and prevent their spread. This approach is known as multimodal therapy. Side Effects of ChemotherapyLike all cancer treatments, chemotherapy can cause side effects. Most side effects are temporary and go away after treatment is complete, but some can be more serious. Common side effects of chemotherapy include:
Less common but more serious side effects of chemotherapy can include damage to the kidneys, lungs, or heart. Patients receiving chemotherapy will be closely monitored for such side effects and given medications to manage them. ConclusionChemotherapy is an important treatment option for patients with peritoneal mesothelioma, a rare form of cancer that is often caused by exposure to asbestos fibers. While chemotherapy can cause side effects, they are often manageable and outweighed by the potential benefits. By combining chemotherapy with surgery and/or radiation therapy, doctors can achieve the best possible outcomes for patients with this challenging cancer. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Pleural MesotheliomaPleural mesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs. It is caused by exposure to asbestos fibers, which can occur in certain work environments such as construction sites, shipyards, and factories. Like other forms of cancer, pleural mesothelioma can be treated with chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses special drugs to kill cancer cells or to stop them from growing and dividing. There are several chemotherapy drugs that have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of pleural mesothelioma. These drugs work by targeting the cancer cells and stopping them from dividing and growing. Some of the commonly used drugs for mesothelioma chemotherapy are:
1. CisplatinCisplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat pleural mesothelioma. It works by attaching to the DNA in cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Cisplatin is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs such as pemetrexed. One of the side effects of cisplatin is nephrotoxicity, which means it can damage the kidneys. Patients receiving cisplatin treatment may also experience nausea, vomiting, and hearing loss. 2. CarboplatinCarboplatin is another chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat pleural mesothelioma. It works in a similar way to cisplatin, by attaching to and damaging the DNA in cancer cells. Carboplatin is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs such as gemcitabine. One of the side effects of carboplatin is anemia, which is a decrease in the count of red blood cells in the body. Patients receiving carboplatin treatment may also experience nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. 3. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of pleural mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the DNA in cancer cells, which prevents them from growing and dividing. Gemcitabine is often used in combination with carboplatin or cisplatin. One of the side effects of gemcitabine is low white blood cell count, which can increase the risk of infection. Patients receiving gemcitabine treatment may also experience nausea, vomiting, and hair loss. 4. PemetrexedPemetrexed is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat pleural mesothelioma. It works by blocking the enzymes that cancer cells need to divide and grow. Pemetrexed is often used in combination with cisplatin. One of the side effects of pemetrexed is myelosuppression, which is a decrease in the count of blood cells in the body. Patients receiving pemetrexed treatment may also experience nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. 5. VinorelbineVinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat pleural mesothelioma. It works by preventing cancer cells from dividing and growing. Vinorelbine is often used in combination with cisplatin. One of the side effects of vinorelbine is peripheral neuropathy, which is damage to the nerves in the arms and legs. Patients receiving vinorelbine treatment may also experience nausea, vomiting, and hair loss. ConclusionChemotherapy can be a very effective treatment for pleural mesothelioma. There are several drugs that have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of this cancer, and they each work in slightly different ways. Depending on the stage and severity of the cancer, doctors may use one or more chemotherapy drugs in combination with other treatments such as surgery or radiation therapy. It is important to note that chemotherapy can have many side effects, so patients should work closely with their doctors to manage these symptoms and monitor their overall health during treatment. However, despite the potential for side effects, chemotherapy can help many patients to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life, and in some cases, it can even help to cure the cancer or extend the patient’s life. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs: An OverviewMesothelioma is an aggressive cancer that affects the mesothelial lining of the organs, predominantly the lungs. This cancer is caused by the inhalation of asbestos fibers, which can lead to chronic inflammation and eventually the development of tumors. Although surgery and radiation therapy are also viable treatment options, chemotherapy is the most commonly used treatment for mesothelioma. Chemotherapy drugs work to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors, which can help improve symptoms and increase survival rates. There are several different chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma, many of which have varying levels of effectiveness and potential side effects. Chemotherapy for Pleural MesotheliomaPleural mesothelioma affects the lung lining and is the most common type of mesothelioma. The following chemotherapy drugs are commonly used to treat pleural mesothelioma:
These chemotherapy drugs are often used in combination to increase effectiveness and reduce side effects. For example, cisplatin and pemetrexed are often given together as a first-line treatment for pleural mesothelioma, as studies have shown this combination to be more effective than cisplatin alone. Chemotherapy for Peritoneal MesotheliomaPeritoneal mesothelioma affects the lining of the abdomen and is less common than pleural mesothelioma. The following chemotherapy drugs are commonly used to treat peritoneal mesothelioma:
Again, these chemotherapy drugs are often used in combination to increase effectiveness and reduce side effects. For example, a common chemotherapy combination for peritoneal mesothelioma is cisplatin and pemetrexed or cisplatin and methotrexate. Chemotherapy for Advanced MesotheliomaChemotherapy is also used as a treatment option for advanced mesothelioma, where the cancer has spread beyond the initial site of origin. The following chemotherapy drugs are commonly used as second-line treatments for advanced mesothelioma:
It’s important to note that these chemotherapy drugs are generally less effective in advanced mesothelioma and may have more severe side effects. Additionally, standard chemotherapy drugs may not be effective in certain cases, and clinical trials may be necessary to find a more effective treatment. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Pediatric MesotheliomaAlthough mesothelioma is most commonly diagnosed in older adults who have had prolonged exposure to asbestos, there have been cases of children and young adults being diagnosed with mesothelioma. In cases of pediatric mesothelioma, chemotherapy is often used as a treatment option. However, because mesothelioma in children is so rare, there is limited data on the most effective chemotherapy drugs and dosages. Additionally, the side effects of chemotherapy in children can be different than in adults, and special care must be taken when administering these drugs to young patients. One study published in the Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology examined the effectiveness of chemotherapy in 10 pediatric patients with mesothelioma. The study found that a combination chemotherapy regimen of cisplatin and doxorubicin was the most effective treatment for this type of cancer in children. Additionally, the study found that children experienced less severe side effects from the chemotherapy drugs compared to adults. However, because pediatric mesothelioma is so rare, there is a lack of standard treatment protocols, and chemotherapy may need to be tailored to each individual patient. It’s important for children with mesothelioma to receive treatment at a specialized facility with experience treating this rare cancer. ConclusionChemotherapy is a common treatment for mesothelioma, as it can help kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. The most effective chemotherapy drugs vary depending on the type of mesothelioma being treated, and these drugs are often used in combination to increase effectiveness and reduce side effects. Additionally, while chemotherapy is also used as a treatment option for pediatric mesothelioma, there is limited data on the most effective chemotherapy drugs and dosages for children. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it’s important to speak with your doctor about the best treatment options for your specific case. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Refractory MesotheliomaMesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer that develops in the lining of the lungs, abdomen or heart. It is caused by exposure to asbestos fibers, which are commonly used in construction, shipyards, and other industrial settings. Mesothelioma has a poor prognosis, and the tumors can become resistant to standard treatments like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. However, several new mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are being developed that show promise for treating refractory mesothelioma. What is refractory mesothelioma?Refractory mesothelioma is cancer that continues to grow or spreads despite treatment. This can happen with any type of cancer, but it is particularly common with mesothelioma, which is often diagnosed at an advanced stage. When mesothelioma tumors become refractory, standard treatments like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy may no longer be effective. How does chemotherapy work?Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs work by targeting cells that divide rapidly, which includes cancer cells. Unlike radiation or surgery, chemotherapy can target cancer cells throughout the body, including those that have spread to other organs or tissues. Chemotherapy can be given orally, as a pill or liquid, or intravenously, through a vein. What are the current mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs?The current mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs include cisplatin and pemetrexed, which are the first-line treatment for mesothelioma. These drugs can shrink and slow the growth of mesothelioma tumors, but they also have side effects such as nausea, loss of appetite, and fatigue. Cisplatin and pemetrexed are often given together in a regimen called “cisplatin plus pemetrexed.” Other mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs that are currently being tested in clinical trials include:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are a new type of cancer treatment that work by boosting the body’s own immune system to fight cancer cells. Multi-kinase inhibitors and FAK inhibitors are drugs that target the pathways that cancer cells use to grow and spread. These drugs are still in clinical trials and are not yet available to the general public. What are the side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs?The side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs depend on the specific drug or combination of drugs being used. Some common side effects include:
Patients should discuss potential side effects with their doctor before starting chemotherapy and report any symptoms that occur during treatment. Many side effects can be managed with supportive care, such as anti-nausea medication or blood cell growth factors. What is the future of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs?Researchers are continuing to develop new mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs with different mechanisms of action and fewer side effects. Some of these drugs are being tested in clinical trials, while others are still in preclinical development. Some promising new drugs and drug combinations for mesothelioma include:
These potential mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and drug combinations are still in the early stages of development, but they offer hope for patients with refractory mesothelioma. Patients can also consider participating in clinical trials to access new treatments and help advance mesothelioma research. ConclusionRefractory mesothelioma is a challenging condition that affects many patients with this rare and aggressive cancer. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs such as cisplatin and pemetrexed have shown some effectiveness, but they also have significant side effects. Researchers are developing new mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs that show promise for treating refractory mesothelioma, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, multi-kinase inhibitors, and FAK inhibitors. Patients with mesothelioma can work with their doctors to explore their treatment options and participate in clinical trials to access new therapies and help advance research. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Multi-Modality TherapyWhen it comes to mesothelioma treatment, chemotherapy is often used to complement surgery and radiation therapy, as part of multi-modality therapy. Chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma aim to target and kill cancer cells, and prevent them from spreading further. Here are some important things to know about mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment. How Chemotherapy Works for MesotheliomaChemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses chemotherapy drugs to kill cancer cells. These drugs work by killing fast-growing cells, including cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be given orally or intravenously (injected into a vein). Mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment can be given before or after surgery, or as a standalone treatment. The goal of mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment is to: – Stop cancer cells from dividing and growing Common Chemotherapy Drugs Used for MesotheliomaThere are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used to treat mesothelioma: – Cisplatin These drugs can be used alone or in combination to maximize their effects. The choice of chemotherapy drugs depends on several factors, such as the stage of mesothelioma, the location of the tumor, and the overall health of the patient. Side Effects of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy TreatmentLike most cancer treatments, chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma can cause side effects. The side effects can vary depending on the specific drugs used and the individual patient’s health. Common side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment include: – Nausea and vomiting Fortunately, most side effects of chemotherapy are manageable with medications and lifestyle modifications. Patients should work closely with their healthcare team to mitigate the side effects and ensure a better quality of life during treatment. Effectiveness of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy TreatmentThe effectiveness of mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment can vary depending on many factors, including the stage of mesothelioma, the location of the tumor, and the overall health of the patient. However, recent studies have shown promising results with mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment combined with surgery and radiation therapy. A study published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology found that patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma who received a combination of chemotherapy and surgery had a median survival of 48 months, compared to 29 months for those who received chemotherapy alone. Another study published in the Annals of Oncology found that patients with advanced mesothelioma who received a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy had a median survival of 18.4 months, compared to 14.2 months for those who received chemotherapy alone. Cost of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy TreatmentThe cost of mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment can vary depending on the drugs used, the length of treatment, and the individual patient’s health insurance coverage. According to the American Cancer Society, the average cost of one course of mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment can range from $10,000 to $30,000. Patients should check with their health insurance provider to determine the extent of their coverage for mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment. They may also want to explore financial assistance options that may be available to them, such as grants from mesothelioma support organizations or medication assistance programs. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy treatment is an important part of multi-modality therapy for mesothelioma. The chemotherapy drugs used aim to kill cancer cells, shrink tumors, and improve the patient’s quality of life. While chemotherapy can cause side effects, most of them are manageable with medical support and lifestyle modifications. Recent studies have shown promising results with mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment, especially when combined with surgery and radiation therapy. Patients should work closely with their healthcare team to determine the best mesothelioma treatment plan that works for their individual needs and circumstances.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Pericardial MesotheliomaMesothelioma is a rare and deadly form of cancer that affects the lining of internal organs such as the lungs, heart, and abdomen. Pericardial mesothelioma is a rare type of mesothelioma cancer that affects the lining of the heart. As with other types of mesothelioma, pericardial mesothelioma is caused by exposure to asbestos, a naturally occurring mineral that was commonly used in construction materials before its toxicity was discovered. The prognosis for pericardial mesothelioma is poor, with an average survival rate of six months to two years after diagnosis. However, there are treatments available that may prolong survival, relieve symptoms, and improve quality of life for patients. Chemotherapy is one of the most common treatments used for pericardial mesothelioma, either as a standalone treatment or in combination with other therapies such as surgery or radiation. Chemotherapy Drugs for Pericardial MesotheliomaChemotherapy drugs work by killing cancer cells or preventing them from dividing and spreading throughout the body. There are several different chemotherapy drugs that may be used to treat pericardial mesothelioma, including:
Alimta is the most commonly used chemotherapy drug for mesothelioma and has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma, which affects the lining of the lungs. However, Alimta has also shown promise in treating pericardial mesothelioma. Platinol and Paraplatin are platinum-based chemotherapy drugs that are often used in combination with Alimta for mesothelioma treatment. Onconase is a newer chemotherapy drug that is being studied for its effectiveness in treating mesothelioma, including pericardial mesothelioma. Chemotherapy as a Treatment for Pericardial MesotheliomaChemotherapy is typically administered through an intravenous (IV) infusion and is given at regular intervals over a period of several weeks. The frequency and dosage of the chemotherapy drugs will depend on the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and other factors. Chemotherapy can help to reduce the size of tumors and slow the progression of the cancer, which may alleviate symptoms such as chest pain, difficulty breathing, and fatigue. However, chemotherapy can also cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and an increased risk of infection. Combination TherapyCombination therapy, which involves the use of multiple treatments, may be more effective than chemotherapy alone for treating pericardial mesothelioma. For example, chemotherapy may be used in combination with surgery to remove the cancerous tissue or radiation therapy to destroy remaining cancer cells after surgery. Other treatments that may be used in combination with chemotherapy for pericardial mesothelioma include immunotherapy, which uses the body’s own immune system to fight cancer cells, and targeted therapy, which uses drugs that specifically target cancer cells without harming healthy cells. Clinical TrialsClinical trials offer hope for patients with pericardial mesothelioma who have exhausted standard treatment options. Clinical trials are research studies that test new treatments or combinations of treatments for different types of cancer. Patients may be eligible to participate in clinical trials if they have advanced or recurrent pericardial mesothelioma that has not responded to standard treatments. Participation in a clinical trial may provide access to promising new treatments and innovative therapies that are not yet available outside of a research setting. However, participation in a clinical trial also involves some risks, and patients should talk to their doctors and carefully consider the potential benefits and drawbacks of participating in a trial. ConclusionPericardial mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer that is difficult to treat. Chemotherapy is one of the most commonly used treatments for pericardial mesothelioma, either alone or in combination with other therapies. The choice of chemotherapy drugs and treatment regimen will depend on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and the presence of other medical conditions. Combination therapy and participation in clinical trials may provide additional treatment options for patients with pericardial mesothelioma. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Laryngeal MesotheliomaLaryngeal mesothelioma is a rare type of mesothelioma that affects the larynx, which is also known as the voice box. It usually has a poor prognosis, and treatment options are limited. Mesothelioma chemotherapy is one of the most common treatments used for laryngeal mesothelioma. Chemotherapy Drugs Used for Laryngeal MesotheliomaThe chemotherapy drugs used for laryngeal mesothelioma are similar to those used for other types of mesothelioma. The main goal of chemotherapy is to kill the cancer cells and prevent them from spreading. While chemotherapy is not a cure for mesothelioma, it can help to shrink tumors and relieve symptoms. The following are some of the most common chemotherapy drugs used for laryngeal mesothelioma:
How Chemotherapy is AdministeredChemotherapy can be administered in several ways, depending on the individual case. The most common methods of chemotherapy administration are: Intravenous (IV) ChemotherapyIV chemotherapy involves injecting the drugs directly into a vein in the arm or hand. The drugs are carried by the bloodstream to the cancer cells throughout the body. IV chemotherapy is usually given in cycles, with several weeks of treatment followed by a rest period to allow the body to recover. Intra-arterial ChemotherapyIn certain cases, intra-arterial chemotherapy may be used to treat laryngeal mesothelioma. This involves injecting the drugs directly into the artery that supplies blood to the affected area. Intra-arterial chemotherapy can be effective in targeting cancer cells with minimal impact on healthy tissue. Intraperitoneal (IP) ChemotherapyIntraperitoneal chemotherapy may be used to treat mesothelioma that has spread to the abdomen. This involves injecting the drugs directly into the abdominal cavity through a special port that is surgically implanted. IP chemotherapy can be effective in slowing the growth of cancer cells in the abdomen. Side Effects of ChemotherapyChemotherapy drugs can cause a range of side effects, some of which can be severe. The specific side effects will depend on the drugs used, the dosage, and the individual’s overall health. Common side effects of chemotherapy include:
Most side effects of chemotherapy are temporary and will go away once treatment is finished. Your healthcare provider can provide medications to manage side effects such as nausea and vomiting. ConclusionChemotherapy is one of the most common treatments for laryngeal mesothelioma and other types of mesothelioma. It can help to shrink tumors, relieve symptoms, and improve quality of life. If you have been diagnosed with laryngeal mesothelioma, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider about all of your treatment options. They can help you make an informed decision about the best course of treatment for your individual case. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Radiation Induced MesotheliomaMesothelioma is a rare type of cancer that affects the mesothelial cells, which are the thin layer of tissue that lines the organs and cavities in the body. Exposure to asbestos is the primary cause of malignant mesothelioma. However, radiation therapy is also a potential risk factor for developing mesothelioma. Thankfully, chemotherapy drugs have proven to be effective in treating both asbestos-related and radiation-induced mesothelioma. There are several chemotherapy drugs used in the treatment of mesothelioma, alone or in combination with each other. In this article, we will take a closer look at some of the most common mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and how they are used to treat radiation-induced mesothelioma. What is Chemotherapy?Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. Chemotherapy works by attacking rapidly dividing cancer cells throughout the body. The drugs used in chemotherapy can be given orally, intravenously, or applied topically, depending on the type and stage of cancer being treated. Chemotherapy can be administered alone as a standalone treatment, or it may be combined with radiation therapy and surgery to treat mesothelioma. Chemotherapy Drugs Used for Mesothelioma TreatmentThere are several chemotherapy drugs available for mesothelioma treatment. In most cases, physicians will prescribe a combination of drugs to maximize their effectiveness. Here are some of the most commonly used chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma:
Chemotherapy for Radiation Induced MesotheliomaRadiation induced mesothelioma is different from other forms of mesothelioma in that it is caused by radiation exposure. The treatment approach for this form of mesothelioma involves the use of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs, along with surgery or radiation therapy. The goal is to reduce the number of cancer cells and slow down the progression of the disease. Chemotherapy has shown to be effective for treating radiation-induced mesothelioma because the chemotherapy drugs damage rapidly dividing cells and disrupt the DNA building blocks needed for cell growth and division. Combination Chemotherapy for Radiation Induced MesotheliomaCombination chemotherapy is a strategy that involves using two or more chemotherapy drugs to treat mesothelioma. The most commonly used combination chemotherapy regimen for radiation induced mesothelioma includes cisplatin and Alimta (pemetrexed). Cisplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy drug that has been shown to be very effective in treating mesothelioma. Alimta is a folate antagonist that works by preventing cancer cells from reproducing. The combination of cisplatin and Alimta has been shown to improve the survival rates of patients compared to using only one of these drugs. Intrapleural ChemotherapyIntrapleural chemotherapy involves the direct injection of chemotherapy drugs into the chest cavity where the cancer is located. This approach is often used for treating mesothelioma because it allows for the delivery of high doses of chemotherapy directly to the cancer cells with fewer side effects. Intrapleural chemotherapy can be used as a standalone treatment for radiation induced mesothelioma, or it can be combined with surgery and/or radiation therapy. The most commonly used chemotherapy drugs in intrapleural chemotherapy are cisplatin and Alimta. ConclusionChemotherapy is an important tool in the fight against mesothelioma. It is an effective way to slow down the progression of the disease and improve the quality of life for many patients. Radiation induced mesothelioma can be effectively treated with mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs. The decision to use chemotherapy as a mesothelioma treatment method will depend on factors such as the patient’s overall health, the extent of the disease, and the stage of cancer. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Benign Multicystic Peritoneal MesotheliomaBenign Multicystic Peritoneal Mesothelioma (BMPM) is a rare type of mesothelioma that is non-cancerous. Although it is not classified as malignant, BMPM can still cause significant discomfort and medical challenges for those who are affected. Chemotherapy is one of the treatments that can be used to manage BMPM, either alone or in combination with surgery or other therapies. Chemotherapy Drugs Used for BMPMThe goal of chemotherapy for BMPM is to shrink the cysts and reduce the symptoms associated with them. The chemotherapy drugs used for BMPM are typically different from those used for malignant mesothelioma because BMPM is not cancerous. The following are some of the chemotherapy drugs that may be used to treat BMPM:
These drugs may be given in various combinations and dosages, depending on the individual patient’s needs and response to treatment. Possible Side Effects of Chemotherapy for BMPMAs with any chemotherapy treatment, there are potential side effects that patients who undergo BMPM chemotherapy may experience. Some of the common side effects of these drugs include:
Patients who are undergoing chemotherapy for BMPM should discuss their treatment options and potential side effects with their healthcare team. They may also be advised to make certain lifestyle changes to help manage their symptoms and improve their overall health. Combination Therapies for BMPMWhile chemotherapy can be effective in managing BMPM, it is often used in combination with other treatments to achieve the best possible outcomes for patients. Depending on the individual case, surgery, radiation therapy, and other treatments may also be used. The specific combination of therapies will vary depending on the patient’s needs and overall health. SurgerySurgery may be performed to remove the cysts associated with BMPM. Depending on the size and location of the cysts, the surgeon may opt to remove them through a traditional open surgical procedure or through minimally invasive means. In some cases, a specialist in peritoneal mesothelioma surgery may be consulted to perform the operation. Radiation TherapyRadiation therapy involves the exposure of the affected area to high-energy radiation to shrink or kill the tumor cells. Radiation therapy is not often used for BMPM, as it is not a cancerous tumor. Other TherapiesOther treatments such as immunotherapy, targeted therapy or palliative care can be used to manage BMPM. Immunotherapy helps the body’s immune system fight against cancer cells, while targeted therapy attacks specific proteins that drive tumor growth. Palliative care involves managing the symptoms and side effects associated with the disease to improve the patients quality of life. ConclusionManaging BMPM can be challenging, but there are treatment options available. Chemotherapy is one of the treatments available, and it is typically used in combination with other therapies to achieve the best possible outcomes. Patients who are diagnosed with BMPM should consult their healthcare team to determine the best treatment options for their individual case. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Well-Differentiated Papillary MesotheliomaWell-differentiated papillary mesothelioma (WDPM) is a rare subtype of mesothelioma that arises from the mesothelial cells that line the serous cavities of the body, such as the pleura, peritoneum, and pericardium. This type of mesothelioma is typically slow-growing and has a better prognosis compared to the more common epithelioid and sarcomatoid types of mesothelioma. However, there is still no cure for mesothelioma, and treatment options for WDPM are limited. Chemotherapy is one of the main treatment modalities for mesothelioma, including WDPM, but its effectiveness in this subtype of mesothelioma is yet to be fully established. What is Chemotherapy?Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells or slow down their growth by targeting their ability to multiply and divide rapidly. Chemotherapy drugs are usually administered intravenously, but they can also be given by mouth, injection, or directly into the affected area. Chemotherapy can be used as a primary treatment or as an adjuvant therapy in combination with other treatment modalities such as surgery and radiation therapy. Chemotherapy Drugs for MesotheliomaThe chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma are usually a combination of two or more drugs to increase their effectiveness and reduce the risk of drug resistance. The most commonly used chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma include:
Effectiveness of Chemotherapy for WDPMThere is limited data on the effectiveness of chemotherapy for WDPM due to its rarity. Most of the available studies have small sample sizes and retrospective designs. Nevertheless, some studies suggest that chemotherapy can be effective in treating WDPM, with response rates ranging from 50% to 80%. The most commonly used chemotherapy regimen for WDPM is a combination of cisplatin and pemetrexed, which has shown promising results in some studies. However, the optimal chemotherapy regimen for WDPM is yet to be established, and further studies are needed to determine its efficacy and safety. Side Effects of Chemotherapy for WDPMChemotherapy can cause a wide range of side effects, which can vary depending on the drugs used, the dosage, and the duration of treatment. Some of the common side effects of chemotherapy for WDPM include:
The side effects of chemotherapy can be managed with supportive care such as anti-nausea medication, growth factors for blood cells, and pain control. The dose and schedule of chemotherapy may also need to be adjusted to minimize the side effects. ConclusionChemotherapy is one of the main treatment options for mesothelioma, including WDPM. Although the effectiveness of chemotherapy for WDPM is yet to be fully established, there is some evidence to suggest that it can be effective in treating this subtype of mesothelioma. The chemotherapy drugs used for mesothelioma can cause a wide range of side effects, which can be managed with supportive care. Further studies are needed to determine the optimal chemotherapy regimen for WDPM and to improve the outcomes of this rare subtype of mesothelioma. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Mesothelioma MetastasisMesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer that develops in the lining of the chest and abdomen. It is caused by exposure to asbestos, which can occur in a variety of settings, including construction, manufacturing, and shipbuilding. Mesothelioma is difficult to treat and typically has a poor prognosis. However, mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can help to slow the progression of the cancer and improve quality of life. In this article, we will explore the various mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and how they are used to treat mesothelioma metastasis. What is Chemotherapy?Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells. The drugs used in chemotherapy are powerful and can travel throughout the body, making them effective in treating mesothelioma that has spread to other parts of the body, also known as metastasis. Chemotherapy can be used in combination with other treatments, such as surgery and radiation therapy, to improve survival and quality of life. Types of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsThere are several different types of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used to treat mesothelioma metastasis. These drugs work in different ways to kill cancer cells and may be used alone or in combination with other drugs.
How Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs are AdministeredMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can be administered in several different ways, depending on the specific drugs being used and the patient’s overall health. Some drugs are given orally, while others are injected into a vein, muscle, or directly into the chest or abdomen. The method of administration will depend on the specific chemotherapy drugs being used and the stage of the cancer. Patients may receive chemotherapy in cycles, with a period of treatment followed by a period of rest to allow the body to recover. Side Effects of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can cause a range of side effects, which can vary depending on the specific drugs being used and the patient’s overall health. Common side effects of chemotherapy include:
Patients who experience side effects of chemotherapy should talk to their healthcare provider about ways to manage these symptoms. In some cases, medications or other interventions can help to relieve side effects and improve quality of life. The Role of Chemotherapy in Treating Mesothelioma MetastasisChemotherapy is an important component of treatment for mesothelioma metastasis. While it cannot cure the cancer, chemotherapy can help to slow the progression of the disease, reduce symptoms, and improve quality of life. In some cases, chemotherapy may be used in combination with other treatments, such as surgery and radiation therapy, to improve survival rates. The specific chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma metastasis will depend on a variety of factors, including the stage and location of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Patients who are receiving chemotherapy for mesothelioma should work closely with their healthcare provider to ensure that they receive the most effective and safe treatment possible. ConclusionMesothelioma is a challenging and aggressive cancer that can be difficult to treat. However, mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can be an effective way to slow the progression of the disease and improve quality of life. By understanding the different types of chemotherapy drugs available, as well as their side effects and how they are administered, patients can work with their healthcare providers to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to their specific needs. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs: Understanding the Treatment for Mesothelioma RecurrenceMesothelioma, a rare and aggressive form of cancer, has been linked to asbestos exposure. Unfortunately, the prognosis for people with mesothelioma is typically poor, with only a handful of treatment options available. Surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy are the three primary treatment options for mesothelioma, and chemotherapy is often used in conjunction with other treatments. Chemotherapy drugs are used to kill rapidly dividing cells – cancer cells divide rapidly, which makes them an attractive target for chemotherapy. There are several chemotherapy drugs that have been shown to be effective in treating mesothelioma, including: 1. PemetrexedPemetrexed is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with cisplatin to treat mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the production of folic acid, which cancer cells require to divide and grow. Pemetrexed is typically given intravenously, and its side effects include nausea, fatigue, and hair loss. 2. CisplatinCisplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with pemetrexed to treat mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA in cancer cells, which can cause them to die. Like pemetrexed, cisplatin is typically given intravenously, and its side effects include nausea, vomiting, and kidney damage. 3. CarboplatinCarboplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is similar to cisplatin but has fewer side effects. It is often used to treat mesothelioma in people who cannot tolerate cisplatin. Like other chemotherapy drugs, carboplatin is typically given intravenously, and its side effects include nausea, fatigue, and hair loss. 4. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that works by inhibiting the production of DNA and RNA, which cancer cells require to divide and grow. It is often used in combination with cisplatin to treat mesothelioma. Gemcitabine is typically given intravenously, and its side effects include nausea, fatigue, and hair loss. 5. VinorelbineVinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that works by inhibiting the division of cancer cells. It is often used in combination with cisplatin to treat mesothelioma. Vinorelbine is typically given intravenously, and its side effects include nausea, fatigue, and hair loss. 6. BevacizumabBevacizumab is a targeted therapy drug that works by inhibiting the growth of blood vessels that support the growth of cancer cells. It is often used in combination with chemotherapy to treat mesothelioma. Bevacizumab is typically given intravenously, and its side effects include high blood pressure, bleeding, and fatigue. 7. ImmunotherapyImmunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that works by stimulating the immune system to attack cancer cells. It is a newer treatment option for mesothelioma, and it is typically used in combination with chemotherapy. There are several types of immunotherapy, including checkpoint inhibitors and CAR T-cell therapy. Chemotherapy Treatment for Mesothelioma RecurrenceUnfortunately, mesothelioma has a high rate of recurrence, which means that the cancer can come back after treatment. Chemotherapy is often used to treat mesothelioma recurrence, and the drugs used are typically the same as those used to treat the initial diagnosis. However, if a person has already received chemotherapy as part of their initial treatment, their options may be more limited. Combination ChemotherapyIn cases of mesothelioma recurrence, combination chemotherapy is often used. This involves using two or more chemotherapy drugs at the same time to increase the chances of killing cancer cells. The combination of drugs used will depend on the person’s individual case and may be different from the drugs used in their initial treatment. Intraperitoneal ChemotherapyIntraperitoneal chemotherapy is a type of chemotherapy that is given directly into the abdominal cavity. It is often used in cases of peritoneal mesothelioma, in which the cancer has spread to the lining of the abdomen. Intraperitoneal chemotherapy can be more effective than systemic chemotherapy, but it can also be more toxic. Targeted TherapyTargeted therapy drugs, such as bevacizumab, are also being studied as a potential treatment for mesothelioma recurrence. These drugs work by targeting specific molecules or pathways that are involved in the growth and division of cancer cells. Targeted therapy drugs may be used in combination with chemotherapy or on their own. Clinical TrialsClinical trials are ongoing to study new chemotherapy drugs and other treatments for mesothelioma recurrence. People who have mesothelioma recurrence may be eligible to participate in clinical trials, which can provide access to cutting-edge treatments that are not yet available to the general public. In conclusion, chemotherapy drugs are an important part of the treatment for mesothelioma recurrence, and there are several drugs that have been shown to be effective. Because mesothelioma has a high rate of recurrence, it is important to explore all treatment options, including combination chemotherapy, intraperitoneal chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and clinical trials. With the help of a qualified oncologist, people with mesothelioma can create a personalized treatment plan that gives them the best chance of beating this devastating disease.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Mesothelioma Metastasis to LiverMesothelioma cancer is a type of cancer that is often caused by prolonged exposure to asbestos. This type of cancer typically affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, and heart. When mesothelioma cancer spreads to other parts of the body, such as the liver, it can become more difficult to treat. What is Chemotherapy?Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells. These drugs are administered either orally or through an IV and are designed to target rapidly dividing cells. Chemotherapy is used as a primary treatment for mesothelioma, as well as a secondary treatment for mesothelioma that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver. What Types of Chemotherapy Drugs are Used for Mesothelioma?There are several types of chemotherapy drugs that are used to treat mesothelioma cancer, including:
These drugs have different mechanisms of action and are used in different combinations depending on the severity and location of the mesothelioma cancer. How Does Chemotherapy Work?Chemotherapy works by targeting rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells. These drugs kill cancer cells by interfering with the DNA and RNA inside them, preventing them from dividing and growing. Chemotherapy drugs can also impact healthy cells that divide rapidly, such as hair follicles and cells lining the digestive tract, which can result in side effects like hair loss, nausea, and vomiting. How is Chemotherapy Administered?Chemotherapy drugs can be administered orally or through an IV. The drugs can be given intravenously on an outpatient basis or through an extended infusion that may require hospitalization. Oral chemotherapy drugs are typically taken at home, either in pill form or liquid. What are the Side Effects of Chemotherapy?Chemotherapy drugs can have a range of side effects, which can vary depending on the specific drugs used and the patient’s overall health. Some of the most common side effects of chemotherapy include:
Fortunately, there are many supportive treatments available that can help alleviate these side effects. Patients should discuss potential side effects with their healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment and supportive care. How Effective is Chemotherapy for Treating Mesothelioma Metastasis to Liver?Chemotherapy can be effective for treating mesothelioma metastasis to the liver, although it can be more difficult to treat mesothelioma cancer that has spread to other parts of the body. Chemotherapy treatment for metastatic mesothelioma is typically focused on managing the symptoms of the cancer rather than curing it. However, many patients have experienced success with chemotherapy treatment, which can help to shrink tumors and improve quality of life. What are the Prognoses for Mesothelioma Metastasis to Liver?The prognosis for individuals with mesothelioma metastasis to the liver can vary depending on the stage of the cancer, the specific location of the metastasis, and the overall health of the patient. However, the prognosis for mesothelioma cancer is generally poor, with a five-year survival rate of less than 10%. ConclusionChemotherapy is a vital treatment option for mesothelioma cancer, both as a primary treatment and as a secondary treatment for mesothelioma that has metastasized to other parts of the body, like the liver. While chemotherapy can have side effects, supportive treatments are available to alleviate them. Overall, patients with mesothelioma metastasis to the liver may still benefit from chemotherapy treatment, and they should work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment for their unique situation. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs: A Comprehensive GuideMesothelioma is a rare but aggressive form of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart. Although the only known cause of this disease is exposure to asbestos fibers, the latency period can last up to 50 years and often results in a late diagnosis. The treatment for mesothelioma depends on the stage of the disease, location of the tumor, and overall health of the patient. One of the most common forms of treatment is chemotherapy, which uses drugs to help kill cancer cells. In this article, we will discuss the different mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs available and their effectiveness in treating mesothelioma metastasis to lymph nodes. What is Mesothelioma Chemotherapy?Mesothelioma chemotherapy is a treatment that uses one or a combination of drugs to slow down the progression of the tumor and kill mesothelioma cells. The drugs can be administered intravenously (IV), orally, or directly into the abdomen or chest cavity, depending on the location of the tumor. The goal of chemotherapy is to help patients live longer, alleviate or manage symptoms, improve their quality of life, and potentially shrink the size of the tumor so that other treatments such as surgery can be more effective. Chemotherapy is often used in conjunction with other treatments such as radiation therapy and immunotherapy to fight mesothelioma. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsThere are several types of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs available. The type of drug or combination of drugs used will depend on the stage of mesothelioma and the patient’s overall health. Some of the most common chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma include:
Some other chemotherapy drugs combinations used in treating mesothelioma include: Cisplatin and raltitrexed, Cisplatin and gemcitabine, Carboplatin and paclitaxel, and many more. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Mesothelioma Metastasis to Lymph NodesWhen mesothelioma has metastasized to lymph nodes, it is likely that the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, making it more challenging to treat. However, chemotherapy can be an effective treatment to control the disease and prolong a patient’s life. In some cases, chemotherapy is used in combination with radiation therapy or immunotherapy, depending on the stage of the cancer and overall health of the patient. The chemotherapy drugs used for mesothelioma metastasis to lymph nodes depend on the location of the tumor. For example, if the mesothelioma is in the chest lining, the chemotherapy drugs administered can be absorbed directly into the pleura, surrounding the lungs. Some of the common chemotherapy drugs used for mesothelioma metastasis to lymph nodes include cisplatin and pemetrexed. Cisplatin and PemetrexedCisplatin and pemetrexed is one of the most common chemotherapy drug combinations used for mesothelioma treatment. Cisplatin works by disrupting the DNA of cancer cells while pemetrexed inhibits their ability to divide. The two drugs are usually given together as a single infusion every three weeks. A study conducted by the National Cancer Institute showed that the combination of cisplatin and pemetrexed extended the survival rate of mesothelioma patients from 9.3 months to 12.1 months compared to cisplatin alone. Another study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology found that the combination therapy led to a response rate of 41%, meaning that the tumor size decreased or remained stable. The study also demonstrated a median overall survival of 12.1 months with this combination therapy. While this chemotherapy combination is effective, side effects are common and can include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and low blood cell count. Patients should discuss the potential side effects with their doctor and develop strategies to help manage them. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy is a common form of treatment used to slow down the progression of the tumor, kill cancer cells, and improve overall quality of life. The type of chemotherapy drug or combination of drugs given depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s overall health. Chemotherapy can be administered in various ways, including IV, oral, or directly into the abdomen or chest. The cisplatin and pemetrexed chemotherapy combination is the most common treatment for mesothelioma patients, including those with lymph node metastasis, but it is not without side effects. Patients should consult with their healthcare provider to decide on the best treatment plan for them. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Mesothelioma Metastasis to BrainMesothelioma cancer is a rare cancer that develops in the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart, and is caused by prolonged exposure to asbestos. It is a deadly disease with a low survival rate, and despite the available treatment options, the prognosis is often poor. Chemotherapy is one of the most effective treatments for mesothelioma patients, especially in cases where the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. What is Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment?Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses chemotherapy drugs to kill cancer cells. The drugs work by targeting rapidly dividing cells in the body, which includes cancer cells. The chemotherapy drugs are usually administered intravenously, meaning through a vein in the arm or chest, and may also be administered in pill form. Chemotherapy can also be given directly into the chest or abdomen. Chemotherapy drugs are typically given in cycles, with a period of treatment followed by a period of rest to allow the body to recover. The length of each cycle and the total number of cycles can vary depending on the type and stage of the cancer, as well as other factors such as the patient’s overall health. Common Chemotherapy Drugs for MesotheliomaSeveral chemotherapy drugs have been shown to be effective in treating mesothelioma. Some of the most common ones include:
These drugs are usually used in combination with each other to increase their effectiveness, and to reduce the risk of the cancer developing resistance to the drugs. The combination of drugs used will depend on the individual case, as well as the severity and stage of the cancer. Side Effects of Chemotherapy DrugsLike most cancer treatments, chemotherapy drugs have side effects. The side effects can vary depending on the type and amount of drugs used, as well as the patient’s individual health and medical history. Common side effects of chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma include:
It is important for patients to discuss potential side effects with their doctor, and to report any symptoms they experience during treatment, as some side effects may be serious and require medical attention. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Metastasis to BrainMetastasis is the term used to describe the spread of cancer cells from the primary site of the cancer to other parts of the body. If mesothelioma spreads to the brain, it can cause a number of symptoms such as headaches, seizures, and difficulty speaking or moving. Chemotherapy can be an effective treatment for mesothelioma that has metastasized to the brain. A combination of chemotherapy drugs such as cisplatin and pemetrexed, along with radiation therapy, can help shrink the size of the tumor, prevent further growth, and manage symptoms. However, treating mesothelioma that has spread to the brain can be challenging due to the presence of the blood-brain barrier, which can prevent chemotherapy drugs from reaching the brain tissue. In some cases, patients may need to undergo surgery to remove the tumor, followed by chemotherapy and radiation therapy. ConclusionChemotherapy is a common treatment for mesothelioma, and can be effective in managing symptoms and improving quality of life for patients. While chemotherapy drugs have side effects, patients can work with their doctor to manage and minimize these effects. For mesothelioma that has spread to the brain, a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy can help manage symptoms and prevent further growth of the tumor. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Mesothelioma Metastasis to BonesMesothelioma is a rare form of cancer that affects the mesothelium, a thin layer of tissue that covers most internal organs. It is often caused by exposure to asbestos, a mineral used in many industries in the past. Mesothelioma can spread to other parts of the body, including the bones. When this happens, chemotherapy may be used to treat the cancer. Chemotherapy for MesotheliomaChemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells. These drugs are usually given intravenously, meaning they are injected into a vein in the arm or hand. The drugs circulate throughout the body and can reach cancer cells in multiple locations. Chemotherapy is often used in combination with other treatments for mesothelioma, such as surgery and radiation therapy. The goal of chemotherapy is to kill as many cancer cells as possible while minimizing the damage to healthy cells. Types of Chemotherapy Drugs for MesotheliomaThere are several drugs that are commonly used in chemotherapy for mesothelioma. They include:
These drugs may be used alone or in combination with each other, depending on the stage of mesothelioma and other factors. The treatment plan will be decided by a team of doctors who specialize in mesothelioma. Chemotherapy for Metastasis to BonesWhen mesothelioma spreads to the bones, it is called metastasis. Chemotherapy can be an effective treatment for metastatic mesothelioma, but it may be used in combination with other treatments, such as radiation therapy and surgery. The chemotherapy drugs used to treat metastatic mesothelioma are the same as those used for mesothelioma in other parts of the body. The treatment plan will depend on the extent of the metastasis and other factors. Side Effects of ChemotherapyChemotherapy can cause a variety of side effects, some of which may be uncomfortable or unpleasant. Common side effects of chemotherapy for mesothelioma include:
These side effects can be managed with medication and other treatments. Your doctor can work with you to develop a plan to help you manage any side effects you may experience. ConclusionChemotherapy can be an effective treatment for mesothelioma, including when the cancer has spread to the bones. There are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used for mesothelioma, and the treatment plan will depend on a variety of factors. If you have been diagnosed with mesothelioma, work with your healthcare team to develop a treatment plan that is right for you. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsMesothelioma is a rare form of cancer that can develop as a result of exposure to asbestos. Treatment for the disease usually involves a combination of chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy. In this article, we will focus on the use of chemotherapy drugs in treating mesothelioma with a particular emphasis on treating the disease when it has metastasized to the abdomen. Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma TreatmentChemotherapy is a common treatment for mesothelioma that has been shown to be effective in managing the disease. The goal of chemotherapy is to shrink the size of tumors, slow down the progression of the disease, and alleviate symptoms, such as pain and difficulty breathing. Chemotherapy drugs are systemic treatments that are delivered throughout the body to kill cancer cells. Mesothelioma chemotherapy typically involves the use of a combination of drugs. Some of the most commonly used drugs include: 1. CisplatinCisplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy drug that is frequently used to treat mesothelioma. The drug works by interfering with the DNA inside cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Cisplatin is often administered in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as pemetrexed. 2. PemetrexedPemetrexed is another chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. Similar to cisplatin, pemetrexed works by interfering with DNA replication in cancer cells. The drug is often used in combination with cisplatin and has been shown to extend the life expectancy of mesothelioma patients. 3. CarboplatinCarboplatin is another platinum-based chemotherapy drug that is used to treat a variety of cancers, including mesothelioma. The drug is less toxic than cisplatin, which may make it a better option for some patients. Carboplatin is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, such as gemcitabine. 4. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat pancreatic cancer, but it has also been shown to be effective in treating mesothelioma. The drug works by interfering with the DNA inside cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Gemcitabine is often used in combination with other drugs, such as cisplatin or carboplatin. Treatment for Mesothelioma Metastasis to AbdomenWhen mesothelioma has metastasized, or spread, to the abdomen, treatment can be challenging. The standard treatment for mesothelioma that has spread to the abdomen is cytoreductive surgery and intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Cytoreductive surgery involves removing all visible tumors from the abdomen, while intraperitoneal chemotherapy involves delivering chemotherapy drugs directly into the abdominal cavity. The chemotherapy drugs used in intraperitoneal chemotherapy are different from those used in systemic chemotherapy. The drugs used in intraperitoneal chemotherapy are delivered directly into the abdominal cavity, which allows for higher concentrations of the drugs to be administered while reducing the side effects of the chemotherapy. 1. Heated Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC)HIPEC is a type of intraperitoneal chemotherapy that involves heating the chemotherapy drugs and delivering them directly into the abdominal cavity. The heat helps to increase the effectiveness of the chemotherapy drugs by improving the penetration of the drugs into the tumors. HIPEC is typically done after cytoreductive surgery. During the surgery, all visible tumors are removed from the abdomen. Once the surgery is complete, the heated chemotherapy drugs are delivered directly into the abdominal cavity. The heated chemotherapy drugs are left in the abdomen for up to two hours before they are removed. 2. Systemic ChemotherapySystemic chemotherapy drugs are also used to treat mesothelioma that has metastasized to the abdomen. However, systemic chemotherapy may not be as effective as intraperitoneal chemotherapy for treating mesothelioma in the abdomen. Systemic chemotherapy drugs are delivered throughout the body, including into the abdominal cavity. However, the concentration of the drugs in the abdominal cavity is lower than it is in other parts of the body. This means that higher doses of the chemotherapy drugs are required to achieve the same effect. ConclusionMesothelioma is a rare form of cancer that is difficult to treat. However, chemotherapy drugs have been shown to be effective in managing the disease. When mesothelioma has metastasized to the abdomen, treatment can be challenging. However, the use of intraperitoneal chemotherapy, including heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy, has been shown to be effective in managing the disease. If you have been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it is important to speak with your doctor to discuss all of your treatment options.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Mesothelioma Metastasis to ChestMesothelioma is a rare, aggressive, and deadly cancer caused by asbestos exposure. This type of cancer affects the lungs, abdomen, and heart. The prognosis for mesothelioma is poor, and the survival rates are low. However, chemotherapy is one of the primary treatment methods for mesothelioma. How Chemotherapy Works for Mesothelioma?Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment for mesothelioma that involves the use of drugs to destroy cancer cells. The goal of chemotherapy is to kill cancer cells throughout the body and slow down the spread of cancer. Chemotherapy drugs may be given orally, intravenously or through chest tubes. Chemotherapy drugs work by interfering with the ability of cancer cells to grow and divide. Most chemotherapy drugs target cells that divide quickly, such as cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs also target the blood vessels that supply cancer cells with nutrients and oxygen. Types of Chemotherapy Drugs for MesotheliomaThere are several types of chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma. These drugs are often used in combination to maximize their effectiveness. The most commonly used chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma are:
Alimta is the only drug approved by the FDA for the treatment of mesothelioma. However, Cisplatin and Carboplatin are often combined with Alimta to increase its effectiveness. Side Effects of ChemotherapyChemotherapy drugs can kill healthy cells along with cancer cells, leading to side effects. The side effects of chemotherapy depend on the type of drug, dosage, and patient’s health. Some common side effects of chemotherapy for mesothelioma are:
Most side effects of chemotherapy can be managed with medication or therapy. Patients should speak with their doctor about managing side effects. Treatment for Mesothelioma Metastasis to ChestMesothelioma metastasis to the chest can make treatment more challenging. Chemotherapy can be used to treat people with mesothelioma that has metastasized to the chest. However, the treatment goal may shift from a curative approach to a palliative approach. In addition to chemotherapy, surgery and radiation therapy may be used to treat people with mesothelioma metastasis to the chest. Surgery may involve removing the tumor and nearby tissue, while radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells. Targeted therapy is also a treatment option that works by targeting specific proteins or genes that promote cancer growth. ConclusionChemotherapy is a standard treatment for mesothelioma. The goal of chemotherapy is to slow down the spread of cancer and kill cancer cells throughout the body. Although chemotherapy has side effects, they can be managed with medication or therapy. People with mesothelioma metastasis to the chest may still receive chemotherapy, but the treatment goal may shift to palliative care. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare team that specializes in treating mesothelioma to determine the best treatment approach. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsMesothelioma is a rare but aggressive form of cancer that affects the mesothelial cells lining the lungs, chest, abdomen, and heart. It is primarily caused by exposure to asbestos, a group of naturally occurring silicate minerals that were commonly used in construction, manufacturing, and shipbuilding industries during the 20th century. Despite concrete efforts to regulate the use of asbestos, cases of mesothelioma are still occurring today due to the delayed onset of symptoms and the long latency period between exposure and disease development. Chemotherapy is one of the most common treatments for mesothelioma, either alone or in combination with surgery and radiation therapy. It works by using drugs to kill the cancer cells or slow down their growth, allowing patients to manage their symptoms and extend their lifespan. The choice of chemotherapy drugs depends on the stage and type of mesothelioma, the patient’s overall health status, and their response to previous treatments. Chemotherapy Drugs for MesotheliomaThere are several types of chemotherapy drugs that have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of mesothelioma. They can be classified into three main categories based on their mechanism of action and their side effects. Pemetrexed and CisplatinPemetrexed and cisplatin are the most commonly used combination chemotherapy regimen for mesothelioma. Pemetrexed is an antimetabolite that inhibits the production of nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA and RNA, by disrupting the folate cycle. Cisplatin is a platinum-based compound that binds to the DNA molecule and causes cross-linking, leading to cell death and DNA damage. The combination of pemetrexed and cisplatin has been shown to improve the survival rate and quality of life of mesothelioma patients, especially those with epithelioid subtype and no significant comorbidities. However, it can also cause severe side effects such as anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. Patients may need to take folic acid and vitamin B12 supplements to reduce these side effects. Carboplatin and AlimtaCarboplatin and alimta are another combination chemotherapy regimen that is similar to pemetrexed and cisplatin in terms of their mechanism of action and indications. Carboplatin is a second-generation platinum compound that is less toxic and more tolerable than cisplatin, but may be less effective. Alimta is a brand name for pemetrexed that is often used in combination with carboplatin as a first-line treatment for mesothelioma. Carboplatin and alimta have shown promising results in clinical trials, with a higher response rate and fewer side effects than pemetrexed and cisplatin. However, they are still associated with an increased risk of anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia, as well as other adverse reactions such as skin rash, fever, and infusion reactions. Patients should be monitored closely for any signs of toxicity and given appropriate supportive care. Gemcitabine and CisplatinGemcitabine and cisplatin are a less common but still effective chemotherapy combination for mesothelioma. Gemcitabine is a nucleoside analog that interferes with the replication of DNA and RNA, while cisplatin works by cross-linking DNA and inducing apoptosis. Gemcitabine and cisplatin have been shown to have a similar efficacy profile as pemetrexed and cisplatin, with a median survival rate of approximately 12-15 months and a response rate of around 40%. However, they can also cause significant side effects such as thrombocytopenia, anemia, fever, nausea, and renal toxicity. Patients with impaired renal function should avoid this combination or receive lower doses of gemcitabine. Treatment for Mesothelioma Metastasis to HeartMetastasis is the spread of cancer cells from the primary site to other parts of the body, usually through the bloodstream or the lymphatic system. Mesothelioma metastasis can occur in various organs, including the heart, which can lead to serious complications and reduced survival rates. The treatment for mesothelioma metastasis to the heart depends on the extent and location of the metastasis, as well as the patient’s overall health status. In some cases, surgery and radiation therapy may be used to remove or shrink the metastatic tumors. However, these options are usually limited due to the delicate nature of the heart and the potential risk of damage. Chemotherapy is still the mainstay of treatment for mesothelioma metastasis to the heart, either alone or in combination with other therapies. The chemotherapy drugs used for this purpose are similar to those used for primary mesothelioma, such as pemetrexed and cisplatin or carboplatin and alimta. However, the dosages may need to be adjusted based on the patient’s cardiac function and the potential risk of cardiac toxicity. Cardiac Supportive CarePatients with mesothelioma metastasis to the heart may also require cardiac supportive care to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. This may include medications to control pain, reduce inflammation, or prevent blood clots, as well as lifestyle modifications such as a low-sodium diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques. In addition, patients may benefit from palliative care, which is a specialized form of care that focuses on symptom management and emotional support for patients who are facing serious illness. Palliative care can help patients and their families cope with the physical, emotional, and spiritual challenges of mesothelioma, and improve their overall wellbeing. ConclusionMesothelioma is a challenging and complex disease that requires a multidisciplinary approach to treatment. Chemotherapy is an effective and well-established option for mesothelioma, and several drugs have been approved for this purpose. Patients with mesothelioma metastasis to the heart may require additional cardiac supportive care, but the overall prognosis depends on the stage, subtype, and response to treatment. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it is essential to seek out a qualified healthcare provider who can provide personalized and compassionate care.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment for Mesothelioma Metastasis to PancreasMesothelioma is a rare but aggressive form of cancer caused by inhaling asbestos fibers. The symptoms of mesothelioma may not appear until 20-50 years after exposure to asbestos, making it difficult to diagnose in its early stages. Unfortunately, mesothelioma is often detected in its advanced stages, and the cancer may have already metastasized or spread to other parts of the body. One possible site for mesothelioma to metastasize to is the pancreas. The pancreas is located behind the stomach and is responsible for producing digestive enzymes and hormones such as insulin. When mesothelioma spreads to the pancreas, it can cause a range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, nausea, jaundice, and unintended weight loss. While there is currently no cure for mesothelioma, various treatment options are available to help manage the condition. One of the most common treatments for mesothelioma is chemotherapy, which uses a combination of drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy can help slow down the progression of the disease and relieve symptoms caused by the cancer. Chemotherapy Drugs Used to Treat MesotheliomaThere are several chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma. Some of the most commonly used drugs include:
The drugs used in chemotherapy can be given intravenously, orally or as direct injection into the abdomen depending on the location of the cancer. The chemotherapeutic drugs can be used alone or in combination with other therapies such as radiation therapy or surgery. Side Effects of Chemotherapy for MesotheliomaWhile chemotherapy is effective in killing cancer cells and slowing the progression of the disease, it can also cause side effects. The side effects of chemotherapy vary from person to person and depend on the type of drug used, the dosage and the duration of treatment. Common side effects of chemotherapy for mesothelioma include:
If you are receiving chemotherapy for mesothelioma, you will be monitored closely by your doctor to manage any side effects and adjust the dosage accordingly. ConclusionIn conclusion, chemotherapy is a commonly used treatment for mesothelioma, including for cases where the cancer has metastasized to the pancreas. There are several drugs used in chemotherapy to help kill cancer cells and slow the progression of the disease. While chemotherapy can cause side effects, the benefits of treatment often outweigh the risks. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs for Treatment of Mesothelioma Metastasis to KidneysMesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer that primarily affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, and heart. One of the major challenges of mesothelioma is that it often metastasizes, or spreads, to other organs, including the kidneys. When mesothelioma metastasizes to the kidneys, it can cause kidney failure and other complications. Chemotherapy is a common treatment for mesothelioma, and it involves the use of drugs to destroy cancer cells. There are several chemotherapy drugs that can be used to treat mesothelioma metastasis to the kidneys. In this article, we will discuss the most commonly used mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and their effectiveness in treating metastasis to the kidneys. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs Used to Treat Metastasis to KidneysThe following chemotherapy drugs are commonly used to treat mesothelioma metastasis to the kidneys:
CisplatinCisplatin is one of the most commonly used chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma. It is a platinum-based drug that interferes with DNA replication in cancer cells, causing them to die. Several studies have shown that cisplatin can be effective in treating mesothelioma metastasis to the kidneys. However, cisplatin has several side effects, including nausea, vomiting, kidney damage, hearing loss, and nerve damage. These side effects can be severe and can limit the dose and duration of cisplatin treatment. In some cases, the use of cisplatin may need to be discontinued if the side effects become too severe. CarboplatinCarboplatin is similar to cisplatin but has fewer side effects. It is also a platinum-based drug that interferes with DNA replication in cancer cells, causing them to die. Several studies have shown that carboplatin can be effective in treating mesothelioma metastasis to the kidneys. However, carboplatin can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, kidney damage, and low blood cell count. These side effects are less severe than those caused by cisplatin, but they can still limit the dose and duration of carboplatin treatment. Alimta (Pemetrexed)Alimta is a chemotherapy drug that targets the enzymes that cancer cells need to grow and multiply. It is usually combined with cisplatin or carboplatin for the treatment of mesothelioma. Alimta has been shown to be effective in treating mesothelioma metastasis to the kidneys. However, Alimta can cause side effects such as anemia, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and kidney damage. These side effects can limit the dose and duration of Alimta treatment. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that interferes with DNA replication in cancer cells, causing them to die. It is usually used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs such as cisplatin for the treatment of mesothelioma. Several studies have shown that gemcitabine can be effective in treating mesothelioma metastasis to the kidneys. However, gemcitabine can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, low blood cell count, and fever. These side effects can limit the dose and duration of gemcitabine treatment. VinorelbineVinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that stops cancer cells from dividing and growing. It is usually used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. Vinorelbine has been shown to be effective in treating mesothelioma metastasis to the kidneys. However, vinorelbine can cause side effects such as fever, headache, pain, and low blood cell count. These side effects can limit the dose and duration of vinorelbine treatment. ConclusionChemotherapy is a common treatment for mesothelioma, and it can be effective in treating mesothelioma metastasis to the kidneys. The chemotherapy drugs discussed in this article are the most commonly used drugs for this purpose, and they have shown varying degrees of effectiveness. However, chemotherapy drugs can cause side effects that can limit their use, and the choice of drug and dose must be carefully balanced against the potential benefits and risks. Patients with mesothelioma metastasis to the kidneys should discuss their treatment options with a qualified healthcare provider to determine the best approach for their individual situation. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and PET ScansMesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsMesothelioma is a rare cancer caused by exposure to asbestos. It usually affects the lining of the lungs, chest, and abdomen. The prognosis for mesothelioma is often poor, and treatment options are limited. Chemotherapy is one of the most common treatment options for mesothelioma patients. Chemotherapy drugs are designed to kill cancer cells and prevent them from growing and spreading. The following are some of the most common mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs:
Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can be administered in different ways, such as orally, through a vein, or through an intraperitoneal catheter. The choice of chemotherapy drug and how it is administered will depend on the individual patient, their stage of cancer, and their general health. New Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsResearch is ongoing to develop new and more effective mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs. Some of the promising drugs currently being tested in clinical trials include:
PET ScansPET (positron emission tomography) scans are a type of imaging test that can help diagnose and monitor mesothelioma. The scan uses a small amount of a radioactive substance, called a tracer, to highlight areas of the body with high metabolic activity, which can indicate the presence of cancer cells. PET scans are often used in combination with other imaging tests, such as CT (computed tomography) scans, to get a more complete picture of the patient’s mesothelioma. They can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of chemotherapy and other treatments. PET Scans in Mesothelioma DiagnosisPET scans can help diagnose mesothelioma by highlighting areas of high metabolic activity in the body that may indicate the presence of cancer cells. During the scan, the patient is injected with a tracer that binds to glucose, which cancer cells require for energy. The tracer emits positrons, which can be detected by the PET scanner, creating a 3D image of the body. PET scans are particularly useful for detecting mesothelioma in its early stages, when it may not be visible on other imaging tests. They can also help determine the extent of the cancer and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. PET Scans in Mesothelioma TreatmentPET scans can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of mesothelioma treatment, particularly chemotherapy. The scan can show whether cancer cells are shrinking or growing in response to treatment, allowing doctors to adjust the patient’s treatment plan accordingly. Studies have shown that PET scans can help predict mesothelioma patients’ survival outcomes by providing information about the extent and activity of their cancer. Patients with higher levels of metabolic activity on their PET scans tend to have poorer prognosis and lower survival rates. PET Scans vs CT ScansPET scans are often used in combination with CT scans to provide a more complete picture of the patient’s mesothelioma. CT scans use X-rays to create detailed images of the inside of the body, while PET scans use radioactive tracers to highlight areas of high metabolic activity. While CT scans are better at detecting the physical characteristics of mesothelioma, such as tumor size and location, PET scans can show functional information about the activity of cancer cells in the body. Combining the two imaging tests can help doctors diagnose and monitor mesothelioma more accurately. ConclusionChemotherapy is one of the main treatment options for mesothelioma patients, and there are several drugs available that can help kill cancer cells. PET scans are also an important tool in mesothelioma diagnosis and treatment, as they can show functional information about cancer cell activity in the body. By combining chemotherapy with PET scans and other imaging tests, doctors can provide more personalized and effective care for mesothelioma patients. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and MRI ScansMesothelioma is a rare type of cancer that develops from the thin layer of tissue that covers many of the internal organs, known as the mesothelium. The most common cause of mesothelioma is exposure to asbestos, a naturally occurring mineral that was widely used in construction, shipbuilding, and other industries for its heat-resistant properties. When mesothelioma is diagnosed, doctors often use a combination of treatments, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. In this article, we will discuss mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and how they are used to treat the disease. How do mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs work?Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs work by targeting fast-growing cancer cells in the body. These drugs are usually given intravenously, meaning they are injected directly into a vein through a needle. They travel through the bloodstream and reach cancer cells throughout the body. Chemotherapy drugs can also have side effects because they target all rapidly dividing cells, not just cancer cells. This means that normal cells in the body, such as hair follicles and the lining of the digestive tract, may also be affected. Common side effects of chemotherapy include hair loss, nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. What are the different types of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs?There are several different types of chemotherapy drugs that may be used to treat mesothelioma, either alone or in combination with other drugs. The most common chemotherapy drugs used for mesothelioma include:
Cisplatin and carboplatin are platinum-based chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used to treat mesothelioma. These drugs work by interfering with the DNA in cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. Pemetrexed is another commonly used chemotherapy drug for mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the enzymes that cancer cells need to divide and grow. Pemetrexed is often given in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin. Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that works by interfering with the DNA in cancer cells. It is sometimes used in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin to treat mesothelioma. Mitomycin-C is another chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA in cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. What are MRI scans?MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a diagnostic imaging tool that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images of the inside of the body. MRI scans are often used to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions, including mesothelioma. During an MRI scan, the patient lies on a table that slides into a tube-shaped scanner. The scanner uses a powerful magnet to create a magnetic field around the patient’s body. Radio waves are then sent into the body, which cause the atoms in the body’s cells to emit signals. These signals are picked up by a computer, which uses them to create detailed images of the inside of the body. How are MRI scans used to diagnose and monitor mesothelioma?MRI scans are often used to diagnose mesothelioma and to monitor how the disease is progressing. MRI scans can show the extent of the mesothelioma tumor, as well as any changes in the size or shape of the tumor over time. During an MRI scan for mesothelioma, the patient may be given a contrast agent, which is a special dye that helps to make the images more detailed. The contrast agent is injected into a vein before the scan begins. In addition to mesothelioma, MRI scans may also be used to diagnose and monitor other types of cancer, as well as many other medical conditions. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are an important treatment option for people with mesothelioma. These drugs work by targeting fast-growing cancer cells in the body and can help to slow the progression of the disease. However, chemotherapy drugs can also have side effects, so it’s important for patients to talk to their doctors about the risks and benefits of treatment. In addition, MRI scans can be a valuable tool for diagnosing and monitoring mesothelioma, as well as many other medical conditions. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and CT ScansIntroduction to MesotheliomaMesothelioma is a rare, aggressive cancer that affects the mesothelium – the tissue lining around the lungs, heart, and abdominal cavity. It is caused by exposure to asbestos, a naturally occurring mineral that was once widely used in construction materials. Symptoms of mesothelioma typically do not appear until decades after exposure, making it difficult to diagnose early on. As a result, mesothelioma is often diagnosed at advanced stages, which limits the treatment options available. Chemotherapy as a Treatment for MesotheliomaChemotherapy is one of the most common treatment options for mesothelioma. It involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. Chemotherapy drugs can be given orally or intravenously. There are several chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma, including:
These drugs may be used alone or in combination to best target the mesothelioma cancer cells. Side Effects of ChemotherapyWhile chemotherapy can be effective in treating mesothelioma, it can also cause side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, hair loss, fatigue, and low blood cell counts. Some patients may also experience neuropathy, which is damage to the nerves that can cause tingling, numbness, or muscle weakness. However, it is important to remember that everyone’s experience with chemotherapy is different and side effects can vary in intensity. Monitoring the Effectiveness of Chemotherapy with CT ScansOnce a patient begins chemotherapy, their doctor will monitor the effectiveness of the treatment through regular CT scans. CT scans use X-rays and computer technology to create detailed images of the inside of the body. These images can help detect changes in the size or shape of the tumors, which can help doctors determine if the chemotherapy is working or if a different treatment should be considered. How CT Scans are ConductedBefore the CT scan, patients may need to change into a hospital gown or remove any metal objects from their body. They will then lie down on a table that slides into a large, circular scanner. During the scan, the table will move slowly through the scanner as X-ray beams take pictures of the body. The images are then fed into a computer, which creates detailed 3D images of the body. The entire process typically takes around 30 minutes to an hour. Preparing for a CT ScanPrior to a CT scan, patients may need to avoid food or drink for a few hours. They should also inform their doctor if they are claustrophobic or have any metal implants in their body, as this may affect the scanning process. ConclusionMesothelioma is a challenging cancer to treat, but chemotherapy and regular CT scans can help effectively manage the disease. While chemotherapy can cause side effects, these can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes. CT scans provide doctors with important information about the effectiveness of treatment, allowing for early intervention if needed. Sources:“Chemotherapy for Malignant Mesothelioma.” Cancer.org, American Cancer Society, 20 Feb. 2019, www.cancer.org/cancer/malignant-mesothelioma/treating/chemotherapy.html. “Computed Tomography (CT or CAT) Scan of the Body.” RadiologyInfo.org, Radiological Society of North America, Inc., 14 June 2017, www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=bodyct. “Mesothelioma.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 18 Feb. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/mesothelioma/symptoms-causes/syc-20375022. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and X-RaysMesothelioma is a rare and deadly cancer caused by exposure to asbestos. It affects the lining of the lungs, heart, and abdomen. Many people with mesothelioma undergo chemotherapy as part of their treatment plan. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsThere are several chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma. These drugs can be used alone or in combination with other drugs. The type of chemotherapy drug used may depend on the stage of the mesothelioma and the overall health of the patient. Some of the most common chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma include:
Chemotherapy can cause side effects, and these vary depending on the type and dosage of drugs used. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, hair loss, changes in appetite, and fatigue. Some patients may also experience kidney damage or nerve problems. Chemotherapy is usually given in cycles, with rest periods in between to allow the body to recover. The length of treatment and the number of cycles depend on the type and stage of mesothelioma. Chemotherapy can be given intravenously, orally, or through injections into the chest or abdomen. How Chemotherapy WorksChemotherapy drugs work by targeting rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs circulate throughout the body, and they can reach cancer cells anywhere in the body. The drugs can destroy cancer cells both during and between cycles of treatment, when the cells are growing and dividing. While chemotherapy drugs target rapidly dividing cells, they can also affect healthy cells that divide quickly, such as those in the lining of the digestive tract and hair follicles. This is why chemotherapy often causes side effects. Mesothelioma and X-RaysX-rays are a type of radiation that can help diagnose mesothelioma. X-rays use high-energy electromagnetic waves to create images of the body, which can help identify tumors or other abnormalities. However, X-rays can also cause cancer. Exposure to high levels of radiation can damage DNA and other cellular structures, leading to mutations and, potentially, cancer. This is why X-rays must be used carefully and avoided when possible. People who have been exposed to asbestos, the primary cause of mesothelioma, may be at greater risk of developing the cancer following exposure to X-rays. This is because the radiation can interact with asbestos fibers in the body, leading to additional damage to cells and tissues. ConclusionChemotherapy is a common treatment for mesothelioma, and there are several drugs available that can help shrink tumors and kill cancer cells. While chemotherapy can cause side effects, it is often an effective treatment option. X-rays can be useful in diagnosing mesothelioma, but they must be used carefully to avoid causing additional harm. It is important for anyone who has been exposed to asbestos to speak with their doctor about their risk of developing mesothelioma and the best course of treatment if they are diagnosed with the cancer. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and UltrasoundsMesothelioma is a rare cancer that typically affects the lining of the lungs, chest, or abdomen. It is linked to exposure to asbestos and can manifest years or even decades after the initial exposure. While there is no cure for mesothelioma, chemotherapy is one of the treatments used to help manage the disease. Ultrasounds are also used in the detection and treatment of mesothelioma. In this article, we explore mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and how they are used in combination with ultrasounds. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsChemotherapy refers to the use of drugs to treat cancer. The drugs are designed to either kill cancer cells or stop them from growing and dividing. In mesothelioma, chemotherapy may be used alone or in combination with other treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy. There are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used in the treatment of mesothelioma. These include: 1. Alimta (Pemetrexed)Alimta is a chemotherapy drug that is often used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking an enzyme that cancer cells need in order to grow and divide. Alimta is usually given in combination with cisplatin, another chemotherapy drug. 2. CisplatinCisplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat a variety of cancers, including mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the DNA in cancer cells, causing them to die. Cisplatin is typically given in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, like Alimta. 3. CarboplatinCarboplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works in a similar way to Cisplatin, by damaging the DNA of cancer cells. Carboplatin is usually given in combination with other chemotherapy drugs. 4. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat several types of cancer, including mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the DNA of cancer cells, which causes them to die. Gemcitabine is usually given in combination with other chemotherapy drugs. 5. VinorelbineVinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works by disrupting the process that cancer cells use to divide and grow. Vinorelbine may be given alone or in combination with other chemotherapy drugs. It is important to note that chemotherapy drugs can have side effects, and these can vary depending on the drug used. Some common side effects of chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma include: – Nausea and vomiting Your healthcare provider can work with you to manage any side effects you experience during chemotherapy treatment. UltrasoundsUltrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses sound waves to create pictures of internal organs and structures. In mesothelioma, ultrasounds may be used for both diagnosis and treatment monitoring. DiagnosisUltrasounds are sometimes used to help diagnose mesothelioma. They can be used to look for changes in the lining of the lungs, chest, or abdomen that may be indicative of mesothelioma. This is often done in combination with other imaging tests, like CT scans or MRIs. Treatment MonitoringUltrasounds are also used to monitor the effectiveness of mesothelioma treatments, such as chemotherapy. They can be used to measure the size of tumors and to check for changes in the lining of the lungs, chest, or abdomen. This can help your healthcare provider determine if your treatment plan is working or if adjustments need to be made. Ultrasound-Guided ProceduresFinally, ultrasounds can also be used to help guide procedures aimed at treating mesothelioma. For example, doctors may use ultrasound to guide needle biopsies or to help position radiation therapy equipment. ConclusionMesothelioma is a challenging cancer to treat, but chemotherapy is one of the options available. By understanding the different chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma and the role ultrasounds play in both diagnosis and treatment monitoring, patients and their healthcare providers can work together to develop a treatment plan that is appropriate for their individual needs. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Genetic TestingMesothelioma is a rare form of cancer that develops in the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart. It develops after exposure to asbestos, and its symptoms typically don’t appear until decades after the exposure. Unfortunately, by the time mesothelioma gets diagnosed, it has already progressed to an advanced stage, making it difficult to treat and cure. Traditional cancer treatments like surgery and radiation therapy have their limitations, which led to the development of chemotherapy drugs that can help fight against the cancer cells. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsChemotherapy drugs work by killing fast-growing cancer cells, but they can also harm healthy cells in the process. There are different types of chemotherapy drugs available, each with its unique way of fighting mesothelioma cancer cells. The following are some of the mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs that doctors prescribe in combination with other treatments like surgery or radiation:
Doctors may use one drug or a combination of drugs depending on the patient’s overall health, the stage of the cancer, and other factors. Chemotherapy usually involves at least two drugs and is administered intravenously. It can be a tough treatment, with side effects that can last for weeks or months, stopping patients from resuming their normal activities. Genetic Testing with Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsGenetic testing is a relatively new way of diagnosing the genetic makeup of cancer cells to determine the best treatment option for patients. Mesothelioma patients have a higher chance of responding well to chemotherapy if doctors know what type of mesothelioma they have. Genetic testing of cancer cells helps determine the precise cancerous tumor location and gives insights into the specific cancer cells’ genetic mutations. This allows the oncologist to identify the best mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs that can work for the patient. Moreover, genetic testing helps verify whether a patient is eligible for the latest clinical trials. Clinical trials are research studies conducted to determine if a new drug or treatment is effective, safe, and has manageable side effects. Several cutting-edge mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs undergo clinical trials to ensure their safety and effectiveness in treating mesothelioma. Molecular profiling tests, such as FoundationOne CDx or Guardant 360, help determine whether a patient is eligible for these clinical trials and whether or not they will benefit from them. Not all patients are eligible for genetic testing, and not all insurance plans cover the costs of testing. However, for those who are eligible for testing, genetic testing can provide valuable information that was previously unavailable, leading to better and more effective mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs. In ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs have helped improve patient outcomes, especially when combined with surgical removal of the cancer and radiation therapy. Genetic testing can help identify the best chemotherapy drugs to use and give oncologists insight into a patient’s eligibility for clinical trials. Therefore, it is essential to speak with an oncologist to determine the best treatment options and explore the benefits and risks of chemotherapy treatment. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Liquid BiopsiesMesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsMesothelioma is a type of cancer caused by asbestos exposure. There is currently no known cure for mesothelioma, but chemotherapy drugs can help to slow the growth of the cancer and relieve symptoms for the patient. Here are some common chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma: CisplatinCisplatin is a type of platinum-containing chemotherapy drug that works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, causing them to die. Cisplatin can be administered intravenously (IV) or directly into the pleural space (the area around the lungs). The drug is typically used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs such as pemetrexed and gemcitabine. PemetrexedPemetrexed is a chemotherapy drug that works by blocking the enzymes necessary for cancer cell division and growth. This drug is also given intravenously and is often used in combination with cisplatin. Pemetrexed has been shown to improve survival rates in mesothelioma patients. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that also works by interfering with cancer cell division and growth. This drug is typically used in combination with cisplatin, but it can also be used alone for patients who cannot tolerate cisplatin. Gemcitabine is given intravenously. BevacizumabBevacizumab is a type of targeted therapy drug that works by preventing the growth of blood vessels that feed the cancer cells. This drug is typically used in combination with chemotherapy drugs such as paclitaxel and carboplatin. Bevacizumab is given intravenously. Side Effects of Chemotherapy DrugsWhile chemotherapy drugs can be effective in treating mesothelioma, they can also cause side effects due to their toxicity to both cancer cells and healthy cells. Some common side effects of chemotherapy drugs include:
It is important for patients undergoing chemotherapy to discuss their treatment options and possible side effects with their healthcare provider. Patients should also inform their provider of any pre-existing health conditions or medications they are taking that may interact with the chemotherapy drugs. Liquid BiopsiesIn addition to traditional tissue biopsies, there is a newer method of diagnosing cancer that is becoming increasingly popular: liquid biopsies. Liquid biopsies are a type of blood test that can detect cancer cells or cancer DNA in the blood. This test can be used to diagnose several types of cancer, including mesothelioma. How Liquid Biopsies WorkDuring a liquid biopsy, a small sample of blood is drawn from the patient and sent to a laboratory for analysis. The lab technicians will search for cancer cells or cancer DNA in the blood sample. If these cells or DNA are present, it indicates that the patient may have cancer. Benefits of Liquid BiopsiesLiquid biopsies have several advantages over traditional tissue biopsies:
Limitations of Liquid BiopsiesWhile liquid biopsies are a promising new technology for cancer diagnosis, they are not without limitations:
Future of Liquid BiopsiesDespite their limitations, liquid biopsies have the potential to revolutionize cancer diagnosis and treatment. In the future, liquid biopsies could be used to monitor cancer progression and treatment response, as well as to detect cancer at its earliest stages. As the technology improves, liquid biopsies are likely to become an increasingly important tool in the fight against cancer.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Serological TestingMesothelioma is a rare and aggressive type of cancer that usually affects the lining of the lungs and chest wall, but it can also affect the lining of the abdomen and other internal organs. Mesothelioma is often caused by exposure to asbestos, which typically occurs in workplaces such as construction sites, shipyards, and mines. The symptoms of mesothelioma include shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing, and fatigue, which can make it difficult to carry out daily activities. One of the treatment options for mesothelioma is chemotherapy, which involves the use of drugs to kill or slow the growth of cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs are typically administered through an intravenous (IV) line or in pill form, depending on the type of drug. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can be used alone or in combination with surgery and radiation therapy to treat mesothelioma. There are several types of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs available, each with its own mechanism of action. The most common mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs include: 1. Alimta (Pemetrexed)Alimta is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma as well as other types of cancer such as lung cancer. Alimta works by blocking the enzymes that cancer cells need to divide and grow. This drug is typically administered through an IV line once every three weeks, and it is often combined with cisplatin, another chemotherapy drug. 2. CisplatinCisplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used in combination with other drugs to treat mesothelioma. Cisplatin works by interfering with the DNA of cancer cells, which prevents them from dividing and growing. This drug is typically administered through an IV line once every three weeks. 3. CarboplatinCarboplatin is a chemotherapy drug that is similar to cisplatin but is less toxic. This drug is typically administered through an IV line once every three weeks, and it is often combined with other chemotherapy drugs to treat mesothelioma. 4. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma as well as other types of cancer such as pancreatic cancer. Gemcitabine works by interfering with the DNA of cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and growing. This drug is typically administered through an IV line once a week. 5. VinorelbineVinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma as well as other types of cancer such as breast cancer and lung cancer. Vinorelbine works by interfering with the microtubules in cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and growing. This drug is typically administered through an IV line once a week. 6. Onconase (Ranpirnase)Onconase is a chemotherapy drug that is used to treat mesothelioma as well as other types of cancer such as pancreatic cancer. Onconase is derived from a protein found in frog eggs, and it works by triggering apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in cancer cells. This drug is typically administered through an IV line once a week. While chemotherapy drugs can be effective in slowing or stopping the growth of mesothelioma, they can also have side effects. Common side effects of chemotherapy include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, hair loss, and an increased risk of infection. In some cases, chemotherapy can also damage the liver, kidneys, and other organs. Serological testing is an important tool used to diagnose and monitor mesothelioma. Serology is the study of blood serum, and serological testing involves the analysis of blood samples for the presence of specific antibodies or antigens. There are several types of serological tests that can be used to diagnose and monitor mesothelioma. These tests include: 1. CA-125 TestThe CA-125 test measures the levels of a protein called CA-125 in the blood, which is produced by some mesothelioma cells. The CA-125 test is not specific to mesothelioma and can also be elevated in other types of cancer and non-cancerous conditions. However, an elevated level of CA-125 in the blood can indicate the presence of mesothelioma. 2. Mesomark TestThe Mesomark test measures the levels of a protein called soluble mesothelin-related peptide (SMRP) in the blood, which is produced by mesothelioma cells. The Mesomark test is specific to mesothelioma and can be used to diagnose and monitor the disease. 3. Fibulin-3 TestThe Fibulin-3 test measures the levels of a protein called fibulin-3 in the blood, which is produced by some mesothelioma cells. The Fibulin-3 test is not specific to mesothelioma and can also be elevated in other types of cancer and non-cancerous conditions. However, an elevated level of Fibulin-3 in the blood can indicate the presence of mesothelioma. 4. Mesothelioma Cell DetectionMesothelioma cell detection involves the analysis of fluids or tissue samples to identify mesothelioma cells. This test is typically performed using a microscope or other imaging technology. Mesothelioma cell detection is the most specific and accurate method of diagnosing mesothelioma. In conclusion, mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and serological testing are important tools in the diagnosis and treatment of this aggressive cancer. While chemotherapy drugs can be effective in slowing or stopping the growth of mesothelioma, they can also have side effects. Serological testing can help diagnose and monitor mesothelioma, and different types of serological tests are available depending on the specific needs of the patient. It is important for mesothelioma patients to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a treatment plan that is personalized and effective for their individual needs.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Tissue BiopsiesMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are a medical option to treat mesothelioma cancer. These drugs help to kill the cancerous cells in the body, retard their growth, and relieve the symptoms of the disease. Since mesothelioma cancer is known for its aggressive nature and tough-to-cure nature, chemotherapy drugs that are specifically designed to treat the disease are increasingly in demand. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsThere are three types of chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma cancer: Alimta (pemetrexed), cisplatin, and carboplatin. The combination of Alimta and cisplatin is the most common chemotherapy treatment for mesothelioma cancer. The combination of cisplatin and carboplatin is also a chemotherapy treatment option for mesothelioma cancer.
Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are mostly given to patients through an IV, which typically takes around 15 to 30 minutes. Cisplatin is also available as a pill and is usually given in a higher dosage than when given through an IV. Chemotherapy treatment usually consists of several sessions, either every three weeks or sometimes weekly. The number of sessions required depends on the stage of cancer and the individual patient’s response to the treatment. Side Effects of Chemotherapy DrugsThe side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs vary depending on the drug, dosage, treatment length, and the patient’s health condition. While chemotherapy drugs can often slow down the growth of cancer, they can also damage the healthy cells of the body. This makes patients more vulnerable to infections and other illnesses. The most common side-effects of chemotherapy drugs are:
Doctors can prescribe medicines to control the side-effects of chemotherapy, and some of the side-effects disappear when the treatment ends. Regular communication with the healthcare provider can ensure that the chemotherapy treatment is going smoothly and help minimize complications. Tissue Biopsies and Mesothelioma DiagnosisTissue biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small part of the body tissue, like the lung or mesothelial tissue, is removed for examination under a microscope. It is the most effective method for diagnosing mesothelioma cancer. In a tissue biopsy, a surgeon may take a small piece of tissue through a needle or make a small incision and remove a larger piece. There are four types of tissue biopsies available to diagnose mesothelioma:
The type of biopsy required depends on the location of the suspected malignant tumor in the body. For example, needle biopsy and mediastinoscopy are used for tumors in the chest area like the organs or the lymph nodes. Tumors in the abdominal cavity, usually diagnosed using peritoneoscopy. The following is a brief outline of the types of tissue biopsies:
Benefits and Risks of a Tissue BiopsyTissue biopsy is an essential diagnostic procedure for mesothelioma cancer. It helps physicians determine the cancer stage and type, which helps to understand the appropriate treatment options. A biopsy is a relatively simple and minimally invasive procedure. However, there are certain risks associated with it:
While there are some risks associated with tissue biopsy, these are outweighed by the benefits of an accurate diagnosis. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient can begin mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs treatment, which is a vital step towards recovery ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and tissue biopsies are two essential tools for diagnosing and treating mesothelioma cancer. While chemotherapy drugs can help slow the growth of cancer and relieve the symptoms caused by the disease, tissue biopsy helps to diagnose and determine the stage of the cancer, which is vital information for developing the appropriate treatment plan. If you suspect you may have mesothelioma, seek medical attention right away. Early diagnosis and treatment offer the best opportunity for successful treatment and recovery. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Other Diagnostic TestsMesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsMesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the tissue lining the lungs, heart, and abdomen. It is often caused by long-term exposure to asbestos, a material that was commonly used in construction and manufacturing industries. Chemotherapy is one of the main treatments for mesothelioma, and there are several drugs that can be used to reduce the spread of cancer cells. Cisplatin and Pemetrexed: Cisplatin and Pemetrexed are two types of chemotherapy drugs that are often used together to treat mesothelioma. Cisplatin is a platinum-based drug that targets cancer cells by interfering with their DNA replication process. Pemetrexed, on the other hand, is an antifolate that blocks the synthesis of nucleic acids, thereby inhibiting the growth of cancer cells. Both drugs are administered intravenously.
Carboplatin: Chemotherapy drug that is often used as an alternative to cisplatin. It works by preventing the growth of cancer cells by inhibiting DNA replication. Carboplatin is administered intravenously and is known to have fewer side effects compared to cisplatin. Gemcitabine: Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is used to fight cancer cells by altering their DNA structure. Administered through intravenous infusion, the drug is given in combination with cisplatin to improve the overall effectiveness of the treatment. Common side effects of gemcitabine include fatigue, fever, and skin rash.
Other Diagnostic TestsIn addition to chemotherapy drugs, there are other diagnostic tests that can help detect and manage mesothelioma. X-Ray: An x-ray is a type of imaging test that uses electromagnetic radiation to create images of the inside of the body. It can be used to detect abnormalities in the lungs and chest cavity that may suggest mesothelioma. However, an x-ray alone cannot confirm the presence of the disease, and further testing is usually required. CT Scan: A computed tomography (CT) scan is a more detailed imaging test that can create cross-sectional images of the body. It can help detect the stage and extent of mesothelioma and may be used to guide biopsy procedures. CT scans use a combination of X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed images of the body. MRI Scan: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a type of imaging test that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s internal organs and tissues. They can be used to detect the spread of cancer cells and can help determine the effectiveness of chemotherapy treatment. PET Scan: Positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a type of imaging test that creates detailed images of the body’s internal organs, including the lungs and heart. PET scans use a radioactive substance called a tracer to create images of the internal organs, which can help identify the location and spread of cancer cells. ConclusionOverall, mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and other diagnostic tests are crucial in the treatment of mesothelioma. As with any cancer, early detection and prompt treatment can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment. Those who may have been exposed to asbestos should monitor their health closely and speak with their doctor if they experience any symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or fluid buildup in the lungs. With proper treatment, patients with mesothelioma can live longer and enjoy a better quality of life. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Clinical Trials for New Diagnostic TestsIntroductionMesothelioma is a rare form of cancer that affects the mesothelial cells, which are the thin layers of tissue that cover most of our internal organs. Exposure to asbestos, a naturally occurring silicate mineral, is the main cause of mesothelioma. Unfortunately, the symptoms of mesothelioma do not usually appear until the cancer has reached an advanced stage, making it difficult to treat. Chemotherapy is one of the primary treatments available for mesothelioma. In recent years, a number of new chemotherapy drugs have been developed that show promise in treating mesothelioma. Clinical trials are ongoing to develop new diagnostic tests that can detect mesothelioma in its early stages. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs1. PemetrexedPemetrexed is a chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. It works by blocking the enzymes that cancer cells need to divide and grow. It is generally administered intravenously, often in combination with cisplatin. Pemetrexed has been found to extend the survival of patients with mesothelioma and is often considered the first-line chemotherapy treatment. 2. CisplatinCisplatin is another chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and growing. It is also administered intravenously, often in combination with pemetrexed. Cisplatin can cause some side effects, including nausea, vomiting, and kidney damage, but these are usually manageable. 3. CarboplatinCarboplatin is another chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma. It works in a similar way to cisplatin, by damaging the DNA of cancer cells. However, it is less toxic than cisplatin and is therefore sometimes preferred for patients who are unable to tolerate cisplatin. It is also administered intravenously. 4. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a newer chemotherapy drug that is currently being studied for its effectiveness in treating mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and preventing them from dividing. Gemcitabine is administered intravenously, usually in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin. Clinical Trials for New Diagnostic Tests1. Blood TestsResearchers are currently developing blood tests that can detect mesothelioma in its early stages. These tests look for biomarkers that are specific to mesothelioma and are not present in healthy individuals. By detecting these biomarkers, doctors may be able to diagnose mesothelioma earlier, when it is more treatable. 2. Breath TestsBreath tests are being developed that can detect volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the breath that are associated with mesothelioma. These tests are non-invasive and may be able to detect mesothelioma in its early stages. 3. Imaging TestsCurrently, CT scans and X-rays are the primary imaging tests used to detect mesothelioma. However, researchers are developing new imaging tests, such as PET scans and MRI scans, that may be more sensitive and accurate in detecting mesothelioma. 4. BiopsiesBiopsies are currently the most reliable way to diagnose mesothelioma, but they are invasive and carry some risks. Researchers are developing new biopsy techniques, such as endoscopic biopsies and CT-guided biopsies, that may be less invasive and more accurate.
ConclusionMesothelioma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer, and chemotherapy is one of the primary treatments available for it. Pemetrexed, cisplatin, carboplatin, and gemcitabine are all chemotherapy drugs that are currently used to treat mesothelioma. In addition, researchers are developing new diagnostic tests, including blood tests, breath tests, imaging tests, and biopsy techniques, that may be able to detect mesothelioma earlier and more accurately. Clinical trials for these new diagnostic tests are ongoing, and there is hope that they will lead to better outcomes for patients with mesothelioma. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment ChallengesMesothelioma is a rare form of cancer that affects the lining of major internal organs, particularly the lungs, heart, and abdomen. It is caused by exposure to asbestos, and the primary cause of death among mesothelioma patients is the lack of effective treatment options. Chemotherapy is one of the most commonly used treatments for mesothelioma, but it presents several challenges. 1. Drug ResistanceOne of the biggest challenges of mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment is drug resistance, where the cancer cells may eventually stop responding to the chemotherapy drugs. Mesothelioma is an aggressive cancer that is notoriously difficult to treat because of its fast growth and high mutation rate. Over time, the cancer cells can evolve and become resistant to chemotherapy drugs, which can reduce the effectiveness of treatment. To overcome drug resistance, oncologists often use a combination of chemotherapy drugs, including cisplatin and pemetrexed. This approach can help to increase the number of cancer cells that respond to the chemotherapy, increase the length of time the chemotherapy is effective, and prolong survival rates. 2. ToxicityChemotherapy drugs can be toxic to healthy cells in the body, and patients undergoing chemotherapy can experience a range of side effects, including nausea, hair loss, and weakened immune systems. This can make it difficult for patients to tolerate chemotherapy for extended periods of time, and some may need to take breaks to recover between cycles. To mitigate the toxic effects of chemotherapy drugs, oncologists may adjust the dose or frequency of treatment. They may also prescribe additional medication to manage chemotherapy-induced symptoms and side effects. 3. Limited Treatment OptionsWhile chemotherapy is a common treatment option for mesothelioma, it is not always effective in treating the cancer. Some mesothelioma patients may have limited treatment options, particularly if they have advanced-stage cancer or are not eligible for surgical intervention. Recent advances in mesothelioma research have identified new potential targets for chemotherapy drugs, including immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and new combination therapies. Clinical trials are currently underway to explore the efficacy of these treatments in mesothelioma patients. 4. Quality of LifeMesothelioma patients often have a reduced quality of life because of the physical and emotional toll of the disease and its treatment. Chemotherapy can be particularly difficult for patients, often requiring frequent hospital visits and extended recovery periods. To improve quality of life, patients may receive supportive care, which includes managing symptoms and pain and providing emotional support. Palliative care services are also available to help alleviate pain and discomfort and improve overall quality of life for mesothelioma patients.
ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy presents several challenges, including drug resistance, toxicity, limited treatment options, and reduced quality of life for patients. However, advancements in mesothelioma research offer hope for new effective treatments and improved quality of life for patients. It is important for patients to consult with medical professionals who are experienced in mesothelioma treatment to determine the most effective individualized treatment plan for their particular situation. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Treatment Success FactorsMesothelioma is a rare but deadly form of cancer caused by exposure to asbestos. It is difficult to diagnose and treat, and the prognosis for patients with mesothelioma is often poor. Chemotherapy is one of the primary treatments for mesothelioma and has been shown to extend the life expectancy of patients. However, the success of mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment depends on several factors, including the type of chemotherapy drugs used, the stage of the cancer, the overall health of the patient, and the responsiveness of the cancer to the treatment. Chemotherapy Drugs Used in Mesothelioma TreatmentThere are several chemotherapy drugs that are used in the treatment of mesothelioma, including:
Other chemotherapy drugs that may be used in mesothelioma treatment include gemcitabine, vinorelbine, and methotrexate. Stage of the CancerThe stage of the cancer at the time of diagnosis is an important factor in determining the success of chemotherapy treatment. In general, patients with earlier-stage mesothelioma have a better chance of responding to chemotherapy and achieving a positive outcome. This is because there is less cancer present in the body, and the cancer cells are less advanced and easier to kill with chemotherapy. Patients with later-stage mesothelioma may still benefit from chemotherapy, but the success rate is generally lower. This is because the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, making it more difficult to treat with chemotherapy drugs. Overall Health of the PatientThe overall health of the patient is also an important factor in determining the success of mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment. Patients who are in good health and have a strong immune system are better able to tolerate chemotherapy drugs and may have a better chance of responding to the treatment. On the other hand, patients who are in poor health or have other medical conditions may not be able to tolerate the side effects of chemotherapy and may not be able to complete the full course of treatment. This can lead to a lower success rate and a poorer outcome for the patient. Responsiveness of the Cancer to ChemotherapyThe responsiveness of the cancer to chemotherapy is another important factor in determining the success of mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment. Some patients may have cancer cells that are more resistant to chemotherapy drugs, making it more difficult to kill them and achieve a positive outcome. Doctors may perform tests to determine the sensitivity of the cancer cells to chemotherapy drugs before starting treatment. This can help them choose the most effective drugs for the patient and improve the chances of success. ConclusionChemotherapy is one of the primary treatments for mesothelioma, and can extend the life expectancy of patients. However, the success of mesothelioma chemotherapy treatment depends on several factors, including the type of chemotherapy drugs used, the stage of the cancer, the overall health of the patient, and the responsiveness of the cancer to the treatment. By considering these factors, doctors can choose the most effective treatment plan for each patient and improve the chances of a positive outcome. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Clinical Trials for Predictive BiomarkersMesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart. It is caused by exposure to asbestos, a mineral that was commonly used in construction and other industries until the 1980s. There is no cure for mesothelioma, but chemotherapy can help to control the disease and improve quality of life. In this article, we will discuss the most common chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma and the latest research on predictive biomarkers. Chemotherapy Drugs for MesotheliomaChemotherapy involves the use of powerful drugs to destroy cancer cells. There are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used to treat mesothelioma, either alone or in combination. The choice of drug(s) will depend on the stage of the disease, general health of the patient, and other factors. Here are some of the most commonly used chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma: 1. CisplatinCisplatin is a platinum-based drug that is often used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs to treat mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the DNA of cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and growing. Common side effects of cisplatin include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and kidney damage. 2. AlimtaAlimta (pemetrexed) is a chemotherapy drug that was specifically approved for the treatment of mesothelioma in 2004. It works by blocking the production of enzymes that cancer cells need to grow and divide. Alimta is often used in combination with cisplatin. Common side effects of Alimta include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and low white blood cell counts. 3. CarboplatinCarboplatin is another platinum-based drug that is sometimes used as an alternative to cisplatin for patients who cannot tolerate or are not responsive to cisplatin. It works in a similar way to cisplatin, by interfering with DNA replication. Common side effects of carboplatin include nausea, vomiting, anemia, and low platelet counts. 4. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with other drugs to treat mesothelioma. It works by disrupting the cell cycle of cancer cells, preventing them from dividing and growing. Gemcitabine is usually given as an infusion through a vein. Common side effects of gemcitabine include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and low white blood cell counts. 5. VinorelbineVinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used to treat mesothelioma, either alone or in combination with other drugs. It works by blocking the spindle fibers that cancer cells need to divide and grow. Vinorelbine is usually given as an infusion through a vein. Common side effects of vinorelbine include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and low white blood cell counts. Clinical Trials for Predictive BiomarkersPredictive biomarkers are biological markers that can be used to predict which patients are likely to respond to a particular treatment. Clinical trials are currently underway to identify predictive biomarkers for mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs. Here are some of the most promising areas of research: 1. BRCA MutationsBRCA genes are involved in DNA repair. Mutations in these genes are associated with an increased risk of breast, ovarian, and other cancers. Recent studies have suggested that patients with mesothelioma who have BRCA mutations may be more likely to respond to platinum-based chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin and carboplatin. 2. MGMT Promoter MethylationMGMT is a gene that is involved in repairing DNA damage caused by chemotherapy drugs. Methylation of the MGMT promoter region has been associated with increased sensitivity to alkylating agents, such as temozolomide. Clinical trials are currently underway to investigate the use of temozolomide in patients with mesothelioma who have methylated MGMT promoters. 3. PD-L1 ExpressionPD-L1 is a protein that is involved in the immune response to cancer cells. Some patients with mesothelioma have been found to have high levels of PD-L1 expression, which may be a predictor of response to immunotherapy drugs. Clinical trials are currently underway to investigate the use of immunotherapy drugs, such as pembrolizumab, in patients with mesothelioma who have high levels of PD-L1 expression. ConclusionChemotherapy drugs are an important part of the treatment of mesothelioma. While they can have significant side effects, they can also help to control the disease and improve quality of life. Research is currently underway to identify predictive biomarkers for mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs, which could help to customize treatment for individual patients. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it is important to speak with a medical professional about all available treatment options.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Personalized MedicineMesothelioma is a rare but aggressive type of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, heart, or abdomen. It is caused by exposure to asbestos, a mineral that was widely used in industries such as construction, shipbuilding, and automotive manufacturing. Although mesothelioma is not curable, treatment options such as chemotherapy can help improve quality of life and prolong survival. In this article, we will discuss mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and the emerging field of personalized medicine. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsChemotherapy is a systemic treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells or slow their growth. It is usually administered intravenously (through a vein) or orally (in pill form) and can be given alone or in combination with other treatments such as surgery and radiation therapy. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are designed to target the DNA and other cellular mechanisms that allow cancer cells to multiply and spread. There are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used to treat mesothelioma: Alimta (Pemetrexed)Alimta is a chemotherapy drug that is specifically approved for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the enzymes that are necessary for the replication and repair of DNA. In clinical trials, Alimta has been shown to improve survival and reduce symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath. It is usually given in combination with cisplatin, another chemotherapy drug. Platinum-Based DrugsPlatinum-based drugs such as cisplatin and carboplatin are commonly used in combination with Alimta or other chemotherapy drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma. They work by binding to the DNA and interfering with its replication. Platinum-based drugs are associated with side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and kidney damage. AntifolatesAntifolate drugs such as methotrexate and raltitrexed are similar to Alimta in that they target the enzymes that are involved in DNA synthesis. They are sometimes used as a second-line treatment for mesothelioma if the cancer does not respond to platinum-based chemotherapy. Antifolates can cause side effects such as mouth sores and low blood counts. Other Chemotherapy DrugsOther chemotherapy drugs that may be used to treat mesothelioma include gemcitabine, vinorelbine, and doxorubicin. These drugs work by different mechanisms of action and may be given alone or in combination with other chemotherapy drugs. It is important to note that chemotherapy drugs can affect both cancerous and healthy cells, which can lead to side effects such as hair loss, fatigue, and infections. However, advances in chemotherapy dosing and scheduling have helped reduce these side effects and improve quality of life for mesothelioma patients. Personalized MedicinePersonalized medicine is an emerging field that aims to tailor medical treatments to an individual’s unique genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. In the context of mesothelioma, personalized medicine can help identify the most effective chemotherapy drugs and dosages for each patient based on their specific tumor characteristics and genetic makeup. Genetic testing, also known as molecular profiling, is a key component of personalized medicine for mesothelioma. This involves analyzing the cancer cells for specific genetic mutations or variations that may make them more or less responsive to certain chemotherapy drugs. For example, a recent study found that mesothelioma patients who had a certain genetic mutation were more likely to respond to Alimta than those without the mutation. Other factors that may be considered in personalized medicine for mesothelioma include the patient’s age, overall health, and medical history. For example, older patients or those with preexisting conditions may be more vulnerable to chemotherapy side effects and may require lower dosages or alternative treatments. Advantages of Personalized MedicineThe main advantage of personalized medicine for mesothelioma is that it can help guide treatment decisions that are tailored to the individual patient. This can improve the effectiveness and reduce the side effects of chemotherapy, as well as help identify alternative treatment options such as targeted therapy or immunotherapy. Another advantage of personalized medicine is that it can help identify patients who may be eligible for clinical trials of new chemotherapy drugs or combinations. By identifying patients with specific genetic mutations or variations, researchers can design clinical trials that target these specific populations and potentially develop more effective treatments for mesothelioma. Limitations of Personalized MedicineThe main limitation of personalized medicine for mesothelioma is that it is still a relatively new and evolving field. There are currently only a few approved genetic tests for mesothelioma, and not all patients may have access to these tests or be able to afford them. Another limitation is that genetic mutations or variations may not be present in all mesothelioma tumors, or may not always predict how the cancer will respond to chemotherapy. Therefore, personalized medicine should be used in conjunction with other treatment approaches and clinical judgment. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs have come a long way in recent years, and personalized medicine is emerging as a promising approach to optimizing treatment for individual patients. By combining the latest chemotherapy drugs with genetic testing and other personalized factors, mesothelioma patients can receive the most effective and least toxic treatment possible, giving them the best chance for a longer and better quality of life. As research in this area continues, personalized medicine is likely to become an increasingly important aspect of mesothelioma treatment.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and PharmacogenomicsMesothelioma is a type of cancer that is often caused by exposure to asbestos. The cancer affects the lining of the lungs, heart, and abdomen, and is often difficult to diagnose and treat. The standard treatment for mesothelioma is a combination of chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy. In this article, we will focus on mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and how pharmacogenomics can help doctors personalize treatment and improve outcomes for patients. Chemotherapy Drugs Used for MesotheliomaThe chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma are designed to kill cancer cells and slow the progression of the disease. Here are some of the most common chemotherapy drugs used in the treatment of mesothelioma:
The chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma can be administered in a variety of ways, including intravenously, orally, or through a catheter inserted into the pleural space. The type of chemotherapy that a patient receives will depend on the stage of their cancer, their overall health, and other factors. Pharmacogenomics and Mesothelioma TreatmentPharmacogenomics is the study of how a person’s genes affect their response to drugs. By analyzing a person’s genetic makeup, doctors can tailor mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs to their individual needs and increase the likelihood of a successful treatment outcome. One of the main challenges in mesothelioma treatment is that not all patients respond to chemotherapy in the same way. By analyzing a patient’s DNA, doctors can identify gene markers that are associated with favorable treatment outcomes, as well as markers that indicate a poor response to certain drugs. For example, some studies have shown that mesothelioma patients with a particular mutation in the BRCA1 gene may be more responsive to chemotherapy regimens that include carboplatin and gemcitabine. Other studies have shown that patients with certain genetic mutations may be more likely to experience side effects from chemotherapy drugs. By using pharmacogenomics to tailor treatment plans to individual patients, doctors can improve the effectiveness of chemotherapy while reducing the risk of side effects. This personalized approach to treatment is known as precision medicine, and has the potential to revolutionize the way that cancer is treated in the future. Side Effects of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsWhile mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can be effective in slowing the progression of the disease, they can also cause a range of side effects. Some of the most common side effects of chemotherapy for mesothelioma include:
While these side effects can be unpleasant, they are usually manageable with the right care and support. Doctors and nurses can provide patients with medications and other interventions to help manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life during treatment. ConclusionMesothelioma is a challenging and often devastating form of cancer. However, with the right treatment approach, many patients are able to achieve improved outcomes and a better quality of life. By using pharmacogenomics to tailor mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs to individual patients, doctors can improve the effectiveness of treatment while minimizing side effects. As precision medicine continues to advance, we can hope to see even greater improvements in the treatment of mesothelioma and other forms of cancer. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and the Immune SystemMesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, and heart. The incidence of mesothelioma is linked to exposure to asbestos, a mineral once widely used in many industrial and construction settings. While there is no cure for mesothelioma, chemotherapy drugs have proven to be an effective treatment approach. In this article, we will explore the role of chemotherapy drugs in mesothelioma treatment, and how they interact with the immune system. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsChemotherapy drugs work by killing cancer cells or slowing their growth. The drugs are usually given intravenously or by mouth and can be administered in different ways, depending on the type and stage of mesothelioma. There are several types of chemotherapy drugs used in mesothelioma treatment, including:
These chemotherapy drugs are used either alone or in combination with other drugs to improve their effectiveness against cancer cells. Combination therapy is often used in mesothelioma treatment, as it allows for a stronger attack against cancer cells while minimizing side effects for the patient. Side Effects of Chemotherapy DrugsWhile chemotherapy drugs are effective in killing cancer cells, they also attack healthy cells in the body, which can lead to side effects. The side effects of chemotherapy drugs can vary depending on the type of drug used, the dosage, and the patient’s health status. Common side effects of chemotherapy drugs include:
Patients receiving chemotherapy are closely monitored by their healthcare team to manage side effects and adjust treatment if necessary. In some cases, patients may receive additional medications or supplements to help manage side effects and improve their overall well-being during treatment. The Immune System and Mesothelioma TreatmentThe immune system plays an important role in the body’s ability to fight against cancer. Mesothelioma, like other types of cancer, can suppress the immune system’s ability to identify and attack cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs can further weaken the immune system as they attack healthy cells, making the patient more susceptible to infections and other illnesses. There are several ways researchers are exploring to strengthen the immune system and improve the effectiveness of mesothelioma treatment: ImmunotherapyImmunotherapy is a type of treatment that uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. This treatment approach works by stimulating the immune system to attack cancer cells, or by using substances that help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. Immunotherapy is still a relatively new approach in mesothelioma treatment, but promising results have been seen in clinical trials using drugs like pembrolizumab and nivolumab. VaccinesResearchers are also exploring the use of vaccines in mesothelioma treatment. Vaccines work by introducing weakened or inactive cancer cells or viruses into the body to stimulate the immune system to attack cancer cells. The vaccine approach has shown promise in treating mesothelioma, with several clinical trials currently underway to study its effectiveness. Nutrition and ExerciseA healthy diet and regular exercise can also help strengthen the immune system and improve overall well-being during mesothelioma treatment. Patients are encouraged to eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Gentle exercise like walking or yoga can help improve energy levels, decrease stress and anxiety, and improve the body’s ability to fight infections. Supportive CareSupportive care is an essential component of mesothelioma treatment, as it can help manage side effects and improve the patient’s quality of life. Supportive care can include pain management, psychological counseling, nutritional counseling, and physical therapy. ConclusionChemotherapy drugs are an important tool in mesothelioma treatment, with several drugs available that can effectively kill cancer cells or slow their growth. While chemotherapy drugs can weaken the immune system and cause side effects, researchers are exploring ways to strengthen the immune system and improve the overall effectiveness of mesothelioma treatment. Patients undergoing mesothelioma treatment are encouraged to work closely with their healthcare team to manage side effects and improve their overall well-being throughout treatment. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and NanotechnologyMesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the mesothelial cells which line the organs in the body. It is commonly associated with exposure to asbestos, a naturally occurring mineral fiber used in building materials and insulation. The cancer has a very low survival rate, making it difficult to treat. One treatment option for mesothelioma is chemotherapy, which involves the use of drugs to destroy cancer cells in the body. Recent advances in nanotechnology have led to the development of new chemotherapy drugs with improved efficacy and reduced side effects. In this article, we will explore mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and nanotechnology in detail. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsThe standard chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma include pemetrexed and cisplatin. Pemetrexed is an antifolate drug that inhibits the production of DNA and RNA in cancer cells, while cisplatin is a platinum compound that prevents cancer cells from dividing and multiplying. These drugs are usually administered intravenously and can cause side effects such as fatigue, nausea, and hair loss. In addition to these standard chemotherapy drugs, there are other drugs that have shown promise in the treatment of mesothelioma. One of these drugs is bevacizumab, which is a monoclonal antibody that targets a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). VEGF is a protein that plays a key role in the growth of blood vessels in tumors. By inhibiting VEGF, bevacizumab can prevent the growth and spread of mesothelioma cancer cells. Another promising drug is gemcitabine, which is a nucleoside analog that inhibits DNA synthesis in cancer cells. Gemcitabine has been shown to improve survival rates in patients with mesothelioma. Table 1: Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs
Nanotechnology and Mesothelioma ChemotherapyNanotechnology involves the manipulation of materials at the nanoscale level, which is smaller than the width of a human hair. This technology has shown promise in the development of new chemotherapy drugs that can effectively target cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells. One approach that has been explored is the use of nanoparticles to deliver chemotherapy drugs directly to cancer cells. Nanoparticles are tiny particles ranging in size from 1-100 nanometers, which allows them to penetrate through cell membranes and accumulate selectively in tumor tissue. This targeted approach allows for higher concentrations of drugs to be delivered to the tumor while reducing toxicity to healthy tissues. Another approach is the use of nanocarriers to encapsulate chemotherapy drugs and protect them from degradation in the body. These nanocarriers can be tailored to release drugs over a prolonged period of time, ensuring that the drugs are delivered in a controlled and sustained manner. This can improve the efficacy of chemotherapy drugs, reduce side effects, and increase patient compliance. Table 2: Examples of Nanoparticles and Nanocarriers Used in Mesothelioma Chemotherapy
ConclusionMesothelioma is a devastating disease with few treatment options. Chemotherapy is one of the main treatment modalities for mesothelioma, but it can cause significant side effects and may not be effective for all patients. The use of nanotechnology has opened up new avenues for the development of effective and targeted chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma. The ability to target cancer cells specifically while minimizing damage to healthy tissues could significantly improve outcomes for mesothelioma patients. As research in this field continues, we can hope for more promising developments in the treatment of mesothelioma and other cancers. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Molecular Targeted TherapyMesothelioma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer, most commonly caused by exposure to asbestos. Treatment options for mesothelioma often involve a combination of surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Chemotherapy drugs are commonly used to combat the spread of cancer, but they can also cause a range of side effects. In recent years, there has been increasing interest in using molecular targeted therapy as a more precise and effective approach to treating mesothelioma. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsChemotherapy drugs work by targeting rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells. There are a variety of chemotherapy drugs that can be used to treat mesothelioma. Some of the most commonly used drugs include:
While chemotherapy drugs can be effective in shrinking tumors and slowing the spread of mesothelioma, they can also cause a range of side effects. Due to the fact that they do not differentiate between healthy cells and cancer cells, chemotherapy drugs often target healthy cells as well, leading to side effects such as hair loss, nausea, and vomiting. Molecular Targeted TherapyMolecular targeted therapy is a more precise approach to cancer treatment that involves identifying and targeting specific molecules that are involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells. This approach aims to minimize the impact on healthy cells, thereby reducing side effects while increasing the effectiveness of treatment. In recent years, there have been a number of new drugs developed for use in molecular targeted therapy for mesothelioma. Some of the most promising include: Crizotinib Crizotinib is a drug that targets a specific gene fusion called ROS1. This gene fusion is present in a small percentage of mesothelioma cases, and crizotinib has been shown to be effective in shrinking tumors in these cases. Immunotherapy Immunotherapy is a relatively new approach to cancer treatment that harnesses the immune system to fight cancer. There are a number of different types of immunotherapy that are being studied for use in treating mesothelioma, including checkpoint inhibitors and adoptive T-cell therapy. Anetumab Ravtansine Anetumab Ravtansine is a drug that targets the mesothelin protein, which is overexpressed in many cases of mesothelioma. It works by delivering a toxin directly to cancer cells, helping to minimize the impact on healthy cells. Tremelimumab Tremelimumab is another immunotherapy drug that is being studied for use in mesothelioma treatment. It works by targeting a protein called CTLA-4 on T cells, which can help to boost the immune response to cancer cells. While molecular targeted therapy shows promise as a more effective and less toxic approach to mesothelioma treatment, more research is needed to determine the long-term effectiveness and safety of these drugs. Combination TherapyAs mesothelioma is a particularly aggressive cancer, treatment often involves a combination of different therapies to maximize effectiveness. This can include a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. Combining different types of therapy can help to reduce the overall toxicity of treatment while increasing the chances of successfully treating the cancer. SummaryMesothelioma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that is most commonly caused by exposure to asbestos. While chemotherapy drugs have long been used to treat mesothelioma, there are now a range of promising molecular targeted therapy drugs that are being studied for use in mesothelioma treatment. Molecular targeted therapy involves identifying and targeting specific molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells, which can help to reduce the side effects of treatment while increasing effectiveness. Combining different types of therapy – including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy – can help to maximize the effectiveness of treatment and increase the chances of successfully treating mesothelioma. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Combinatorial TherapiesMesothelioma has long been considered a difficult cancer to treat due to late diagnosis and limited treatment options available for patients. Despite this, chemotherapy remains a promising option for treating mesothelioma, with numerous drugs and combinations available to patients. Understanding the different chemotherapy drugs and combinatorial therapies available can help mesothelioma patients and their doctors make informed treatment decisions. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsChemotherapy drugs aim to kill cancer cells by targeting their ability to divide and grow. While there are many chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma, some of the most commonly used include: CisplatinCisplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy drug that works by binding to DNA and inhibiting cell division. Cisplatin is often used in combination with other drugs and has been shown to improve patients’ survival rates. However, cisplatin can cause significant side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and kidney damage. CarboplatinLike cisplatin, carboplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy drug that targets DNA. However, carboplatin is generally considered less toxic than cisplatin, with fewer side effects. Carboplatin is often used in combination with other drugs to treat mesothelioma. PemetrexedPemetrexed is a chemotherapy drug that works by inhibiting the production of DNA and RNA, preventing cell division and growth. Pemetrexed is often used in combination with cisplatin to treat mesothelioma and has been shown to improve patients’ survival rates. Pemetrexed can cause side effects such as fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and anemia. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that inhibits DNA synthesis and prevents cell division. Gemcitabine is sometimes used in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin to treat mesothelioma. Gemcitabine’s side effects can include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and flu-like symptoms. MitomycinMitomycin is a chemotherapy drug that works by preventing DNA synthesis and cell division. Mitomycin is often used in combination with other drugs to treat mesothelioma. Mitomycin can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and anemia. BevacizumabBevacizumab is a targeted therapy drug that works by preventing the formation of new blood vessels in tumors. Bevacizumab is sometimes used in combination with chemotherapy drugs to treat mesothelioma. Bevacizumab can cause side effects such as high blood pressure, bleeding, and blood clots. Immunotherapy DrugsImmunotherapy drugs are a relatively new type of treatment for mesothelioma that works by activating the patient’s immune system to fight cancer cells. Some examples of immunotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma include pembrolizumab and nivolumab. Immunotherapy can cause side effects such as fatigue, fever, and rash.
Combinatorial TherapiesCombinatorial therapies involve using multiple drugs or treatment modalities to treat mesothelioma. Combinations of chemotherapy drugs are often used to increase their effectiveness and minimize side effects. Other combinatorial therapies used for mesothelioma include: Surgery and ChemotherapySurgery is often used to remove as much of the mesothelioma tumor as possible, followed by chemotherapy to kill any remaining cancer cells. This approach can improve patients’ survival rates and is often used for early-stage mesothelioma. Radiation and ChemotherapyRadiation therapy involves using high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. When used in combination with chemotherapy, radiation therapy can improve patients’ survival rates and reduce the risk of the cancer returning. Radiation therapy can cause side effects such as fatigue, skin irritation, and nausea. Immunotherapy and ChemotherapyImmunotherapy drugs can be used in combination with chemotherapy to improve patients’ outcomes. Combination treatments such as pembrolizumab and platinum-based chemotherapy have been shown to improve patients’ overall survival rates and progression-free survival rates. Multimodal Combinatorial TherapyMultimodal combinatorial therapy involves using surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy together to treat mesothelioma. This approach is often used for advanced-stage mesothelioma and can improve patients’ survival rates. Overall, there are many chemotherapy drugs and combinatorial therapies available for patients with mesothelioma. By working with their doctors, patients can make informed decisions about the best treatment options for their individual cases. While mesothelioma is a challenging cancer to treat, chemotherapy remains a valuable tool in the fight against the disease. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it is important to explore all treatment options available. Consult with your doctor to determine the best course of action for your individual case and to discuss the potential benefits and risks of chemotherapy drugs and combinatorial therapies. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and ChemoresistanceMesothelioma is a rare form of cancer that affects the mesothelium, a membrane that covers the lungs, chest, abdomen, and other organs in the body. It is primarily caused by asbestos exposure and has a very poor prognosis. Mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are one of the main treatment options for this disease. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsChemotherapy for mesothelioma involves using drugs that target cancer cells and stop them from growing and spreading. Some of the most commonly used mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs include:
These drugs are usually given in a combination to increase their effectiveness. Chemotherapy can be administered before or after surgery to remove the cancerous tissue. It can also be used as a standalone treatment when the cancer is inoperable, or the patient cannot undergo surgery due to other health issues. ChemoresistanceUnfortunately, not all mesothelioma patients respond to chemotherapy. Some tumors are resistant to the drugs, causing the treatment to be ineffective. Chemoresistance can occur due to several reasons: Genetic mutationsSome mesothelioma cancer cells have genetic mutations that make them resistant to chemotherapy. These mutations can occur naturally or be caused by exposure to certain chemicals and substances. Cancer stem cellsCancer stem cells are a type of cancer cell that is thought to be resistant to chemotherapy. These cells can survive the treatment and go on to regenerate new tumors, leading to a recurrence of the disease. MicroenvironmentThe microenvironment surrounding the cancer cells can also affect their response to chemotherapy. For example, the cancer cells can form a protective shield, making it difficult for the drugs to reach the tumor. Additionally, the tumor microenvironment can also promote the growth of cancer cells and contribute to chemoresistance. MDR PumpMDR stands for a multi-drug resistance pump. These pumps are found on the surface of cancer cells and remove chemotherapy drugs out of the cells. This mechanism makes the cancer cells become resistant to chemotherapy. Overcoming ChemoresistanceResearchers have been working on finding new ways to overcome chemoresistance in mesothelioma chemotherapy. Some of the approaches being explored include: ImmunotherapyImmunotherapy is a treatment that uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It helps to activate the immune cells, which recognize and attack cancer cells. This approach has shown promising results in treating mesothelioma and overcoming chemoresistance. Gene therapyGene therapy involves modifying the patient’s DNA to make the cancer cells more susceptible to chemotherapy. It works by targeting the genetic mutations that cause the cancer cells to be resistant to the drugs. Nanoparticle delivery systemsNanoparticles are tiny particles that can be engineered to deliver chemotherapy drugs directly to the cancer cells. This approach helps to bypass the protective shield around the tumor and deliver higher doses of the drugs to the cancerous tissue. Targeted therapyTargeted therapy involves using drugs that target specific molecules and pathways in the cancer cells. This approach reduces the side effects of traditional chemotherapy and improves the effectiveness of the treatment. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy drugs are an essential part of the treatment for this disease. However, chemoresistance is a significant challenge that needs to be overcome to improve the outcomes for mesothelioma patients. Researchers are exploring new approaches to overcome chemoresistance and increase the effectiveness of chemotherapy in treating mesothelioma. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Tumor ImmunologyMesothelioma is a type of cancer that develops in the lining of the lungs or other internal organs and is caused by asbestos exposure. It is a rare disease that is often difficult to diagnose and treat. Chemotherapy is one of the primary treatments for mesothelioma, and there are several drugs that are commonly used. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the use of immunotherapy for the treatment of mesothelioma. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsChemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to destroy cancer cells. These drugs can be given orally or intravenously, and they circulate throughout the body to kill cancer cells. There are several chemotherapy drugs that are used for the treatment of mesothelioma, and they are often used in combination. The following are some of the most common chemotherapy drugs used for mesothelioma: CisplatinCisplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy drug that is commonly used to treat mesothelioma. It works by damaging the DNA in cancer cells, which causes them to die. Cisplatin is usually given intravenously and can cause side effects such as kidney damage, hearing loss, and nerve damage. CarboplatinCarboplatin is another platinum-based chemotherapy drug that is used for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works in a similar way to cisplatin, but it is less toxic and has fewer side effects. Carboplatin is also given intravenously. PemetrexedPemetrexed is a chemotherapy drug that is often used in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells. Pemetrexed is given intravenously and can cause side effects such as fatigue, nausea, and low white blood cell counts. VinorelbineVinorelbine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the growth of cancer cells. Vinorelbine is usually given intravenously and can cause side effects such as fatigue, nausea, and low white blood cell counts. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a chemotherapy drug that is sometimes used for the treatment of mesothelioma. It works by interfering with the growth of cancer cells. Gemcitabine is usually given intravenously and can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and low white blood cell counts. Tumor ImmunologyImmunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses the body’s own immune system to fight cancer. It is a relatively new approach to cancer treatment, and it has shown promise in the treatment of mesothelioma. Tumor immunology is the study of the interaction between the immune system and cancer cells. The immune system is capable of recognizing and destroying cancer cells, but cancer cells can often evade the immune system and grow unchecked. Immunotherapy drugs work by boosting the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack cancer cells. There are several types of immunotherapy drugs that are being tested for the treatment of mesothelioma. The following are some of the most promising immunotherapy drugs for mesothelioma: Checkpoint InhibitorsCheckpoint inhibitors are a type of immunotherapy drug that is designed to block a specific protein that tumors use to evade the immune system. By blocking this protein, checkpoint inhibitors allow the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Checkpoint inhibitors have shown promise in the treatment of mesothelioma, and they are currently being tested in clinical trials. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs)Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) are immune cells that have the ability to recognize and attack cancer cells. TILs can be isolated from a patient’s tumor and grown in the laboratory, and then infused back into the patient to boost the immune system’s ability to attack the cancer. TIL therapy has shown promise in the treatment of mesothelioma, and it is currently being tested in clinical trials. Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell TherapyCAR T-cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy that involves modifying a patient’s own immune cells to recognize and attack cancer cells. CAR T-cell therapy has shown promise in the treatment of other types of cancer, and it is currently being tested in clinical trials for the treatment of mesothelioma. Oncolytic VirusesOncolytic viruses are viruses that are genetically modified to target and destroy cancer cells. These viruses can infect and replicate within cancer cells, causing them to die. Oncolytic viruses have shown promise in the treatment of mesothelioma, and they are currently being tested in clinical trials. ConclusionMesothelioma is a difficult cancer to treat, and chemotherapy is one of the primary treatments. There are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used, including cisplatin, carboplatin, pemetrexed, vinorelbine, and gemcitabine. However, there is growing interest in the use of immunotherapy for the treatment of mesothelioma. Immunotherapy drugs work by boosting the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack cancer cells. Checkpoint inhibitors, TIL therapy, CAR T-cell therapy, and oncolytic viruses are all being tested for the treatment of mesothelioma and show promise as future options. It is important for patients and their families to discuss all available treatment options with their healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment for their individual case.
Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Cancer Stem CellsMesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the protective lining of the lungs, abdomen and chest. It is caused by exposure to asbestos and typically takes decades to manifest. Mesothelioma typically has a poor prognosis and treatment options are limited. Chemotherapy is a common treatment for mesothelioma, but it is not a cure. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells and slow or stop their growth. However, not all mesothelioma cells respond to chemotherapy, especially if they are cancer stem cells. Cancer stem cells are a type of cell found in many types of cancer, including mesothelioma. They are different from other cancer cells in that they have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into different cell types. This means they can generate new tumors and make it difficult to treat cancer with chemotherapy. Cancer stem cells are resistant to many conventional treatments and can survive after chemotherapy, leading to disease recurrence and progression. Researchers are studying new chemotherapy drugs and drug combinations that target cancer stem cells in mesothelioma. These drugs aim to kill or disable cancer stem cells, which could improve treatment outcomes and prevent cancer recurrence. Several chemotherapy drugs have shown promise in preclinical studies and clinical trials. Chemotherapy Drugs for MesotheliomaChemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma are usually given intravenously (IV) or by mouth (orally). Chemotherapy can be administered alone or in combination with other treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy. The most commonly used chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma are:
Cisplatin and carboplatin are platinum-based drugs that are commonly used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma. They work by damaging DNA in cancer cells, which prevents cell division and growth. Pemetrexed is another drug that is often used in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin. It blocks the production of enzymes that cancer cells need to divide and grow. Gemcitabine and methotrexate are other chemotherapy drugs that may be used alone or in combination with other drugs. Limitations of Chemotherapy for MesotheliomaChemotherapy can have side effects, including nausea, vomiting, hair loss, fatigue, and anemia. These side effects can be managed with medication or other treatments, but they can impact quality of life. Chemotherapy may also reduce the body’s ability to fight infections and increase the risk of bleeding or bruising. In addition, chemotherapy has limitations in treating mesothelioma. It may not be effective in all cases, especially if the cancer is advanced. Chemotherapy can also have limited effect on cancer stem cells, which can lead to disease recurrence and progression. Researchers are studying new drugs and drug combinations that target cancer stem cells in mesothelioma to improve treatment outcomes. These drugs include: New Chemotherapy Drugs for MesotheliomaNew chemotherapy drugs and drug combinations for mesothelioma are being developed to target cancer stem cells and improve the effectiveness of treatment. Some of these drugs are still in the early stages of development, while others are being studied in clinical trials. Here are some of the new chemotherapy drugs for mesothelioma: CBP-201CBP-201 is a new drug that targets cancer stem cells in mesothelioma. It works by inhibiting a protein called BMI-1, which is required for the self-renewal of cancer stem cells. In preclinical studies, CBP-201 has been shown to reduce the growth of mesothelioma tumors and improve overall survival. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of CBP-201 in mesothelioma patients. VD-159VD-159 is a drug combination that includes two chemotherapy drugs, cisplatin and vinorelbine, and a third drug, vismodegib, which targets cancer stem cells. Vismodegib works by blocking a signaling pathway that is important for the growth and self-renewal of cancer stem cells. In preclinical studies, VD-159 has been shown to improve the effectiveness of chemotherapy and reduce the size of mesothelioma tumors. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of VD-159 in mesothelioma patients. OX40OX40 is a protein found on the surface of immune cells that is involved in the immune response to cancer cells. In preclinical studies, OX40 has been shown to improve the effectiveness of chemotherapy and boost the immune response to cancer. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of OX40 in mesothelioma patients. ConclusionMesothelioma is a difficult-to-treat cancer that has limited treatment options. Chemotherapy is a common treatment for mesothelioma, but it has limitations in targeting cancer stem cells, which can lead to disease recurrence and progression. Researchers are studying new chemotherapy drugs and drug combinations that target cancer stem cells in mesothelioma to improve treatment outcomes. These drugs are still in the early stages of development, but they show promise in preclinical and clinical studies. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs and Clinical Trials for New TherapiesMesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer that develops in the mesothelium, which is a thin layer of tissue that covers most of our internal organs. One major risk factor for mesothelioma is exposure to asbestos, which was commonly used in buildings and construction materials until the 1970s. While there is no cure for mesothelioma, chemotherapy drugs can be effective at reducing tumor size, relieving symptoms, and prolonging the patient’s life. In this article, we will explore the different types of mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs and the latest clinical trials for new therapies. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsChemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells. These drugs can be given orally, intravenously, or through a catheter directly into the affected area. The most common chemotherapy drugs used for mesothelioma are: 1. CisplatinCisplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy drug that works by damaging the cancer cells’ DNA, preventing them from dividing and multiplying. It is usually given in combination with another drug called pemetrexed. According to a study by the National Cancer Institute, cisplatin and pemetrexed combination therapy is the most effective first-line chemotherapy for mesothelioma patients. 2. CarboplatinCarboplatin is another platinum-based chemotherapy drug that works similarly to cisplatin. It is typically given to patients who are not able to tolerate cisplatin or have other health problems. Carboplatin is less toxic and has milder side effects compared to cisplatin, but it may not be as effective. 3. Alimta (pemetrexed)Alimta, also known as pemetrexed, is a folate antimetabolite chemotherapy drug that works by blocking the growth and division of cancer cells. It is usually given in combination with cisplatin and has been shown to improve survival rates in patients with mesothelioma. Alimta can cause side effects such as fatigue, nausea, and low blood cell counts. 4. GemcitabineGemcitabine is a nucleoside analogue chemotherapy drug that works by blocking the DNA synthesis of cancer cells. It is usually given in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin and has been shown to have moderate efficacy in mesothelioma patients. Gemcitabine can cause side effects such as flu-like symptoms, hair loss, and rash. Clinical Trials for New TherapiesClinical trials are research studies that test new treatments, therapies, or procedures for cancer patients. The goal of clinical trials is to find new and better ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat cancer. There are several ongoing clinical trials for mesothelioma that are testing new chemotherapy drugs, immunotherapy drugs, targeted therapy drugs, and combination therapies. Some of the most promising clinical trials for mesothelioma are: 1. Keytruda and Lenvima Combination TherapyKeytruda and Lenvima are two immunotherapy drugs that work by boosting the patient’s immune system to fight cancer cells. A phase II clinical trial is currently testing the safety and efficacy of combining Keytruda and Lenvima in mesothelioma patients. Preliminary results from the trial showed promising response rates and survival benefits, with manageable side effects. 2. Tazemetostat Targeted TherapyTazemetostat is a targeted therapy drug that works by inhibiting a protein called EZH2, which is overexpressed in mesothelioma cells. A phase II clinical trial is currently testing the safety and efficacy of tazemetostat in mesothelioma patients with EZH2 mutations. Preliminary results from the trial showed promising response rates and durable clinical benefits, with manageable side effects. 3. CB-103 Targeted TherapyCB-103 is a targeted therapy drug that works by inhibiting a protein called CD47, which is overexpressed in mesothelioma cells. A phase I clinical trial is currently testing the safety and tolerability of CB-103 in mesothelioma patients. Preliminary results from the trial showed promising antitumor activity and manageable side effects. 4. Naptumomab Estafenatox ImmunotherapyNaptumomab estafenatox is an immunotherapy drug that works by activating T-cells to attack mesothelioma cells. A phase II clinical trial is currently testing the safety and efficacy of naptumomab estafenatox in mesothelioma patients who have failed prior chemotherapy. Preliminary results from the trial showed promising clinical benefits and manageable side effects.
In conclusion, mesothelioma is a rare and deadly cancer that requires aggressive treatment with chemotherapy drugs. Cisplatin and pemetrexed combination therapy is the most effective first-line chemotherapy for mesothelioma patients, but there are other chemotherapy drugs that can be used depending on the patient’s health status and preferences. Moreover, there are several ongoing clinical trials for mesothelioma that are testing new chemotherapy drugs, immunotherapy drugs, targeted therapy drugs, and combination therapies. These clinical trials offer hope for patients with mesothelioma and their families, and they represent the latest advancements in cancer research. Future Directions of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy ResearchAs the field of oncology continues to advance, researchers and medical professionals are exploring promising avenues for mesothelioma treatment options. While chemotherapy has shown efficacy in reducing tumor growth and improving patient outcomes, there is still much to be learned about the potential for new drugs and combination therapies to further improve mesothelioma treatment. Here are some exciting developments in mesothelioma chemotherapy research: 1. ImmunotherapyImmunotherapy is a rapidly growing area of cancer treatment that uses the body’s own immune system to attack cancer cells. While immunotherapy has shown success in treating some cancers, it has yet to be widely studied in mesothelioma patients. However, several early-stage clinical trials are underway to investigate the potential of immunotherapy in mesothelioma treatment. These trials involve drugs that target specific immune system pathways, such as PD-1 and CTLA-4, that can help the body fight cancer cells more effectively.
These early studies are showing promising results, with some patients showing significant reductions in tumor size and improved rates of survival. As more clinical trials are conducted, immunotherapy may become a more prevalent treatment option for mesothelioma patients. 2. Combination ChemotherapyWhile chemotherapy has been a mainstay of mesothelioma treatment for decades, researchers are continuing to explore new combinations of drugs to improve efficacy and reduce adverse side effects. Currently, the most common chemotherapy regimen for mesothelioma patients is a combination of cisplatin and pemetrexed. However, recent studies have suggested that adding additional drugs to this combination, such as gemcitabine or vinorelbine, may further improve patient outcomes. These combination regimens may be especially effective for patients with mesothelioma that has already spread beyond the initial site of the tumor. By attacking cancer cells through multiple pathways, combination chemotherapy can be a powerful tool in reducing tumor growth and improving patient prognosis. 3. Targeted TherapyTargeted therapy is a type of cancer treatment that involves drugs designed to attack specific mutations or proteins within cancer cells. While targeted therapy has been highly effective in some cancers, it has yet to be widely used in mesothelioma treatment due to the lack of known specific mutations in mesothelioma cells. However, recent research has identified several potential targets for mesothelioma therapy, including the genetic mutations BAP1 and NF2.
These drugs are currently in early-stage clinical trials, but early results have shown promising efficacy in reducing tumor size and improving patient outcomes. Targeted therapy may be an important treatment option for mesothelioma patients in the near future. 4. Nanoparticle ChemotherapyNanoparticle chemotherapy is a relatively new approach to cancer treatment that involves delivering chemotherapy drugs directly to cancer cells using microscopic particles. This approach has several advantages over traditional chemotherapy, including reduced toxicity to healthy cells and improved drug efficacy. While nanoparticle chemotherapy has been studied in several types of cancer, there has been limited research done in mesothelioma patients. However, early-stage clinical trials are showing promising results. Some nanoparticle chemotherapies, such as SP1049C and NC-6004, have already shown effectiveness in reducing tumor size and improving patient survival in pre-clinical studies. As more research is done in mesothelioma patients, nanoparticle chemotherapy may become an important treatment option for patients with this difficult-to-treat cancer. 5. Personalized MedicinePersonalized medicine is an emerging field of cancer treatment that involves tailoring therapeutic approaches to individual patients based on their genetic makeup, tumor characteristics, and other factors. While still in the early stages of development, personalized medicine has the potential to dramatically improve mesothelioma treatment outcomes by allowing for more precise and targeted treatments. One promising area of research in personalized medicine is the use of liquid biopsies, which involve analyzing tumor DNA that is circulating in the bloodstream, to identify genetic mutations and other markers that can inform treatment decisions. Liquid biopsies could allow oncologists to identify the most effective treatment options for individual patients without the need for invasive tissue biopsies.
While personalized medicine is still in the early stages of development, the potential for this approach to improve mesothelioma outcomes is significant. As more research is done in this area, personalized medicine may become a more prevalent treatment option for mesothelioma patients. ConclusionMesothelioma chemotherapy research is continuing to advance rapidly, with promising developments in immunotherapy, combination chemotherapy, targeted therapy, nanoparticle chemotherapy, and personalized medicine. While mesothelioma remains a difficult-to-treat cancer, these new approaches represent promising avenues for improving patient outcomes and reducing the burden of this devastating disease. Closing Message for Blog Visitors About Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsThank you for taking the time to read this article about mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs. We hope that the information provided has been helpful in understanding the treatment options available for individuals diagnosed with mesothelioma. Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that is usually caused by exposure to asbestos. There is currently no cure for mesothelioma, but chemotherapy drugs can help to slow the progression of the disease, alleviate symptoms, and improve the quality of life of the patient. Chemotherapy drugs work by targeting and killing cancer cells. They are often used in combination with other treatments, such as surgery and radiation therapy, to effectively manage mesothelioma. It is important to note that chemotherapy drugs can have side effects that vary from person to person. These side effects may include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, hair loss, and a weakened immune system. Your oncologist will work with you to manage these side effects and minimize their impact on your daily life. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it is important to seek out a team of healthcare professionals who specialize in the treatment of this disease. This team may include an oncologist, a surgeon, a radiation oncologist, and a palliative care specialist. At the end of the day, the goal of mesothelioma chemotherapy is to improve the quality of life of the patient. It is important to have an open and honest conversation with your healthcare team about your goals for treatment and any concerns you may have. People Also Ask about Mesothelioma Chemotherapy DrugsWhat are the most common chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma?There are several chemotherapy drugs that are commonly used to treat mesothelioma. These drugs include Pemetrexed, Cisplatin, Carboplatin, and Gemcitabine. These drugs are often used in combination with other treatments to effectively manage mesothelioma. How is chemotherapy administered for mesothelioma?Chemotherapy for mesothelioma can be administered in several ways, including intravenously (through a vein), orally (in the form of a pill), or through an implanted port. The method of administration will depend on the specific treatment plan developed by your healthcare team. What are the side effects of mesothelioma chemotherapy?The side effects of chemotherapy for mesothelioma can vary from person to person, but may include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, hair loss, and a weakened immune system. Your oncologist will work with you to manage these side effects and minimize their impact on your daily life. How effective is chemotherapy for mesothelioma?Chemotherapy can be an effective way to manage mesothelioma, but its effectiveness will depend on a number of factors, including the stage of the disease, the type of chemotherapy used, and the individual patient’s response to treatment. Can chemotherapy cure mesothelioma?Currently, there is no cure for mesothelioma. However, chemotherapy drugs can help to slow the progression of the disease, alleviate symptoms, and improve the quality of life of the patient. In conclusion, mesothelioma chemotherapy drugs can be an effective way to manage this aggressive form of cancer. It is important to work with a team of healthcare professionals who specialize in the treatment of this disease and to have an open and honest conversation about your goals for treatment and any concerns you may have. With the right treatment plan, it is possible to improve the quality of life of individuals diagnosed with mesothelioma. |